Integration with Heroku Application Logs
This guide explains how to stream Heroku application logs—including app, router, error, and system logs—into OpenObserve using a forwarding app that parses Logplex syslogs into structured JSON.
Overview
Heroku’s Logplex consolidates logs from your app (stdout/stderr), router (HTTP requests), and system events (dyno restarts). While convenient, it’s limited by retention length (1,500 lines or one week) and raw text format, which is hard to analyze.

OpenObserve ingests these logs in structured JSON format, enabling fast search, rich visualization, and proactive alerting.
Steps to Integrate
Prerequisites
- OpenObserve account (Cloud or Self-Hosted)
- An existing Heroku application already deployed and generating logs
- Heroku CLI installed and authenticated
- Node.js, npm, Git, and terminal access
Step 1: Retrieve OpenObserve Endpoint and Credentials
-
In OpenObserve: go to Data Sources → Custom → Logs → Syslog-NG section

-
Keep the credentials handy.Construct the Heroku-specific ingestion endpoint:
Step 2: Build a Forwarding App to Parse and Send Logs
-
Initialize a new forwarding app:
-
Create
index.jsand paste:const express = require('express'); const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const fetch = require('node-fetch'); const app = express(); app.use(bodyParser.text({ type: '*/*' })); const OPENOBSERVE_URL = 'https://api.openobserve.ai/api/<organization_id>/heroku_logs/_json'; const OPENOBSERVE_USER = 'your-username@example.com'; const OPENOBSERVE_PASS = 'your_password'; const logRegex = /^(\d+) <\d+>1\s+([\d-:.+]+)\s+host\s+(\w+)\s+(\w+)\.(\d+)\s*-\s*(.*)$/; const routerRegex = /^(\d+) <\d+>1\s+([\d-:.+]+)\s+host\s+heroku\s+(\w+)\s*-\s+at=info\s+(.*)$/; app.post('/logs', async (req, res) => { const rawLogs = req.body.split('\n').filter(log => log.trim()); const enriched = rawLogs.map(log => { let match = log.match(logRegex); if (match) { const [, , timestamp, source, dynoNum, dynoId, message] = match; return { app: "your-heroku-app-name", dyno: `${dynoNum}.${dynoId}`, message, source: source.toLowerCase(), timestamp }; } match = log.match(routerRegex); if (match) { const [, , timestamp, source, details] = match; const params = details.split(' ').reduce((acc, pair) => { const [key, value] = pair.split('='); acc[key] = value.replace(/^"(.*)"$/, '$1'); return acc; }, {}); return { app: "your-heroku-app-name", dyno: params.dyno, message: details, source: source.toLowerCase(), timestamp, ...params }; } console.warn(`Unparsed log: ${log}`); return { message: log, timestamp: new Date().toISOString() }; }); try { const resp = await fetch(OPENOBSERVE_URL, { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': `Basic ${Buffer.from(`${OPENOBSERVE_USER}:${OPENOBSERVE_PASS}`).toString('base64')}` }, body: JSON.stringify(enriched) }); if (!resp.ok) throw new Error(`Ingestion failed: ${resp.status}`); console.log(`Forwarded ${enriched.length} logs`); res.sendStatus(200); } catch (err) { console.error('Error forwarding logs:', err.message); res.status(500).send('Forwarding failed'); } }); app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000, () => console.log(`Forwarder running on port ${process.env.PORT || 3000}`)); -
Update placeholders (
<organization_id>, credentials, and app name) accordingly - Create a proc file
web: node index.js - Update
package.jsonfile:
Step 3: Deploy Forwarding App to Heroku and Configure Log Drain
-
Deploy the forwarding app:
git init git add . git commit -m "Heroku log forwarder" heroku create heroku-log-forwarder git push heroku mainNote the deployed URL (e.g.,
https://heroku-log-forwarder.herokuapp.com). -
Configure the log drain from your existing app:
- Optionally, reduce sampling rate if you encounter buffer overflows:
- Verify drain setup:
Step 4: Verify Logs in OpenObserve
- In OpenObserve, go to Logs → heroku_logs and run a query to see structured entries.
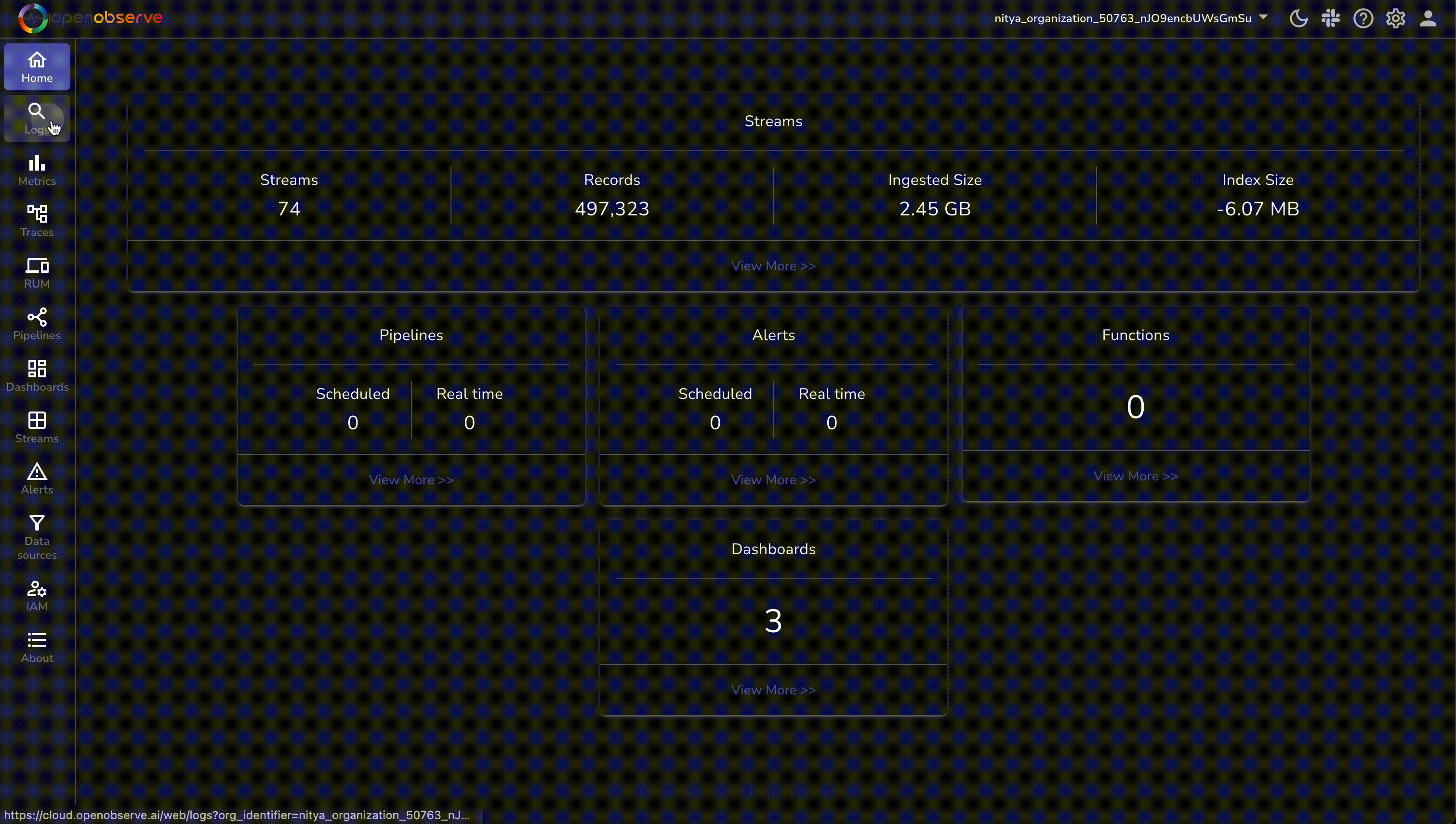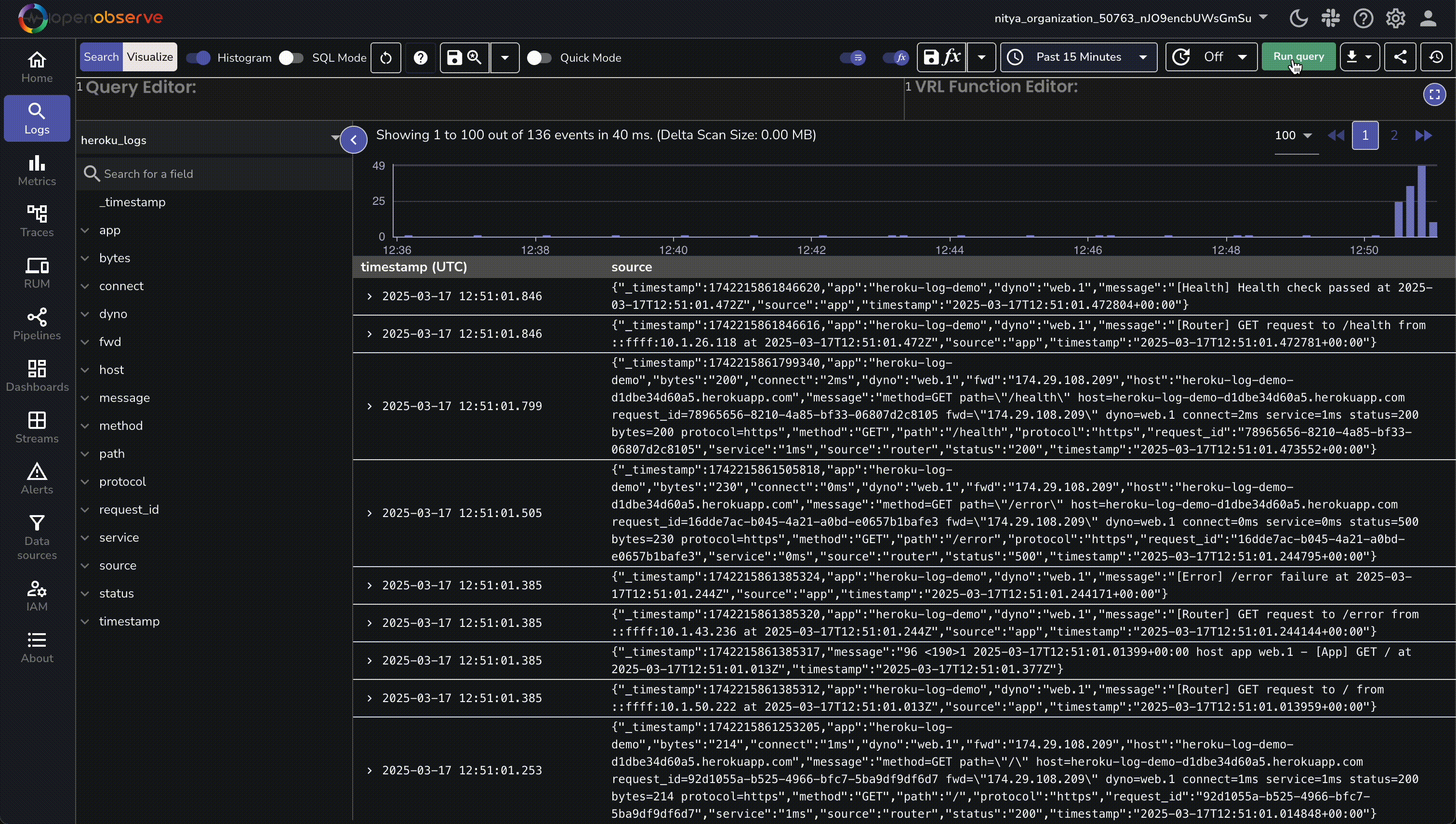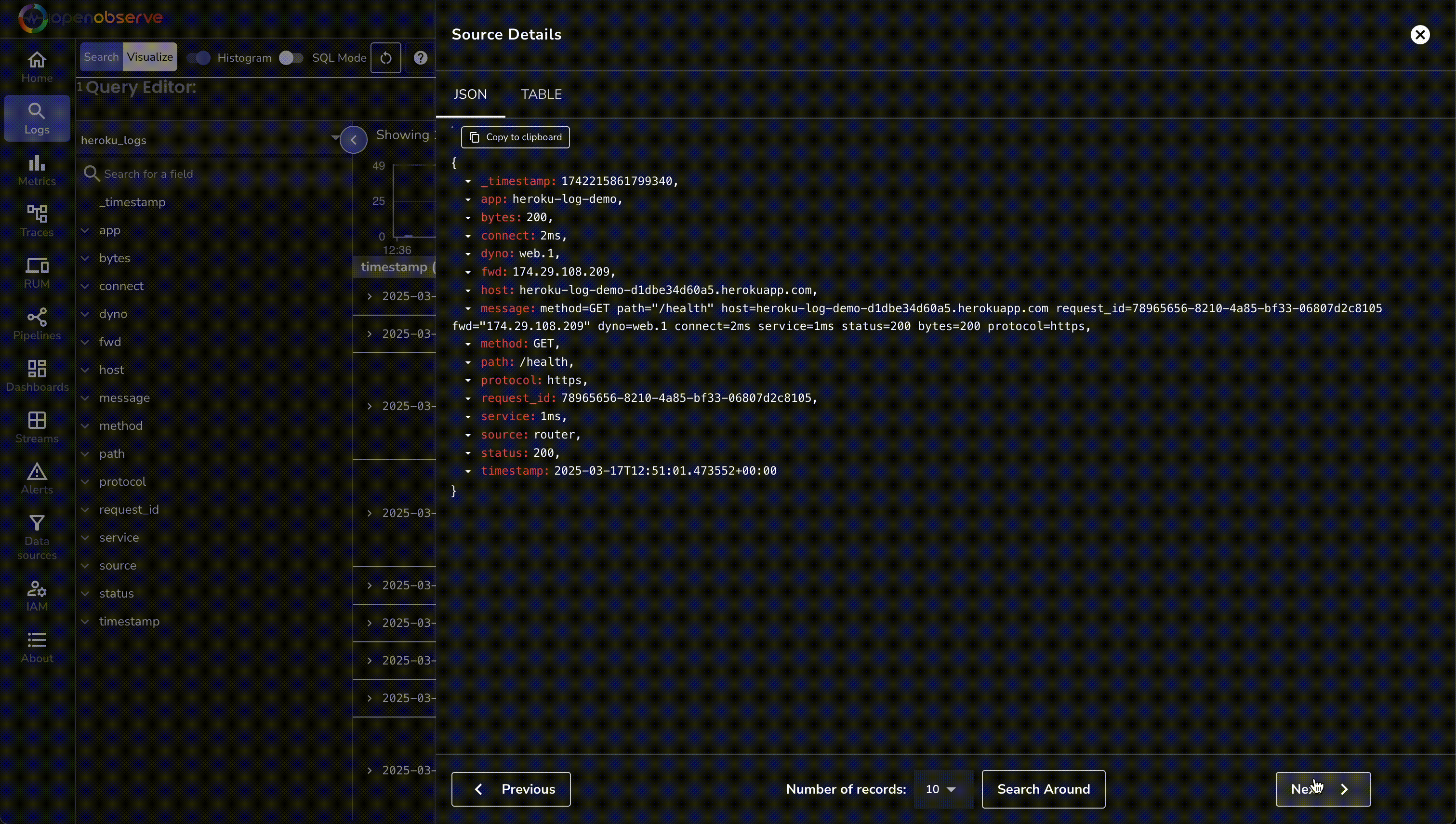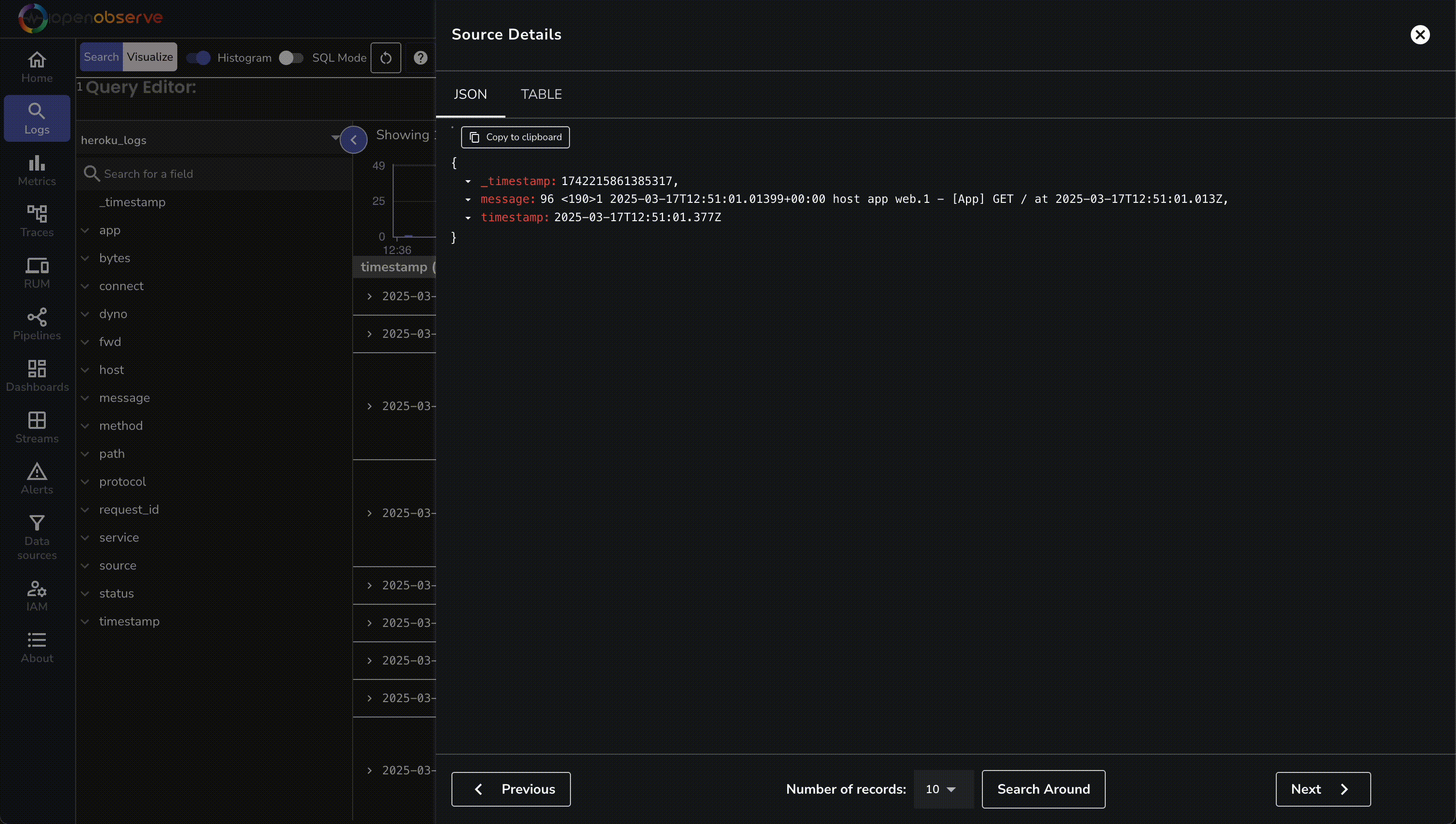
Troubleshooting
No logs or some log types missing
- Check Heroku app logs (More → View logs) to confirm log generation (Router, App, Error types)
- Confirm the drain is active:
- Tail your forwarder logs for warnings or errors
Buffer overflow (Error L10)
- Reduce sampling rate:
Unparsed logs
- Review
Unparsed logwarnings in forwarder logs - Adjust regex patterns in
index.js
Truncated logs
- Heroku truncates lines >10 KB. Simplify log message content in forwarding app and redeploy
Slow log delivery
- Increase heartbeat interval in
index.jsor reduce traffic volume