Integration with AWS Route 53 Query Logging via CloudWatch & Firehose
This guide explains how to configure AWS Route 53 query logging, stream logs to OpenObserve using CloudWatch Logs and Kinesis Firehose, and optionally transform them with VRL for advanced analysis.
Overview
Route 53 query logs capture DNS requests processed by public or private hosted zones. These logs can be streamed into OpenObserve for real-time monitoring and analysis of DNS patterns, resolver behavior, and potential anomalies.
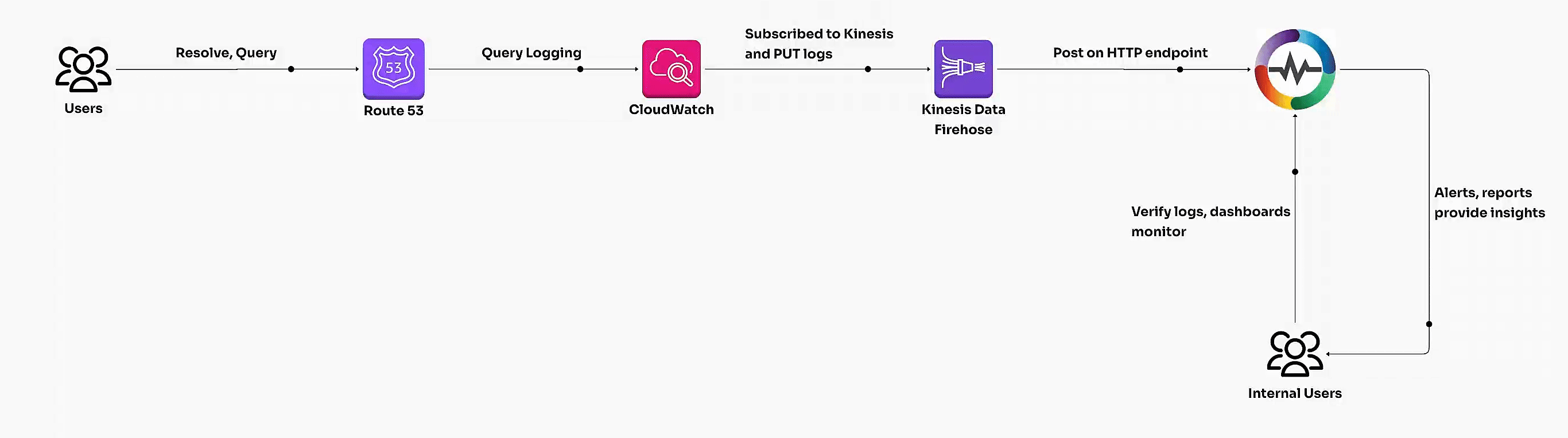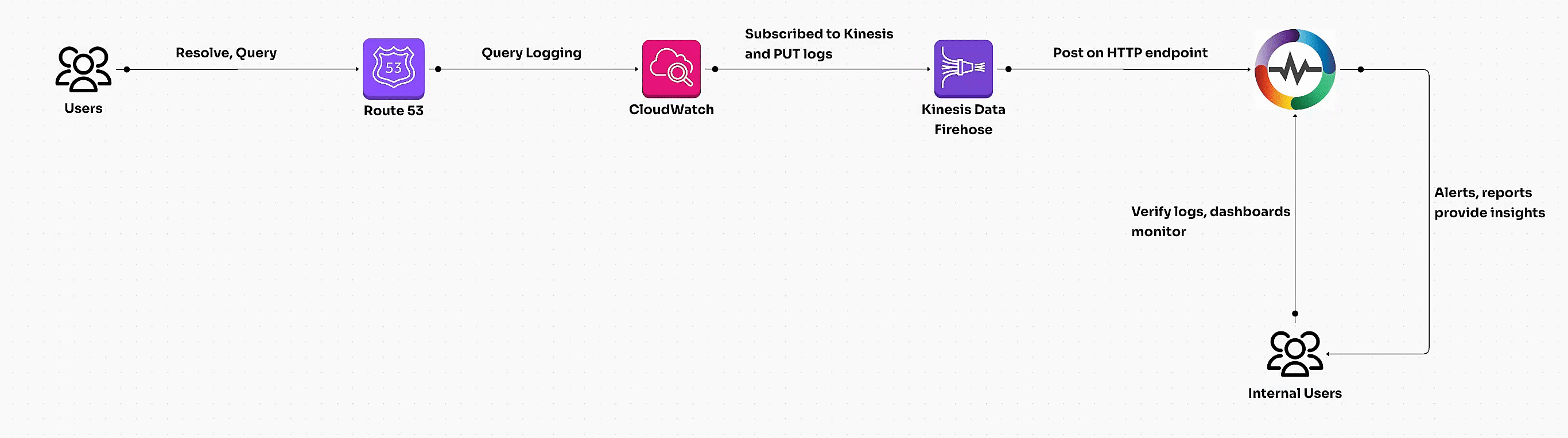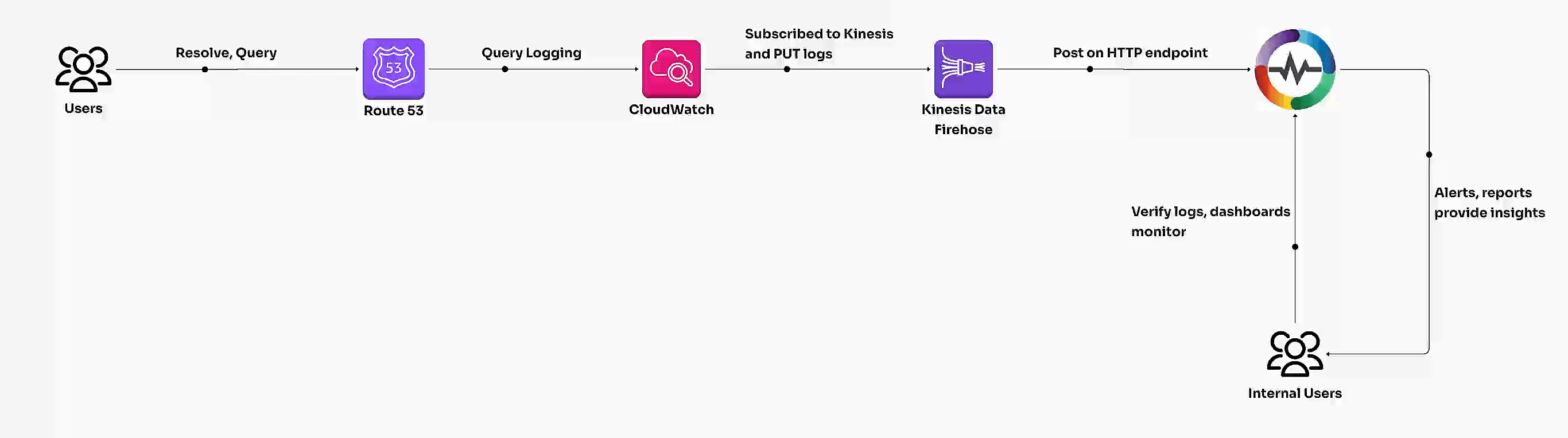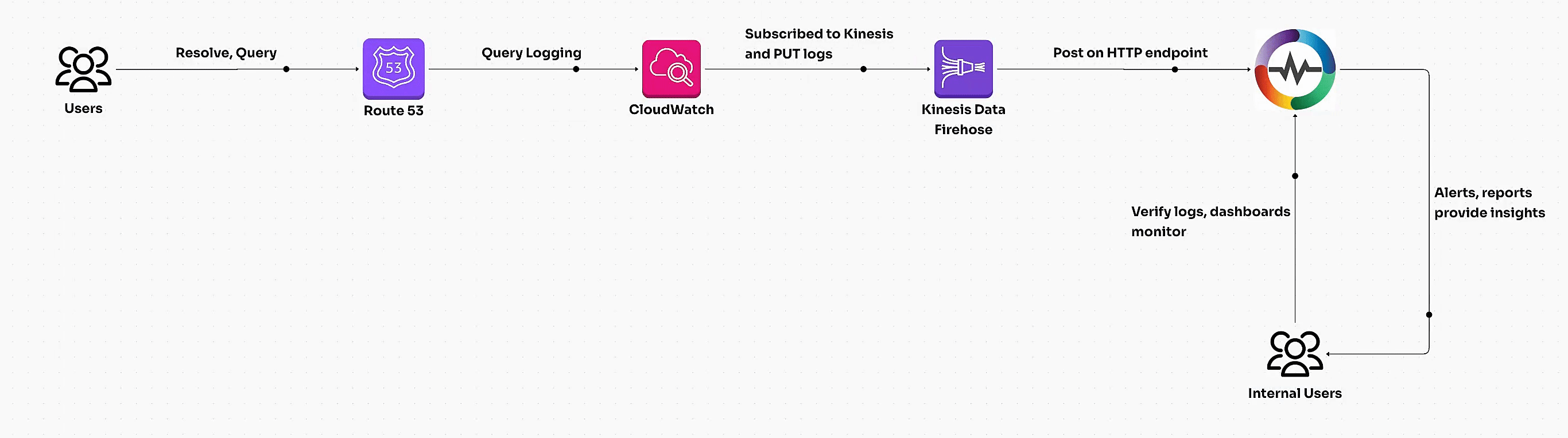
Steps to Integrate
Prerequisites
- OpenObserve account (Cloud or Self-Hosted)
- AWS IAM permissions to manage Route 53, CloudWatch Logs, IAM roles, and Firehose
- S3 bucket for Firehose backup (optional but recommended)
- OpenObserve ingestion URL and Access Key
Step 1: Enable Route 53 Query Logging
- Go to Route 53 → Hosted Zones
- Select a hosted zone → Click Enable query logging
- Provide or create a CloudWatch Log Group (e.g.,
/aws/route53/logs) - Save changes

Optional: Set a retention policy on the log group in CloudWatch to manage storage.
Step 2: Create a Kinesis Data Firehose Delivery Stream
- Navigate to Kinesis → Firehose → Create delivery stream
- Choose:
- Source:
Direct PUT - Destination:
HTTP Endpoint
- Source:
- Input:
- Endpoint URL: your OpenObserve Firehose ingestion URL
- Access Key / Secret Key: from OpenObserve
- (Optional) Enable S3 backup for failed records
- Name the stream (e.g.,
route53-query-logs) and create it
Step 3: Create CloudWatch Logs Subscription Filter
- Go to CloudWatch → Log groups
- Select your Route 53 log group (e.g.,
/aws/route53/logs) - Click Actions → Create subscription filter
- Configure:
- Destination:
Kinesis Data Firehose - Delivery stream: select the one you created
- Filter pattern: leave blank to capture all logs
- Destination:
- Click Start streaming
Step 4: Verify Log Ingestion in OpenObserve
- Go to Logs → select your log stream → Set time range → Click Run Query
Optional: Transform Logs with VRL
You can parse and enrich the Route 53 log lines using VRL in your OpenObserve ingestion pipeline.
parsed = parse_regex!(.message, r'^(?P<version>\d+\.\d+) (?P<timestamp>[^ ]+) (?P<hosted_zone_id>[^ ]+) (?P<query_name>[^ ]+) (?P<query_type>[^ ]+) (?P<response_code>[^ ]+) (?P<protocol>[^ ]+) (?P<edge_location>[^ ]+) (?P<resolver_ip>[^ ]+) (?P<answer>[^ ]+)$')
.route53_version = parsed.version
.route53_query_timestamp = parsed.timestamp
.route53_hosted_zone_id = parsed.hosted_zone_id
.route53_query_name = parsed.query_name
.route53_query_type = parsed.query_type
.route53_response_code = parsed.response_code
.route53_protocol = parsed.protocol
.route53_edge_location = parsed.edge_location
.route53_resolver_ip = parsed.resolver_ip
.route53_answer = parsed.answer
Tip: Enrich resolver IPs with geo-location using MaxMind:
NOTE: You can download our prebuilt dashboards from our git repository.if is_ipv4(string!(.route53_resolver_ip)) { .geo = get_geoip(.route53_resolver_ip, "maxmind_city") }
Troubleshooting
-
No logs in OpenObserve?
- Check Route 53 query logging is enabled
- Validate CloudWatch Logs retention
- Ensure subscription filter is active
- Confirm Firehose stream is healthy (review S3 failed backups)
- Check OpenObserve URL and access keys
-
VRL parsing errors
- Confirm log lines match the regex
- Adjust grouping to fit custom field formats
- Test VRL transformations with individual log samples in pipeline preview
-
Geo-IP enrichment fails
- Confirm MaxMind tables (
maxmind_city,maxmind_asn) are available and referenced - Verify
route53_resolver_ipis a valid IPv4/IPv6
- Confirm MaxMind tables (