Integration with Ansible
This guide walks you through forwarding Ansible logs from an Ubuntu machine to OpenObserve using Fluent Bit.
Overview
Ansible doesn’t send logs to external systems by default. This integration configures a local playbook to write logs to a file, and uses Fluent Bit to tail that file and send logs to OpenObserve over HTTP.
Steps to Integrate
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu machine (local, virtual machine, or cloud VM)
- User with
sudoprivileges - Basic familiarity with Ansible and Fluent Bit
- OpenObserve account (Cloud or Self-Hosted)
- Ansible Installed
Step 1: Configure Ansible log File
- Configure log output path in
ansible.cfg:
Step 2: Create a Local Ansible Task (Optional)
- Create a sample playbook:
-
Add the following contents:
--- - name: Ansible Local Task Demo hosts: localhost connection: local tasks: - name: Create a sample file ansible.builtin.file: path: /tmp/ansible_log_demo.txt state: touch - name: Write a message to the sample file ansible.builtin.copy: content: "This is a demo log entry from Ansible." dest: /tmp/ansible_log_demo.txt -
Run the playbook:
After running, check /tmp/ansible_log_demo.txt to confirm logs are generated.
Step 3: Install Fluent Bit on Ubuntu
-
Install Fluent Bit using the official script:
For manual install or using package managers, refer to Fluent Bit Docs
-
Verify installation:
Step 4: Configure Fluent Bit for Ansible Logs
-
Edit Fluent Bit config file:
-
Add the following configuration:
[SERVICE] Flush 5 Daemon Off Log_Level info [INPUT] Name tail Path /tmp/ansible_log_demo.txt Tag ansible.demo Refresh_Interval 5 [OUTPUT] Name http Match * URI /api/<O2_ORG_NAME>/<O2_STREAM_NAME>/_json Host <O2_HOST> Port 443 tls On Format json Json_date_key _timestamp Json_date_format iso8601 HTTP_User <O2_USER> HTTP_Passwd <O2_PASSWORD> compress gzip
Note - Replace
<O2_ORG_NAME>,<O2_STREAM_NAME>,<O2_HOST>,<O2_USER>, and<O2_PASSWORD>with your OpenObserve values. - Example URI:/api/default/ansible/_jsonfor thedefaultorg andansiblestream.
Step 5: Start Fluent Bit
- Start the Fluent Bit service:
- Check service status:
Ensure there are no startup errors. Logs will now be tailed and sent to OpenObserve.
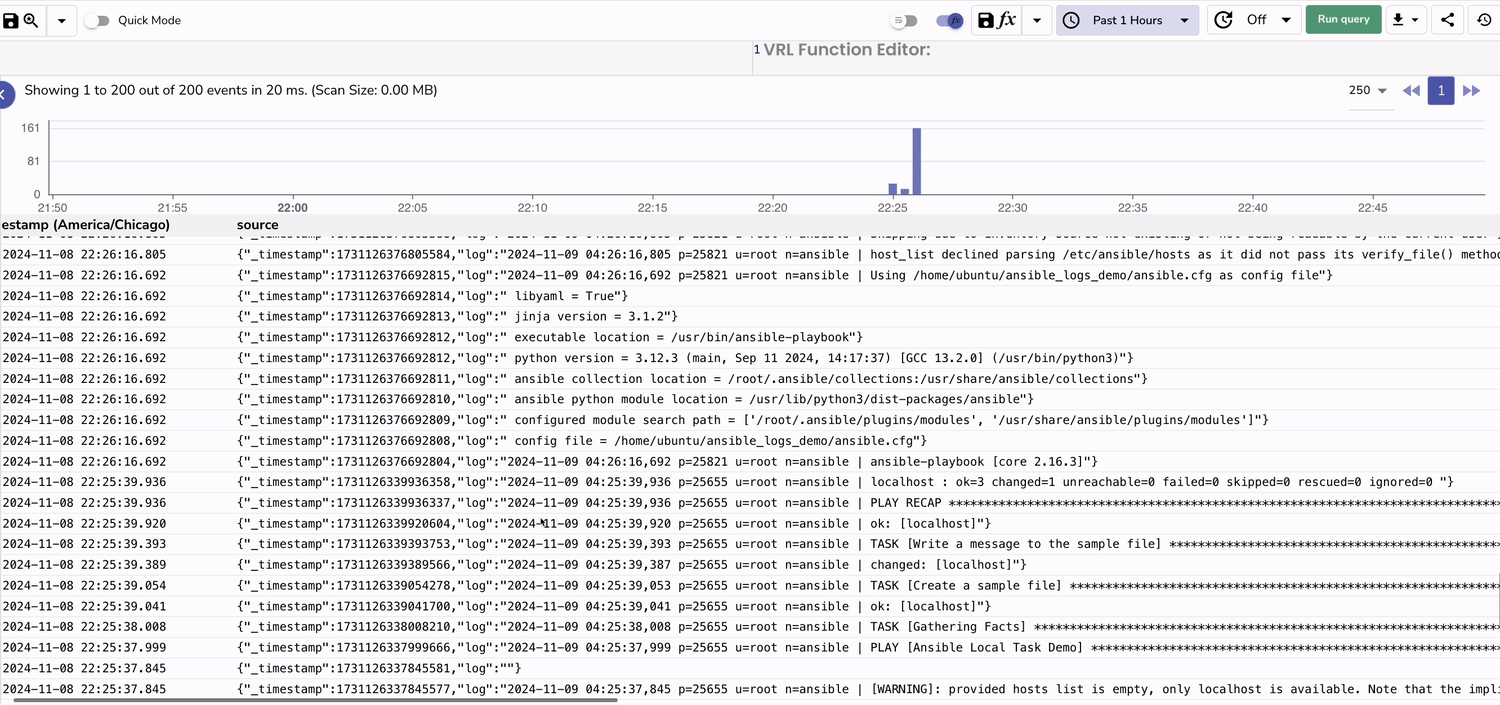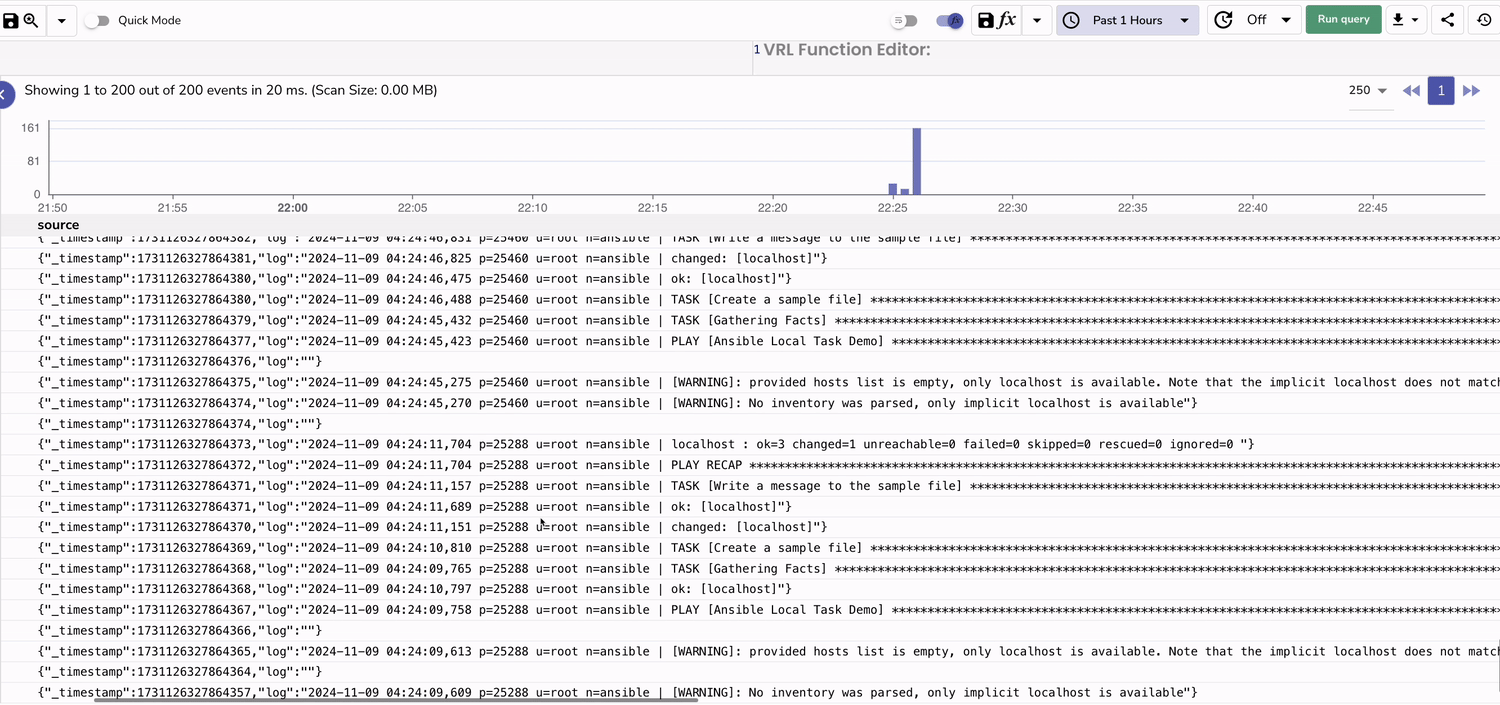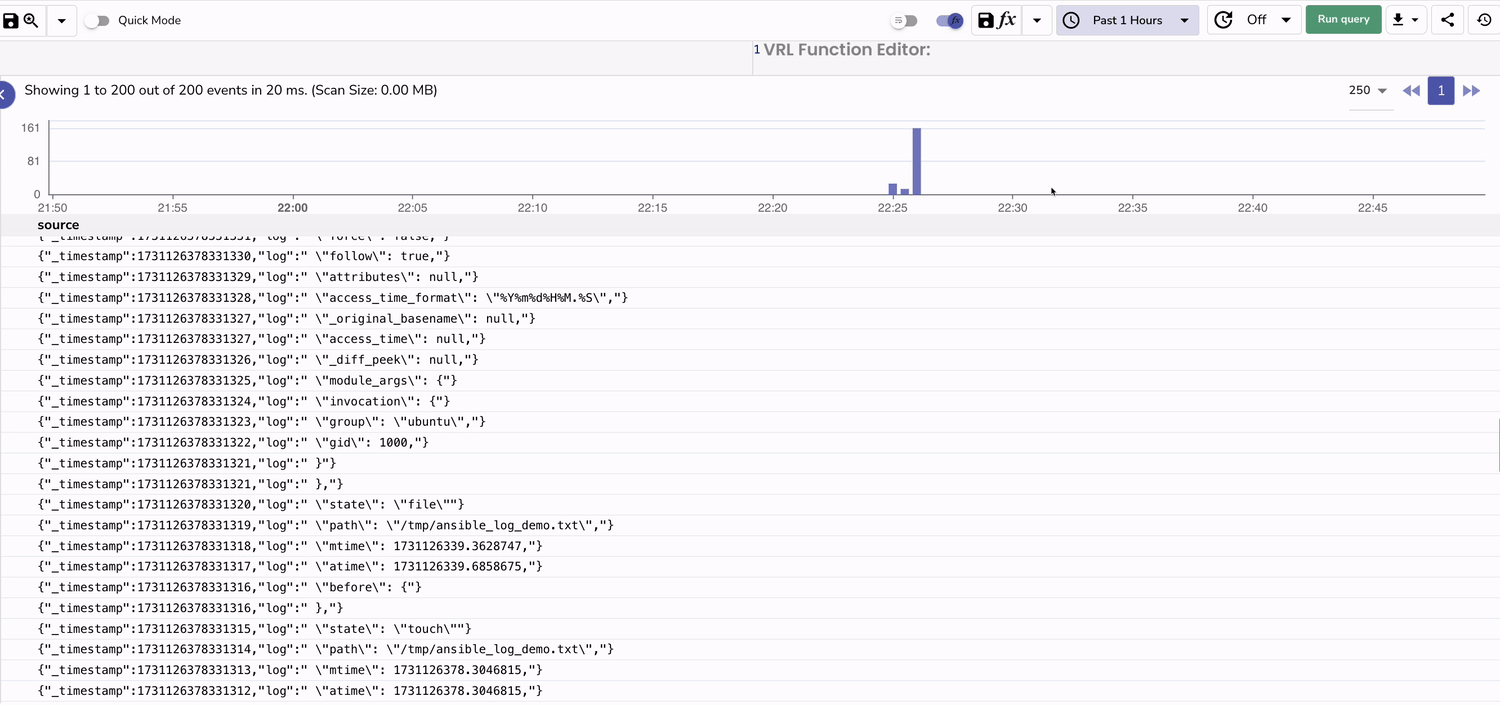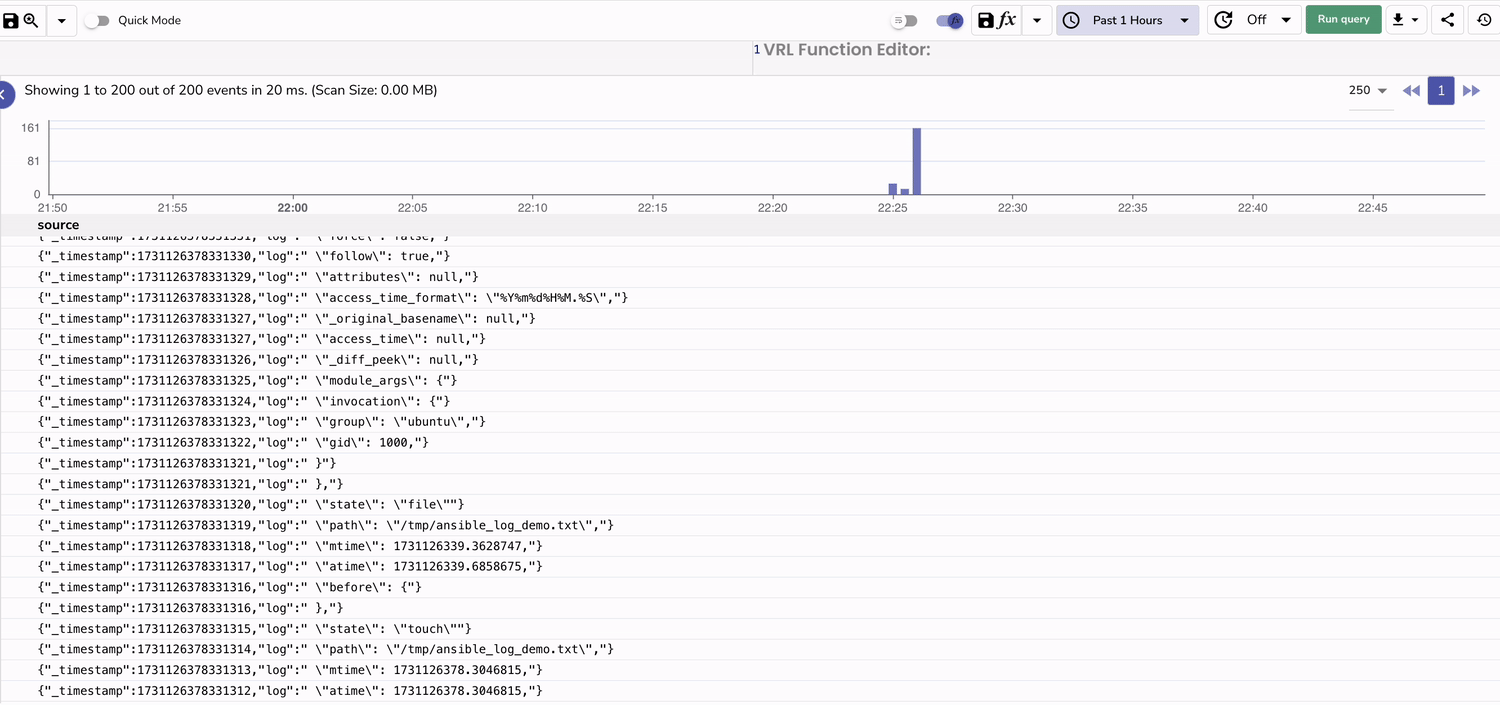
Step 6: Verify Logs in OpenObserve
-
In your Openobserve instance, Go to Logs → select your log stream → Set time range → Click Run Query
Troubleshooting
No logs in OpenObserve?
- Ensure Fluent Bit is running:
sudo systemctl status fluent-bit - Double-check the HTTP config and authentication
- Use Fluent Bit in debug mode:
Ansible log file not updating?
- Confirm
log_pathis correctly set inansible.cfg - Use verbose flags (
-v,-vv,-vvv) to produce more logs - Confirm Ansible has permission to write to
/tmp