AWS Network Firewall Explained: Setup and Log Analysis Made Easy


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free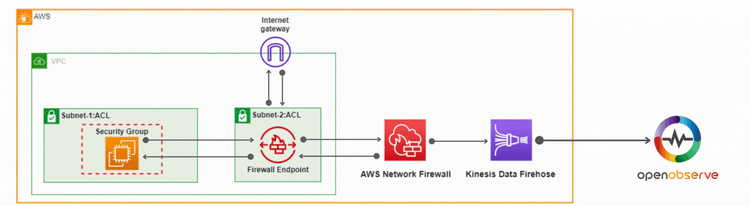
In today’s cloud world, securing your network infrastructure is not just a necessity—it's a priority. AWS Network Firewall, a fully managed service, offers powerful network protection for your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). If you're looking for a beginner-friendly yet comprehensive guide, you're in the right place. This blog will help you understand AWS Network Firewall, its components, how it differs from other AWS security services, and how to set it up.
We’ll also walk you through a step-by-step demo, where we’ll configure the firewall, control traffic, and analyze logs using OpenObserve for actionable insights. By the end, you'll know how to protect your AWS workloads like a pro.
When you deploy workloads in the cloud, managing network security on AWS becomes critical. AWS offers several tools to control traffic, including security groups, NACLs (Network Access Control Lists), and firewalls.
Security groups are like virtual firewalls for your EC2 instances, controlling inbound and outbound traffic. They’re stateful, meaning if inbound traffic is allowed, the response traffic is automatically allowed.
NACLs work at the subnet level to allow or deny traffic. Unlike security groups, they are stateless, requiring rules for both inbound and outbound traffic.
While these tools are great for basic security, more sophisticated traffic filtering requires a solution like AWS Network Firewall.
AWS Network Firewall is a managed service that helps protect your Amazon VPCs by automatically scaling with your network traffic. It allows you to create custom firewall rules to control traffic, such as blocking harmful outbound requests. You can also import existing rules from open-source formats or AWS partners. Integrated with AWS Firewall Manager, it makes it easy to manage and apply firewall policies across multiple VPCs and accounts from a central location.
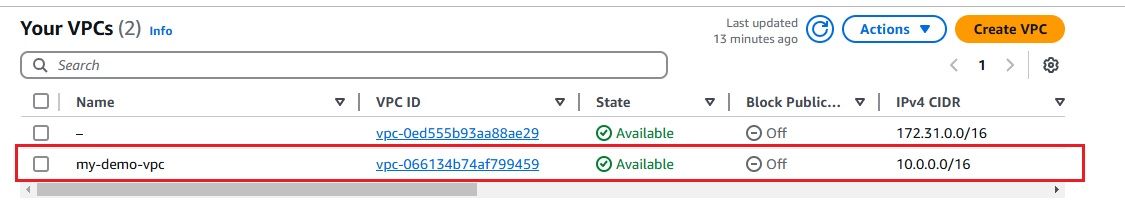
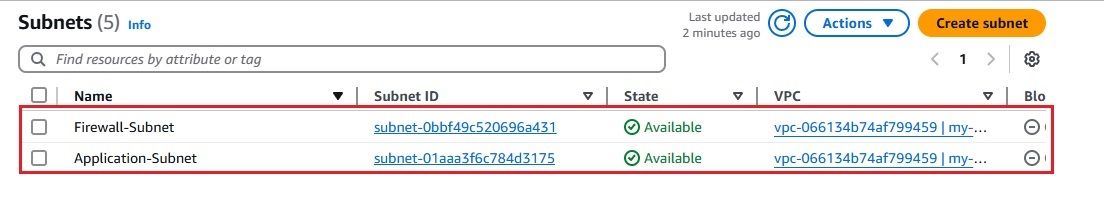
In this section, we'll walk through the process of setting up a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with two subnets: one for the AWS Network Firewall and another for your application. We'll deploy the AWS Network Firewall in the firewall subnet and set up firewall rules to control traffic, including allowing SSH and controlling traffic based on domain names.
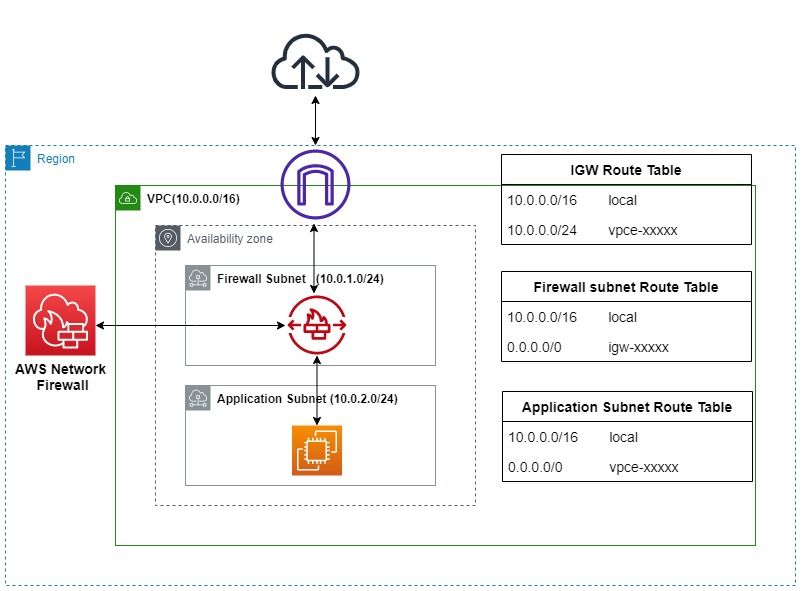
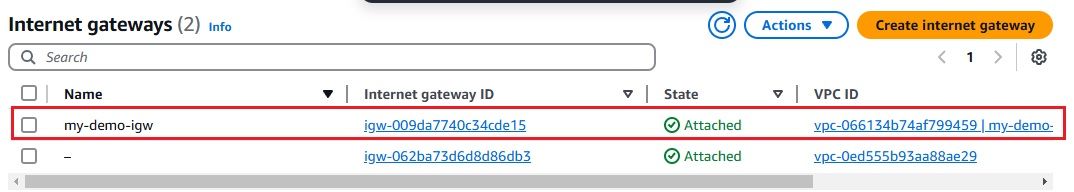
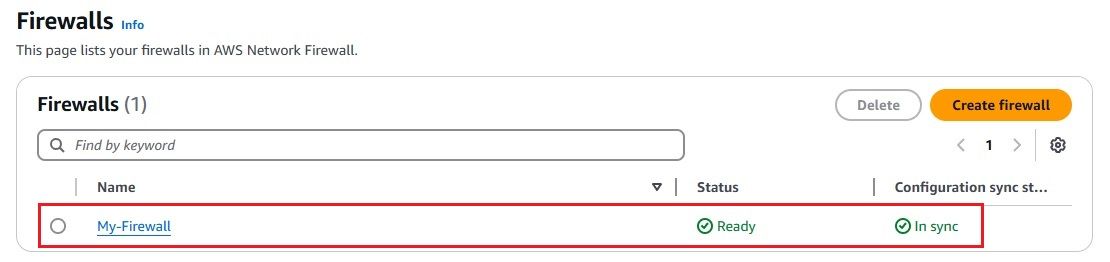
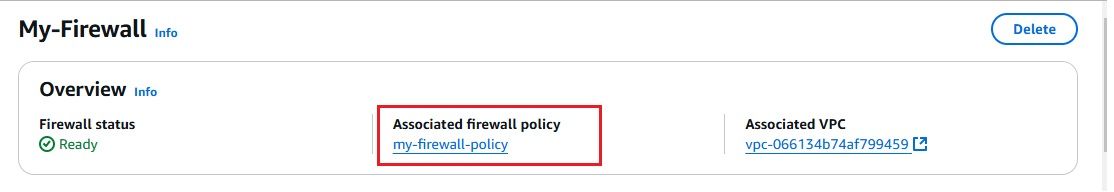
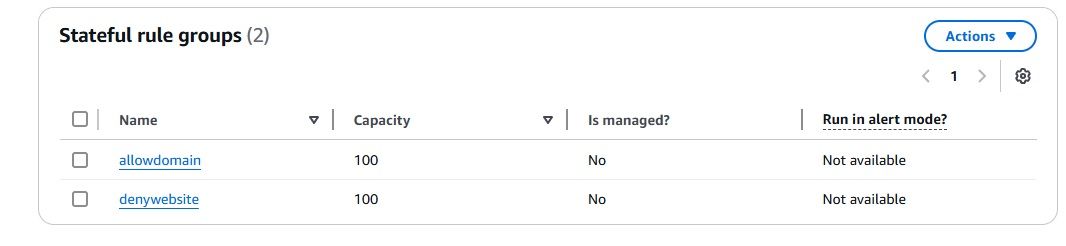

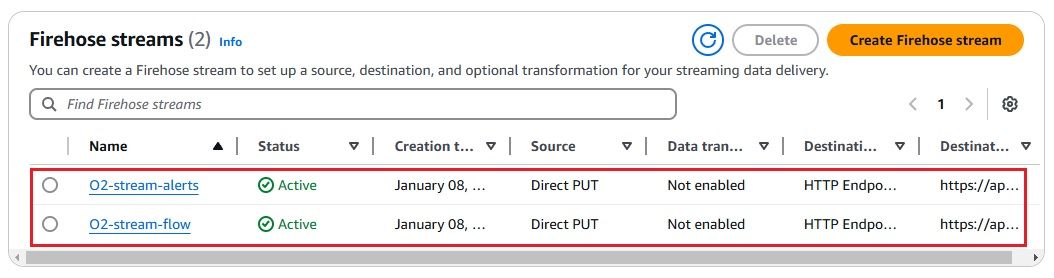
t2.micro for demo purposes). port 22) and any required application ports. Since we have configured the firewall with a stateful rule to allow traffic only to the domain google.com, any attempt to access other domains from the EC2 instance launched in the Application Subnet will be blocked.
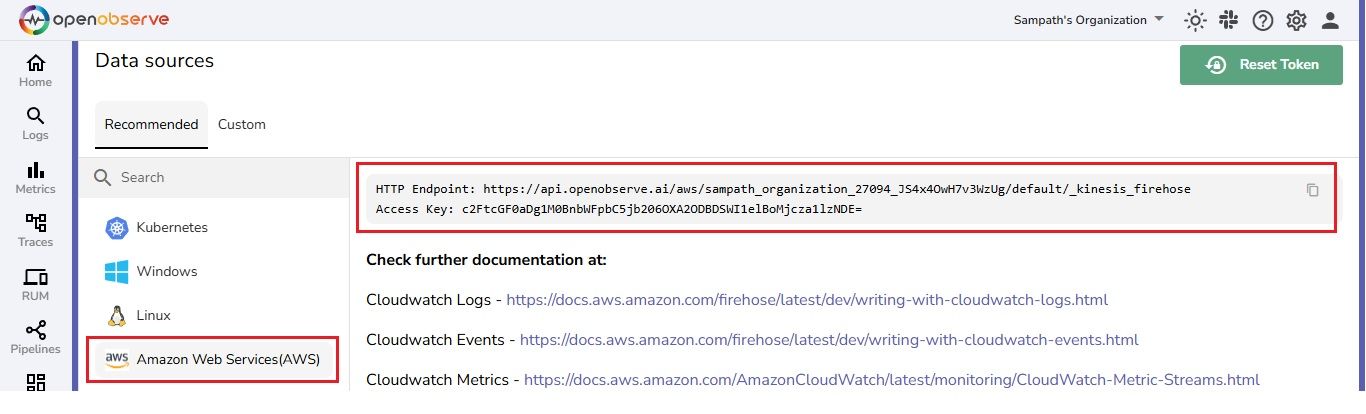
Additionally, we have enabled logging for AWS Network Firewall to send both Flow Logs and Alert Logs to OpenObserve for monitoring and analysis.
Now, let’s test the setup by using curl to access google.com and a few other domains. We should only be able to reach google.com, while requests to other domains will be blocked by AWS Network Firewall. When this happens, the firewall will drop the packets, and an Alert Log will be generated, which can be viewed in OpenObserve.
We are sending Flow Logs and Alert Logs as two separate streams to OpenObserve for better tracking and analysis.
In the alert stream, we can see the Alert Logs from AWS Network Firewall.
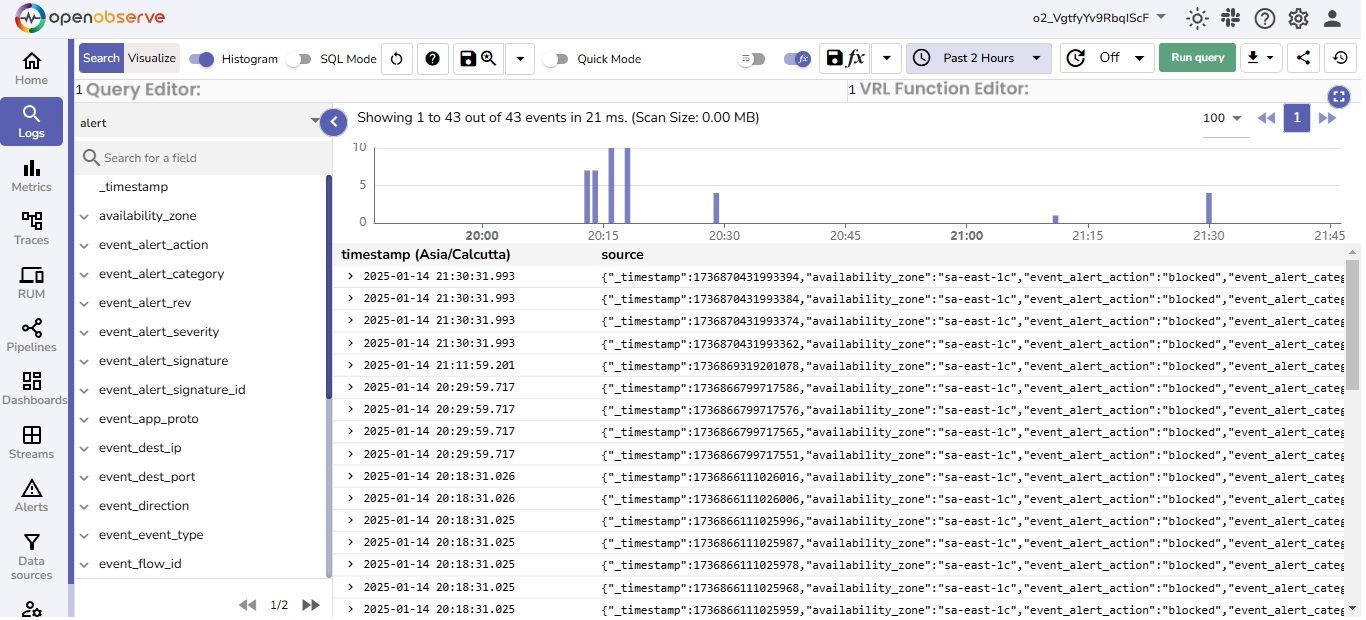
In the flow stream, we can see the Flow Logs from AWS Network Firewall.
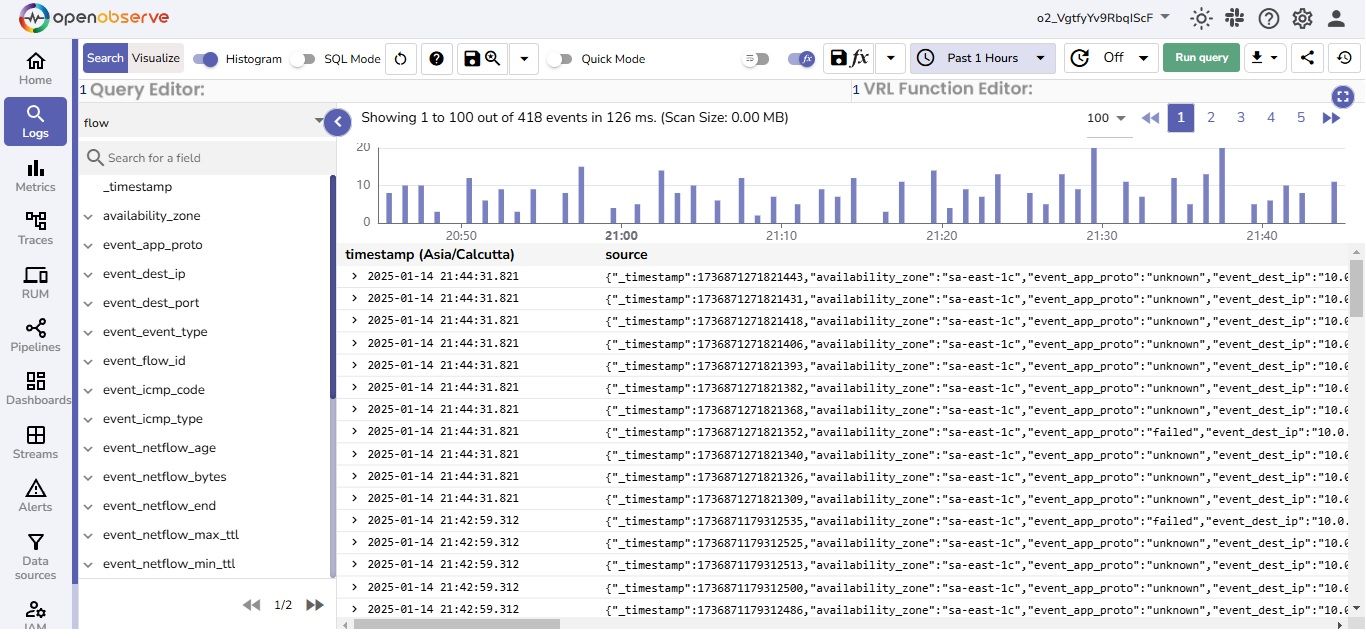
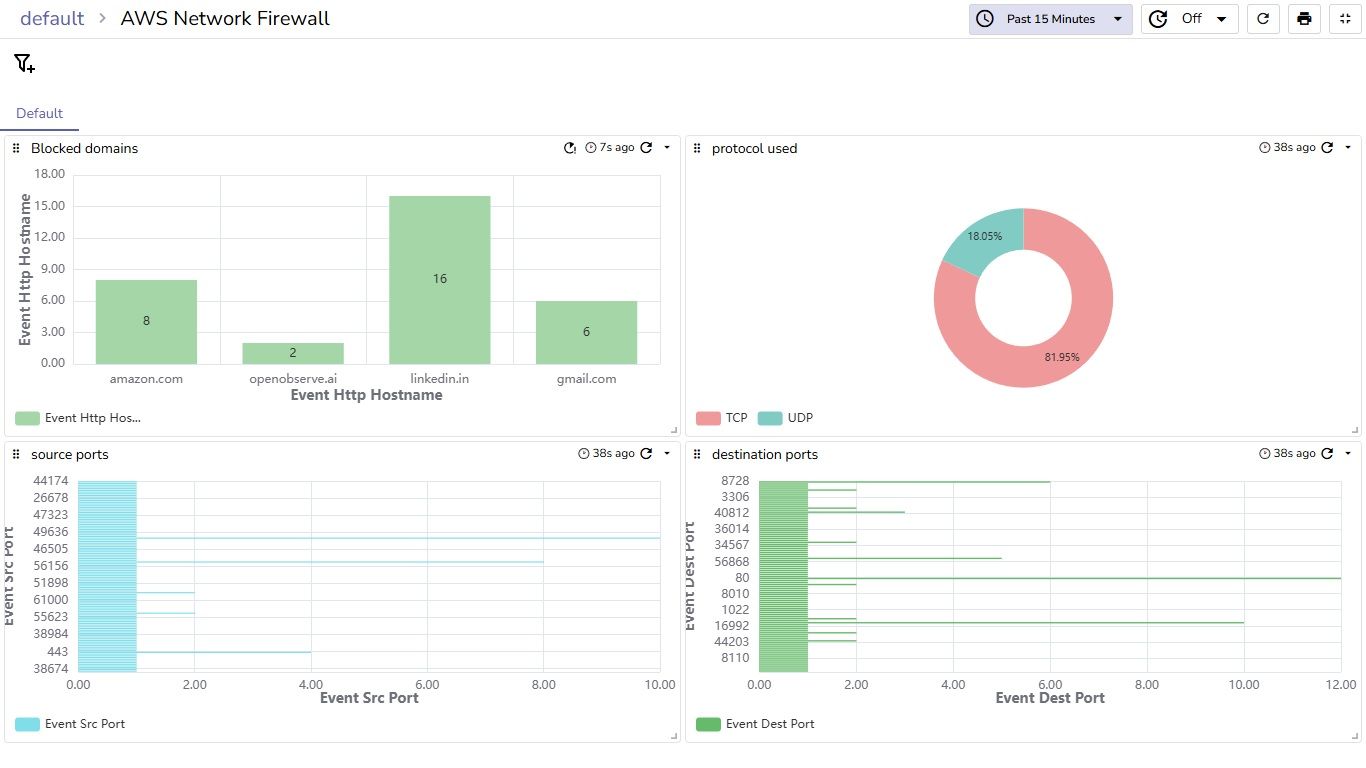
The AWS Network Firewall dashboard provides essential insights into network security and traffic patterns through Alerts and flow logs.
Overall, this dashboard is a vital tool for monitoring security incidents, analyzing traffic flows, and optimizing firewall configurations to enhance network security.
AWS Network Firewall offers advanced, managed security for your VPC with customizable rules to control traffic. By sending its logs to OpenObserve, you can easily analyze network activity, detect issues, and gain valuable insights for better security management and compliance, enhancing your overall network protection strategy.