Introduction
Many applications, especially those that rely on Amazon DynamoDB, benefit significantly from monitoring item-level changes as they occur. For instance, a popular mobile app might update its data thousands of times per second, while another service captures these updates to provide near-instantaneous usage metrics. Similarly, financial applications that modify stock market data in DynamoDB can have parallel systems that track these changes in real time, compute value-at-risk metrics, and automatically rebalance investment portfolios based on stock price movements.
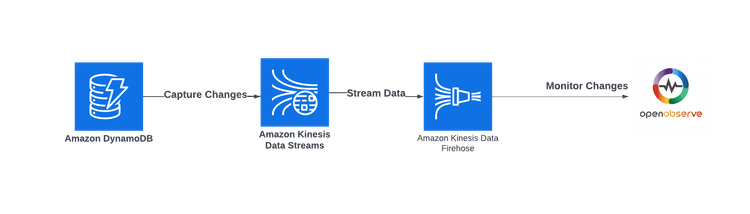
To achieve such capabilities, developers can leverage Amazon Kinesis Data Streams. This service captures item-level modifications in DynamoDB tables and replicates them to a Kinesis data stream. By doing so, devs can access these streams and monitor changes almost immediately, enabling them to continuously capture and store vast amounts of data efficiently. This blog will guide you through the entire process, from setting up your DynamoDB table to analyzing your data in OpenObserve. Let’s get started!
What is Amazon DynamoDB?
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that excels in providing fast and predictable performance at scale. It’s designed for applications that require low-latency responses, making it ideal for scenarios like gaming, IoT, and mobile applications. With features like auto-scaling, built-in security, and backup options.
What are Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose and Data Streams?
Kinesis Data Streams
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams is a robust service that allows you to collect and process real-time data streams. It captures item-level changes in your DynamoDB table and replicates them to a Kinesis data stream. This means you can access and analyze these changes almost instantly!
Kinesis Data Firehose
Kinesis Data Firehose complements Data Streams by making it easy to load streaming data into various AWS services like Amazon S3, Redshift, or OpenObserve. With Firehose, you can transform and deliver your data in real time, enabling you to create dashboards, generate alerts, and implement dynamic analytics without any complex coding.
Prerequisites
Before we jump into the setup, make sure you have the following:
- An AWS account.
- A basic understanding of AWS services, particularly Kinesis Firehose and DynamoDB.
- OpenObserve set up and running.
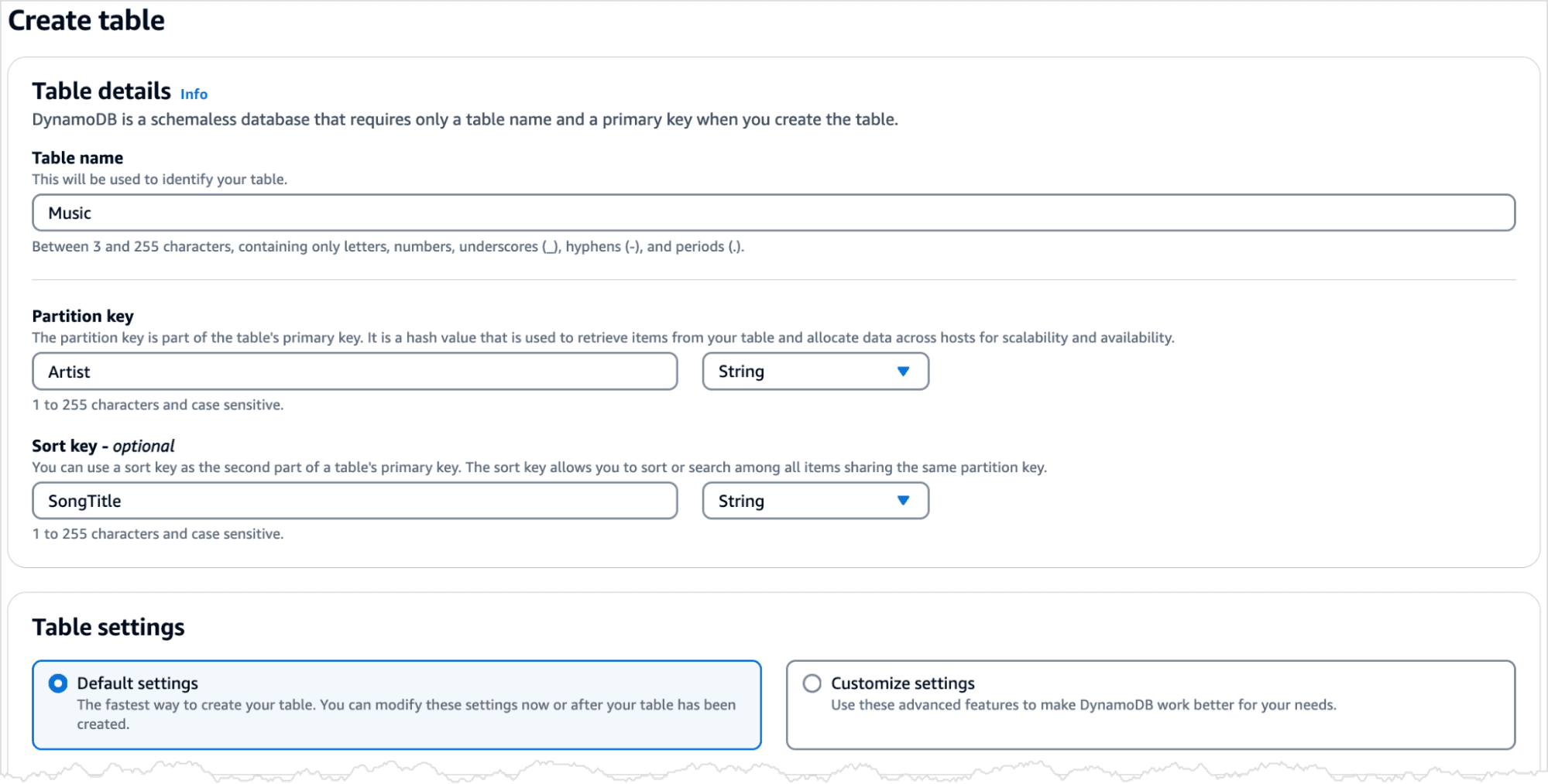
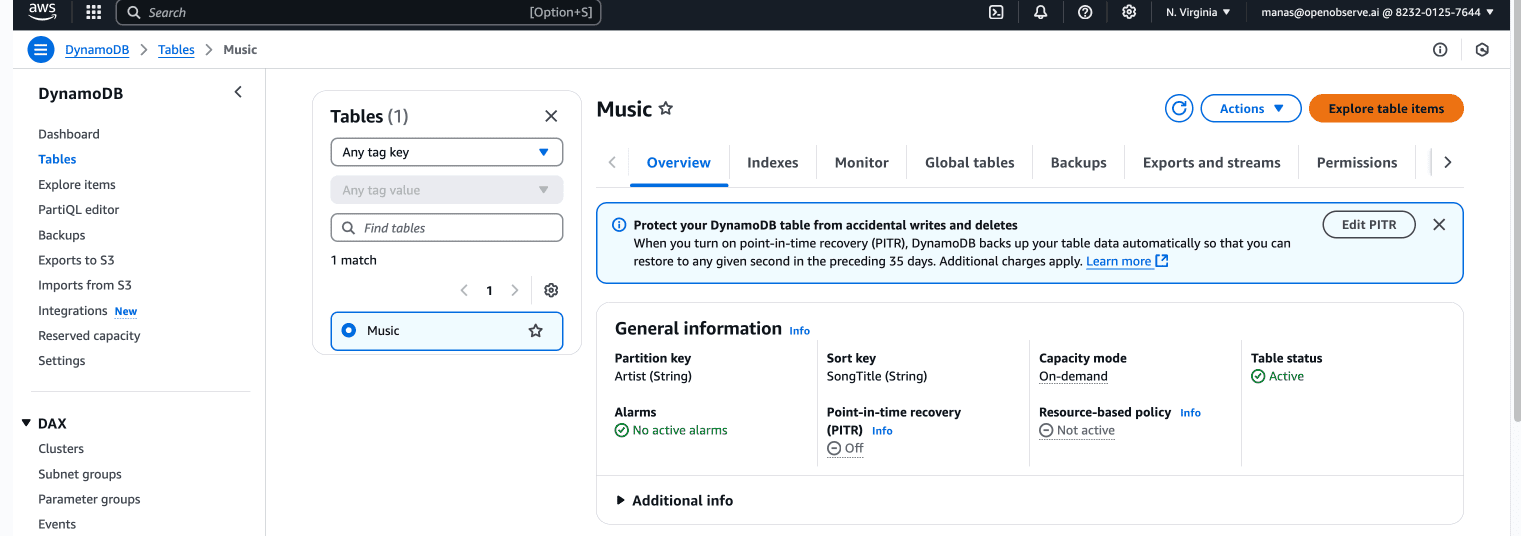
Step 1: Create a Table in DynamoDB
To create a new Music table using the DynamoDB console:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the DynamoDB console at DynamoDB Console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Tables.
- Choose Create table.
- Enter the table details as follows:
- For Table name, enter
Music.
- For Partition key, enter
Artist.
- For Sort key, enter
SongTitle.
- For Table settings, keep the default selection of Default settings.
- Choose Create table to create the table.
Step 2: Write Data to a DynamoDB Table
Now that your table is ready, let's add some data:
- Open the DynamoDB console at DynamoDB Console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Tables.
- On the Tables page, choose the Music table.
- Choose Explore table items.
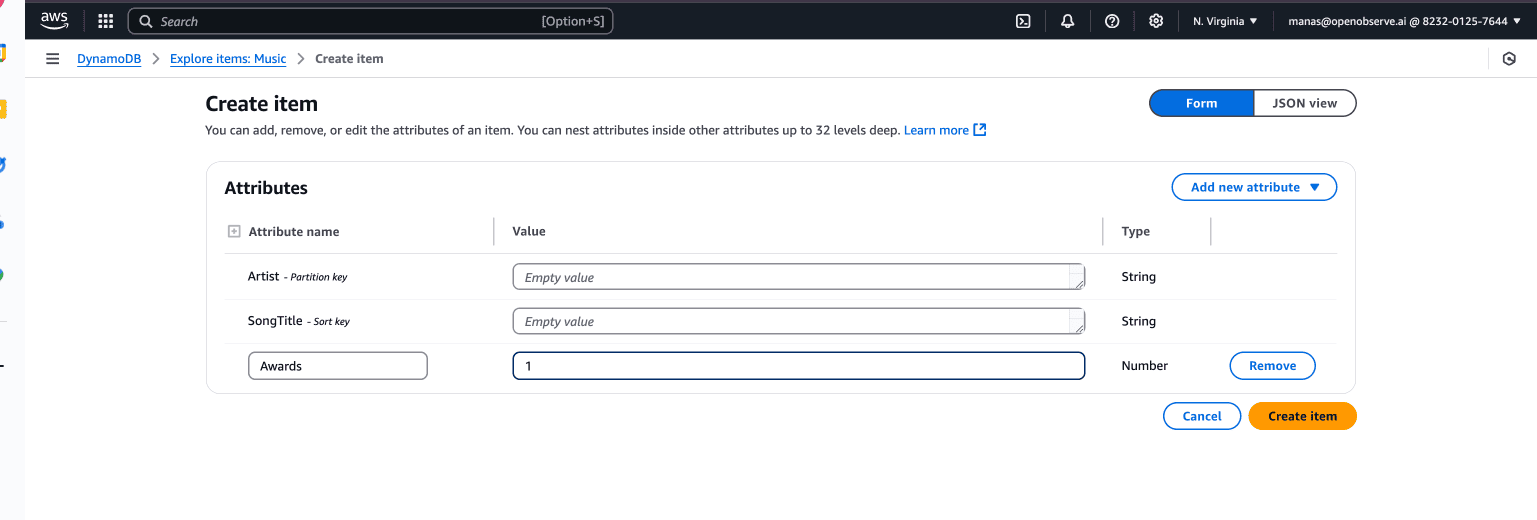
- In the Items returned section, choose Create item.
On the Create item page, do the following to add your first item:
- Choose Add new attribute, and then choose Number.
- For Attribute name, enter
Awards.
- Repeat this process to create an AlbumTitle of type String.
- Enter the following values for your item:
- For Artist, enter
No One You Know.
- For SongTitle, enter
Call Me Today.
- For AlbumTitle, enter
Somewhat Famous.
- For Awards, enter
1.
- Choose Create item.
Now, let's add another item:
- Repeat the process to create another item with the following values:
- For Artist, enter
Acme Band.
- For SongTitle, enter
Happy Day.
- For AlbumTitle, enter
Songs About Life.
- For Awards, enter
10.
- Choose Create item.
Finally, add one more item with the same artist but different values:
- Repeat the process to create another item with the following values:
- For Artist, enter
Acme Band.
- For SongTitle, enter
PartiQL Rocks.
- For AlbumTitle, enter
Another Album Title.
- For Awards, enter
8.
- Choose Create item.
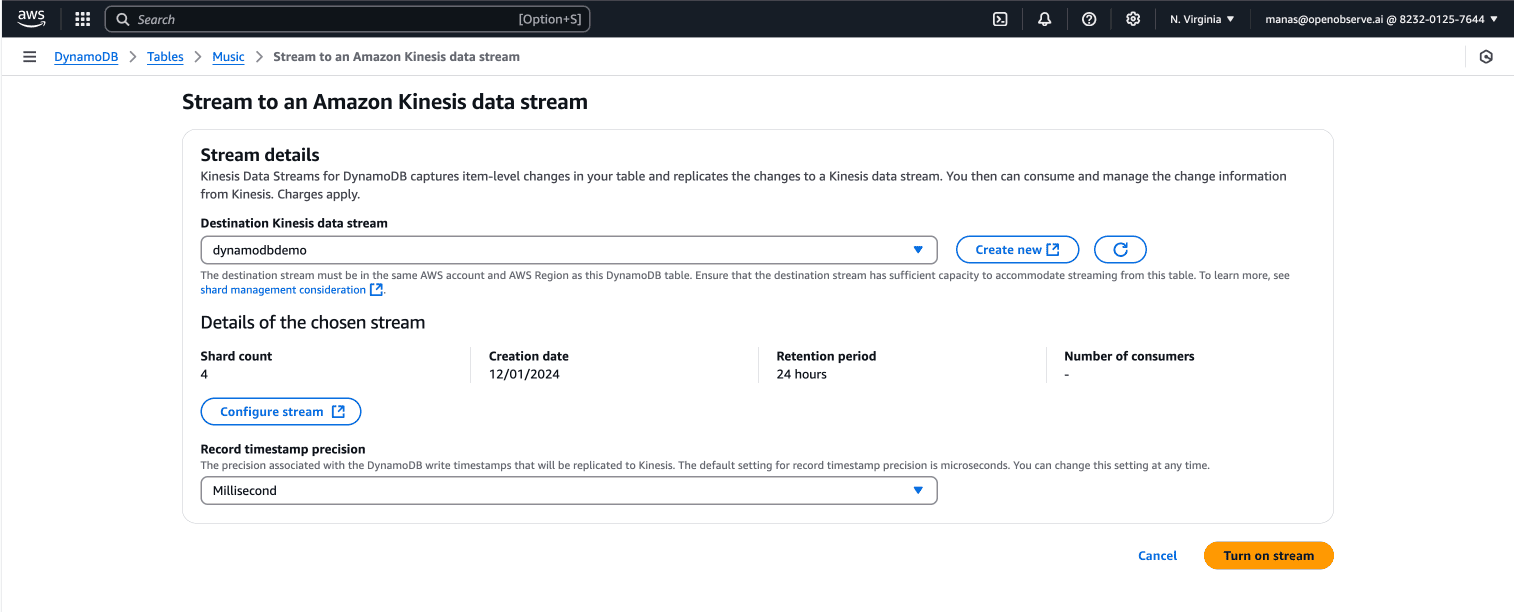
Step 3: Creating an Active Amazon Kinesis Data Stream
Now, let’s create a Kinesis Data Stream and connect it to your DynamoDB table:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Kinesis console at Kinesis Console.
- Choose Create data stream.
- Follow the instructions to create a stream called
dynamodbdemo.
- Open the DynamoDB console at DynamoDB Console.
- In the navigation pane on the left side of the console, choose Tables.
- Choose the Music table.
- Choose the Exports and streams tab.
- Choose the Turn On button.
- (Optional) Under Amazon Kinesis data stream details, you can change the record timestamp precision from microsecond (default) to millisecond.
- Choose
dynamodbdemo from the dropdown list.
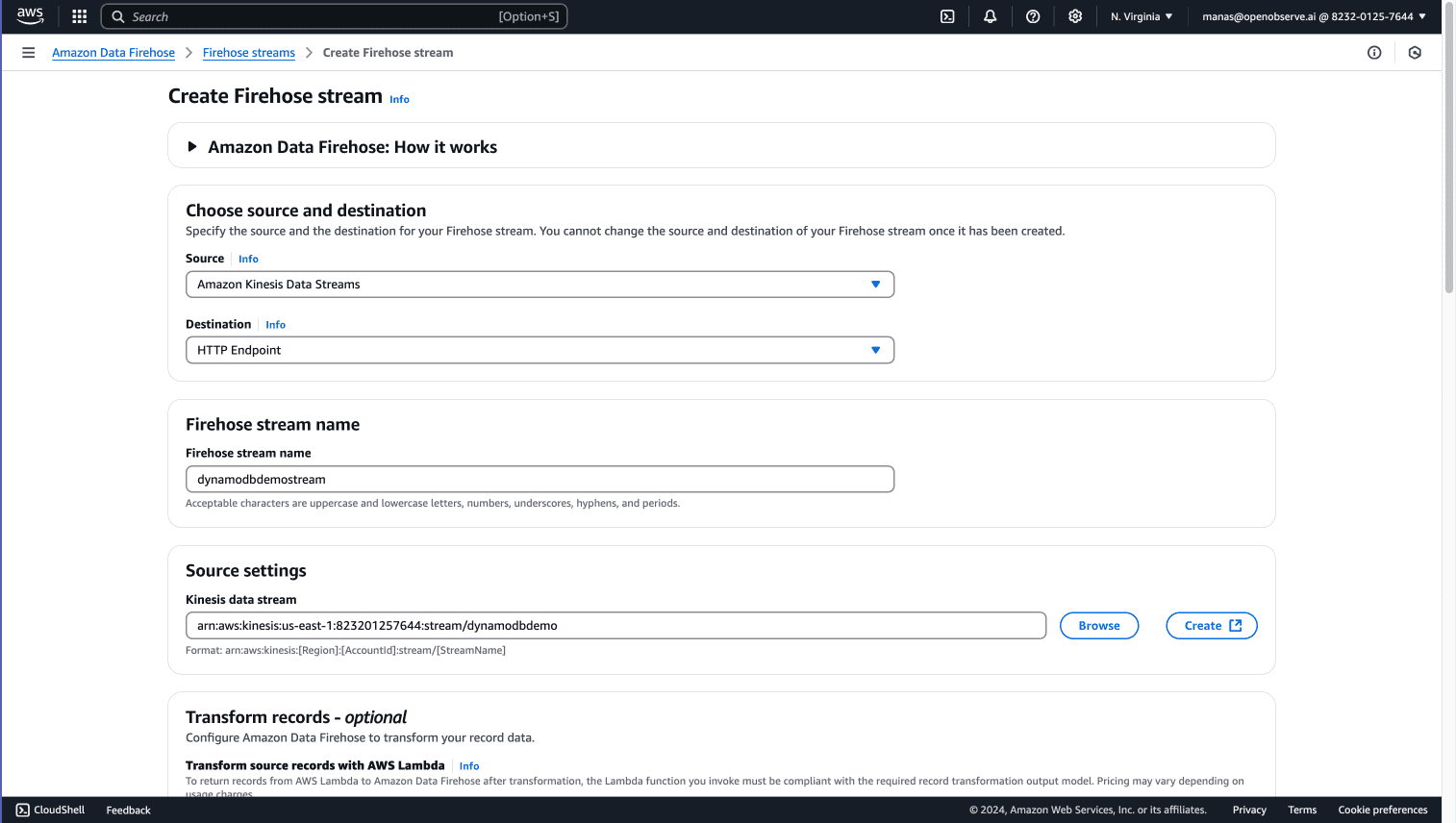
Step 4: Create an Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
Navigate to Kinesis Console
- In the AWS services menu, search for Kinesis and select it.
Create a Delivery Stream
- Click on Create Firehose Stream.
- For the Source, select Kinesis Data Stream, and choose your stream (
dynamodbdemo).
- Click Next.
Configure Destination
- Select HTTP Endpoint as the destination.
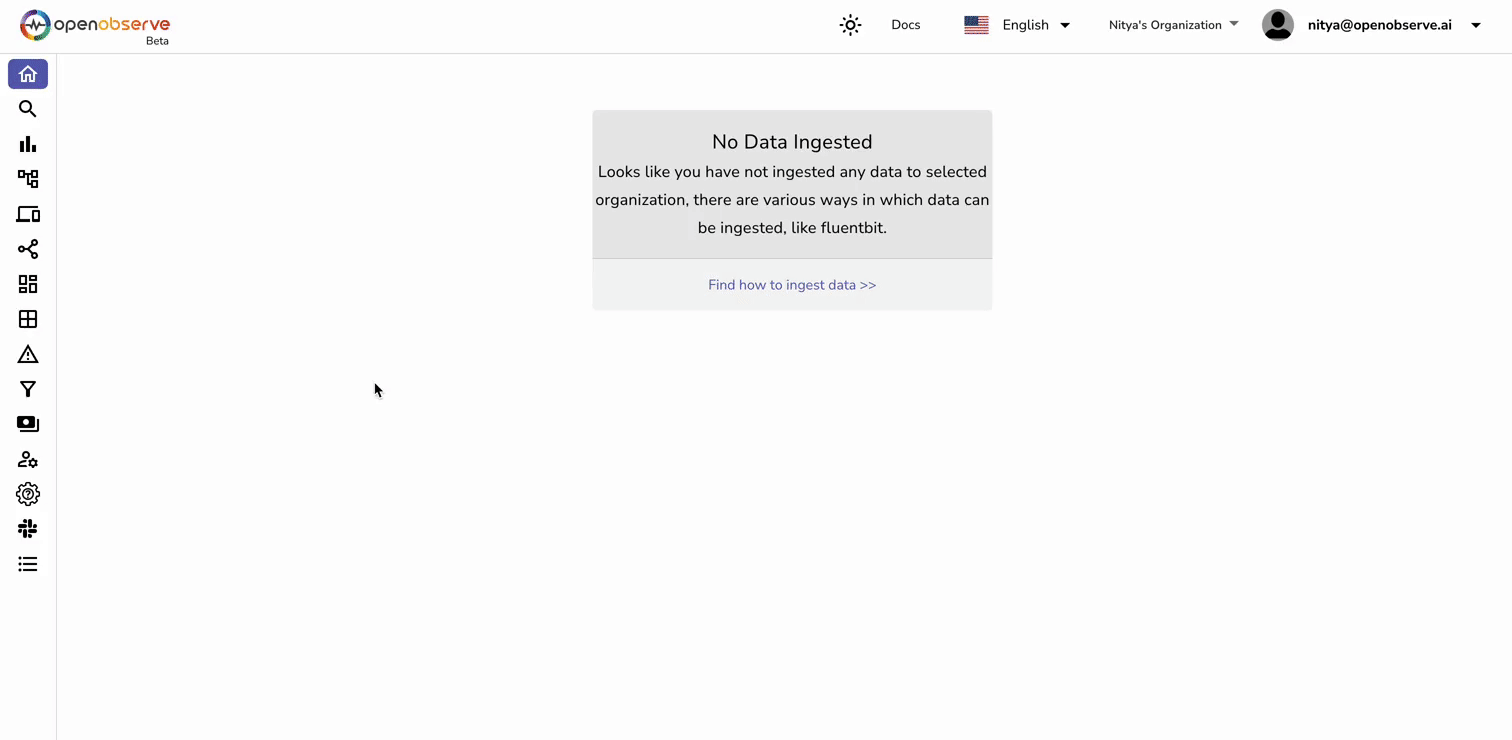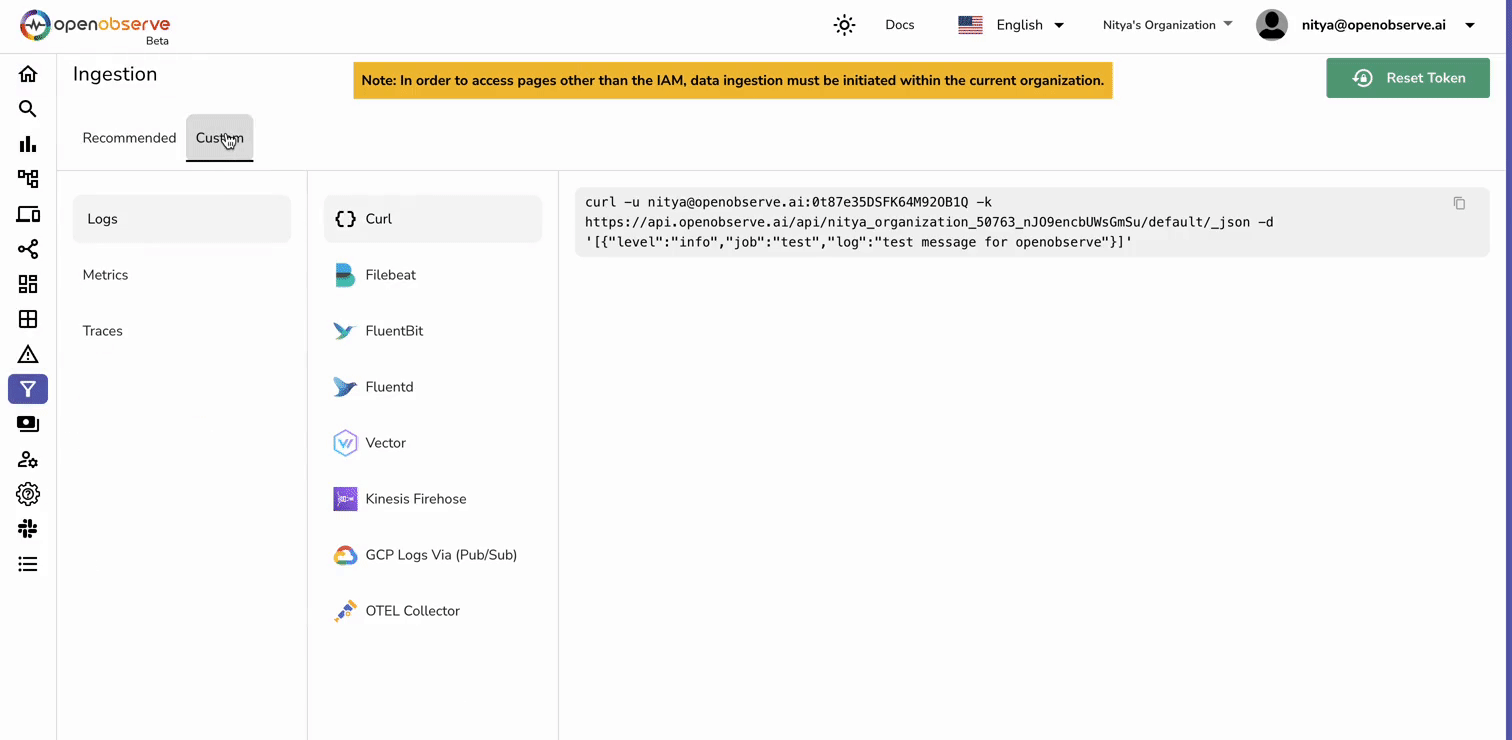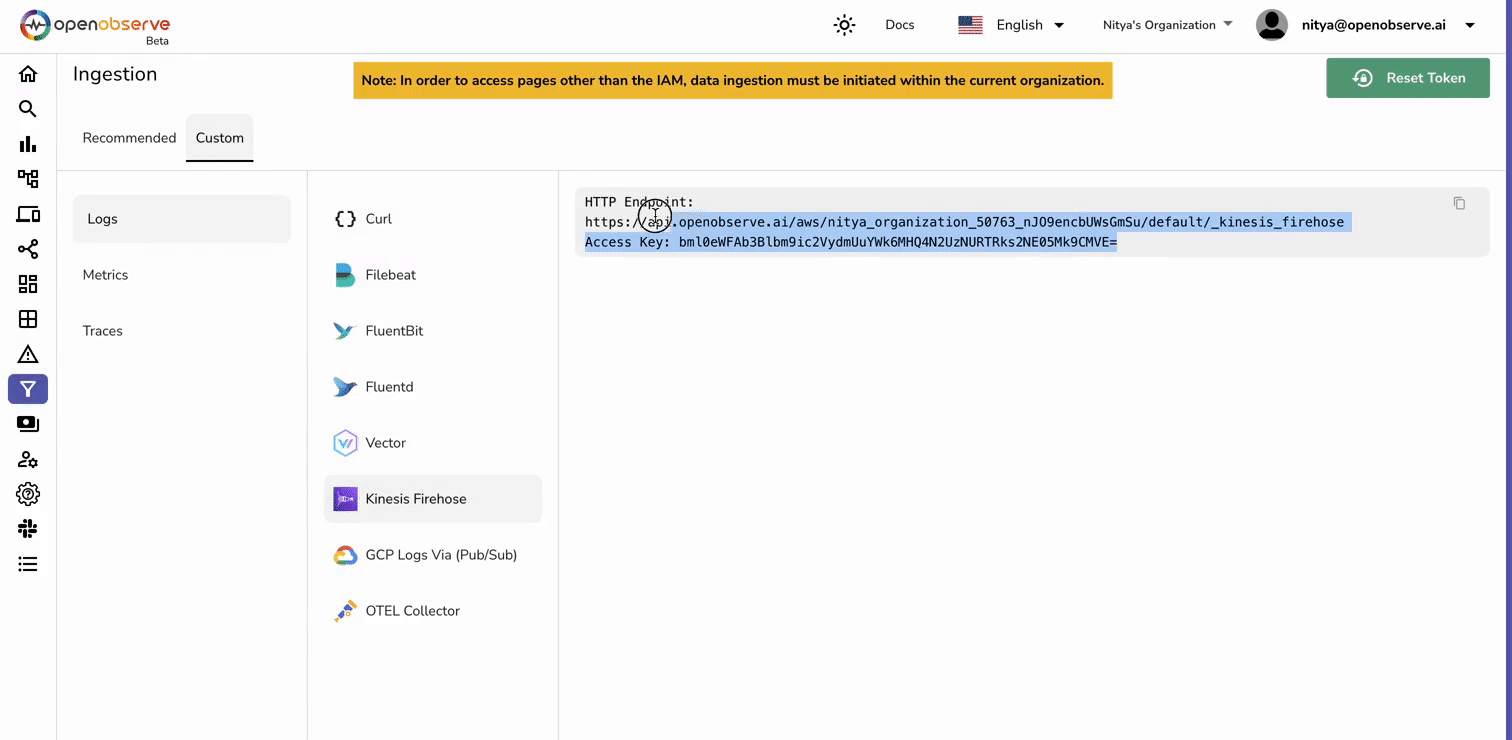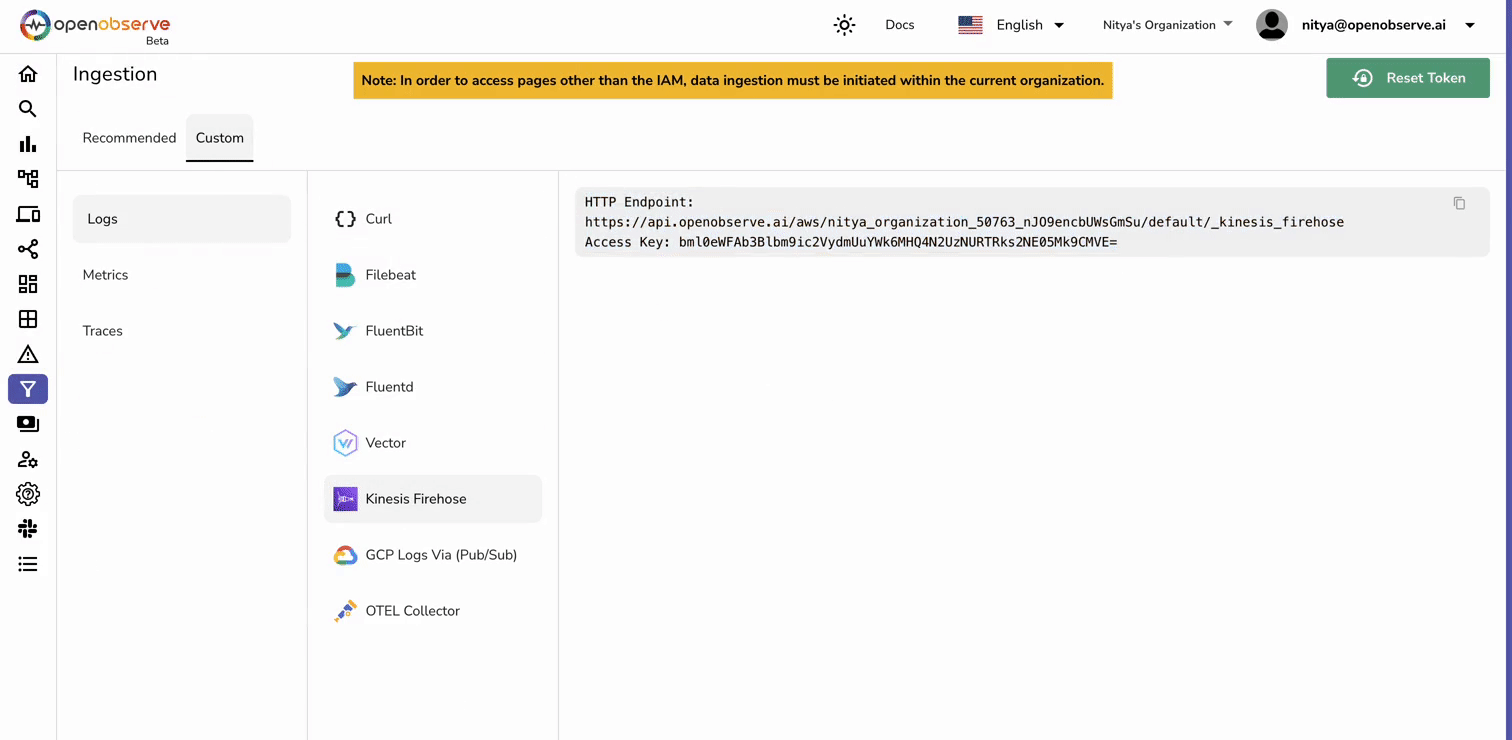
- Endpoint URL: Enter your OpenObserve Kinesis Firehose endpoint (obtain this from OpenObserve -> Ingestions -> Custom -> Amazon Kinesis Firehose.
- Authentication Type: Choose Use access key and enter your OpenObserve access key.
- Click Next.
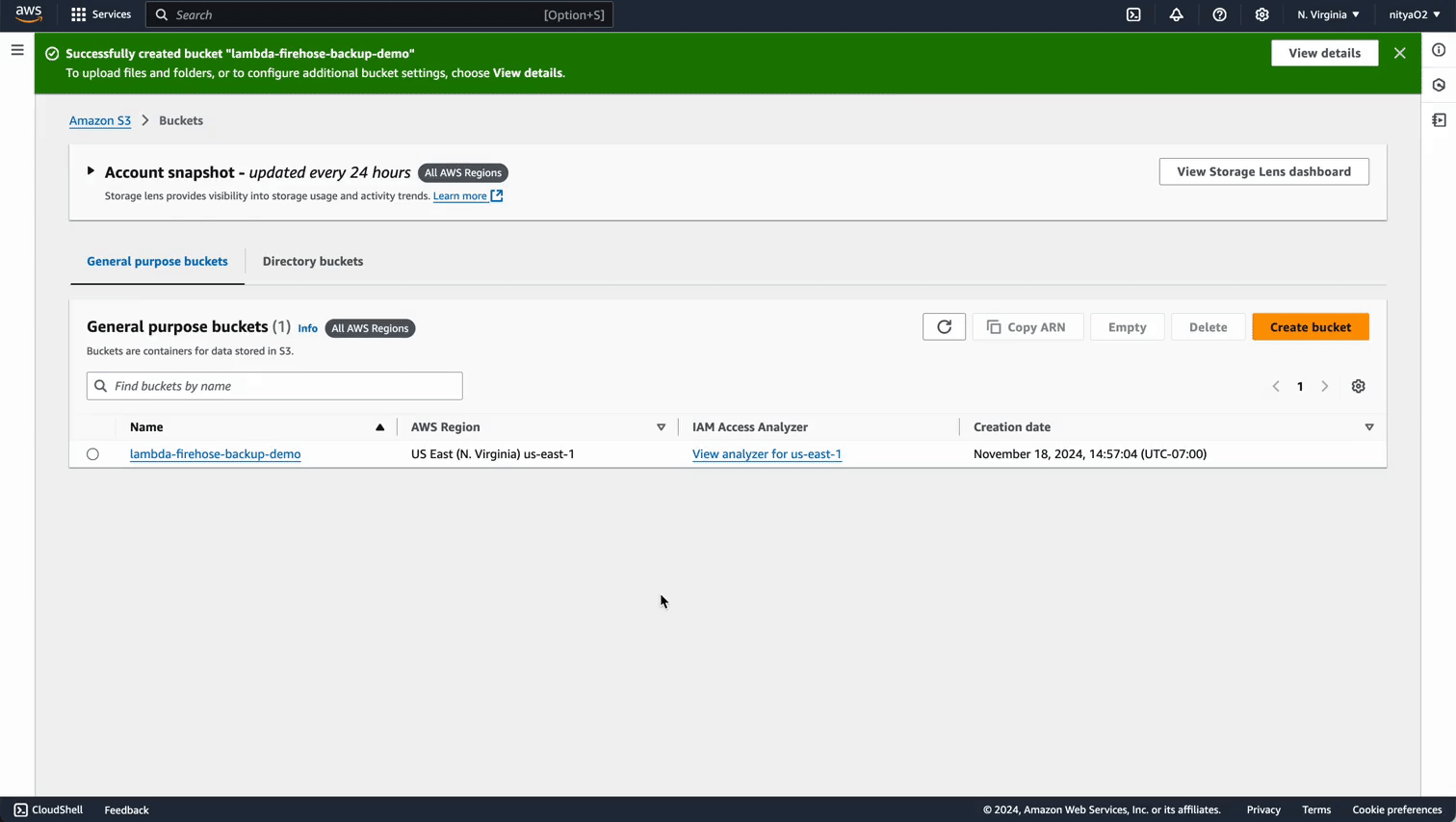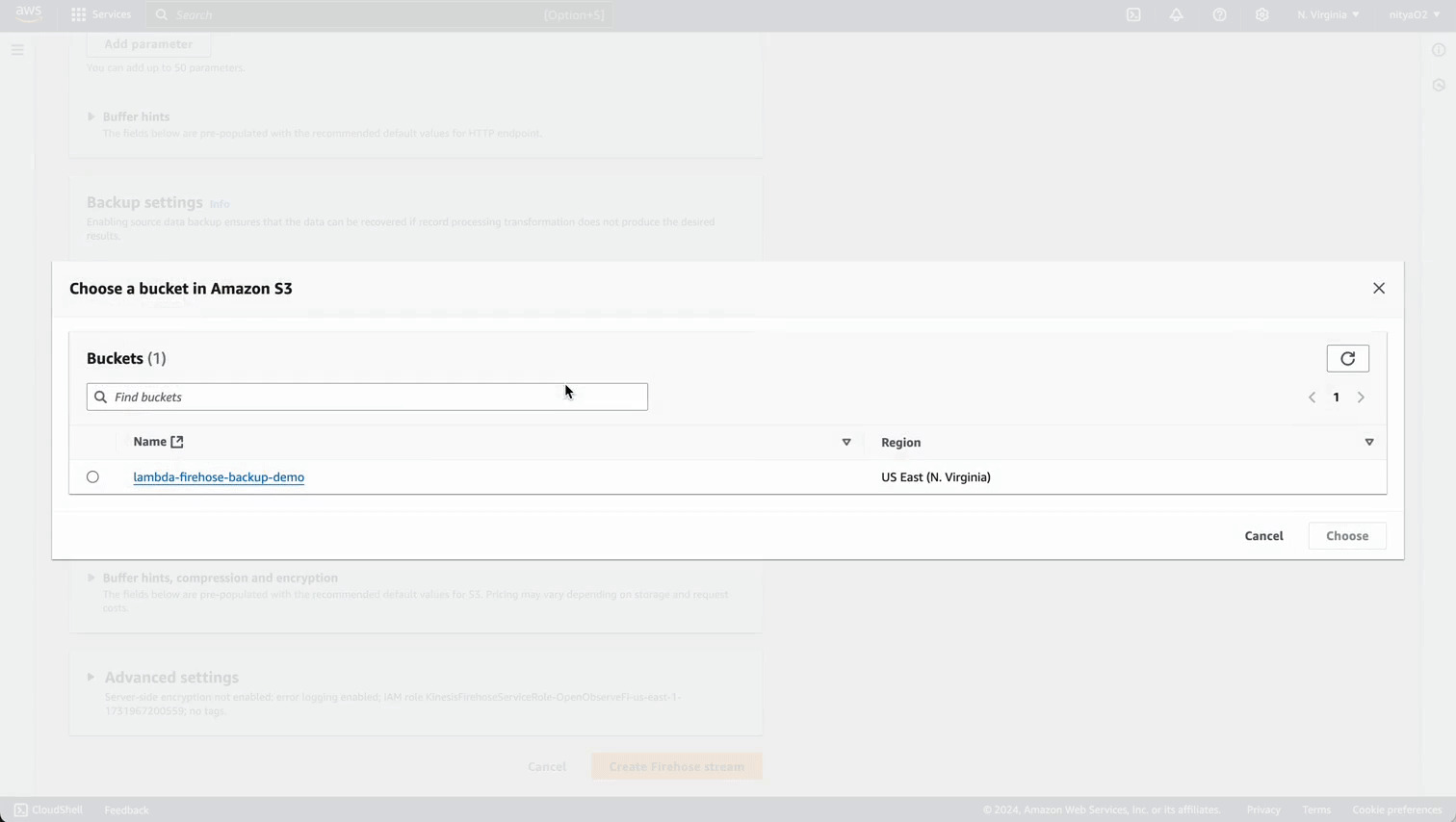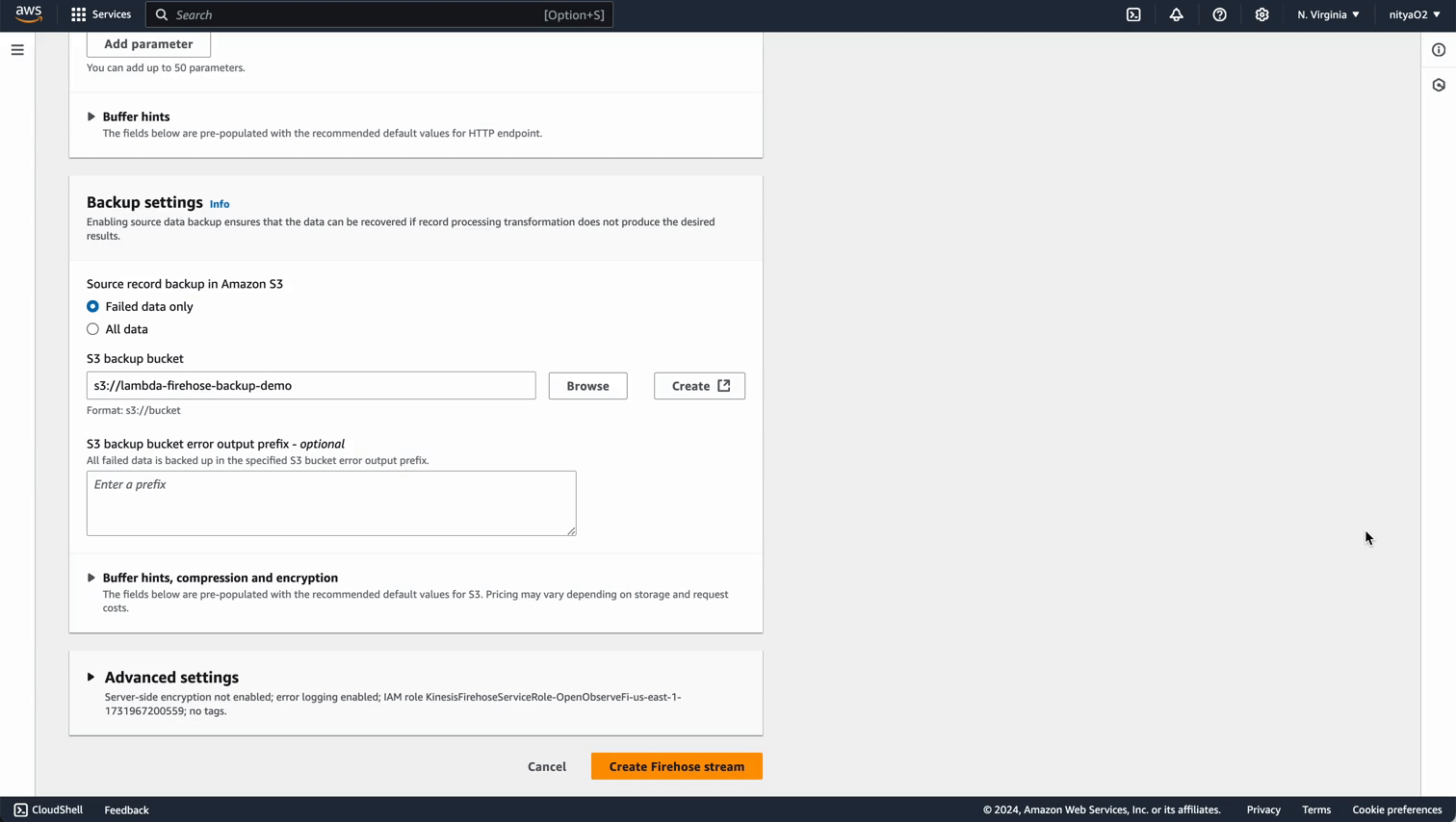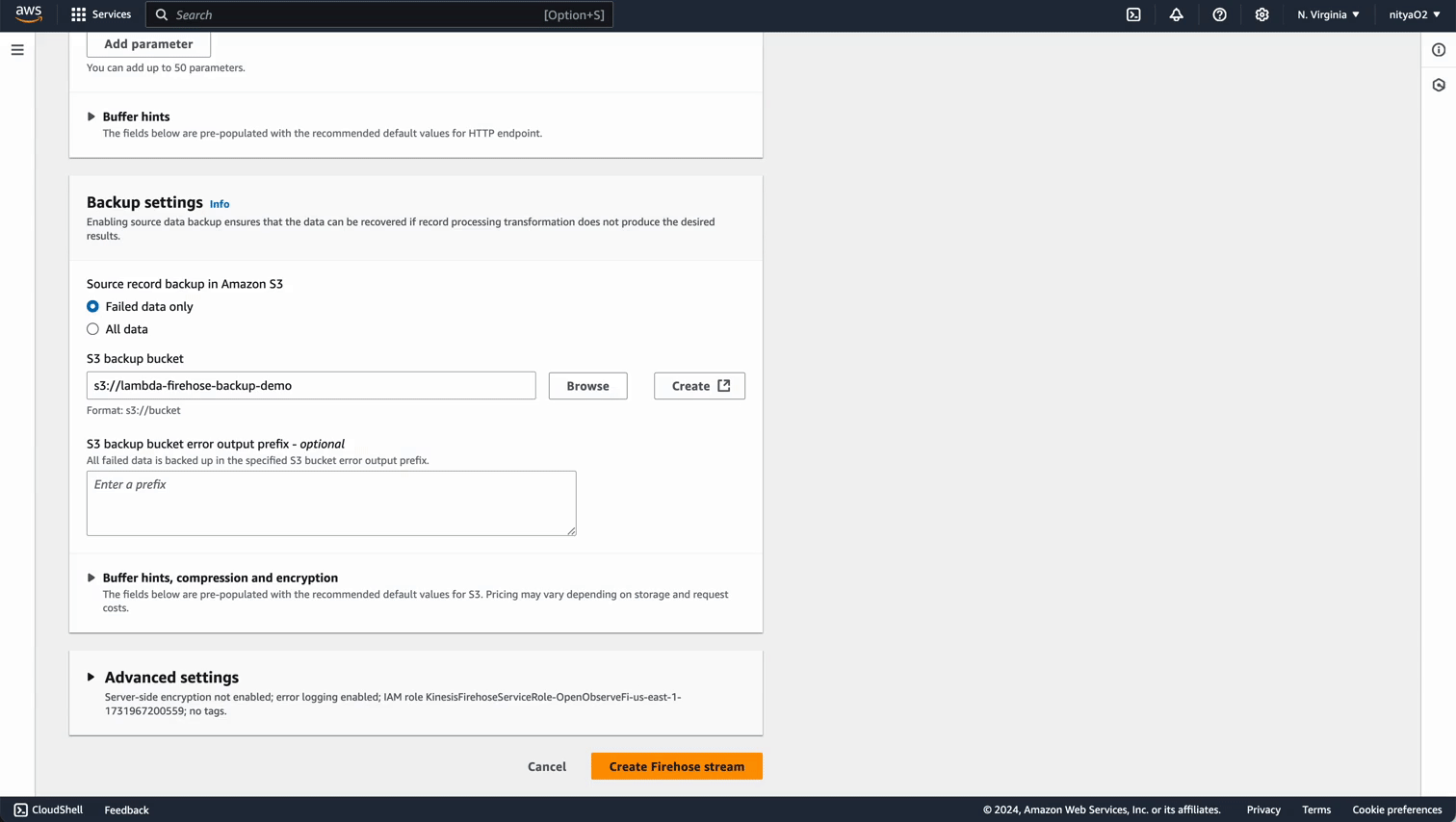
Configure Backup Settings
- Choose whether to back up all data or only failed data. For this example, select Failed data only.
- Choose an existing S3 bucket or create a new one for backups (e.g.
dynamodbdemostream).
- Click Next.
Finalize Firehose Stream Setup
- Click Next, configure buffer size and interval as needed (default values will suffice for this example), then click Next again.
- Review all settings and click on Create Firehose stream.
Step 5: Monitoring Changes in OpenObserve
Now that your data is flowing through Kinesis Firehose, let’s explore how to monitor changes made to your DynamoDB table using OpenObserve.
Understanding the Log Records
As changes occur in your DynamoDB table, they are captured and sent to OpenObserve in JSON format. Each log record contains several fields that provide valuable information about the changes.
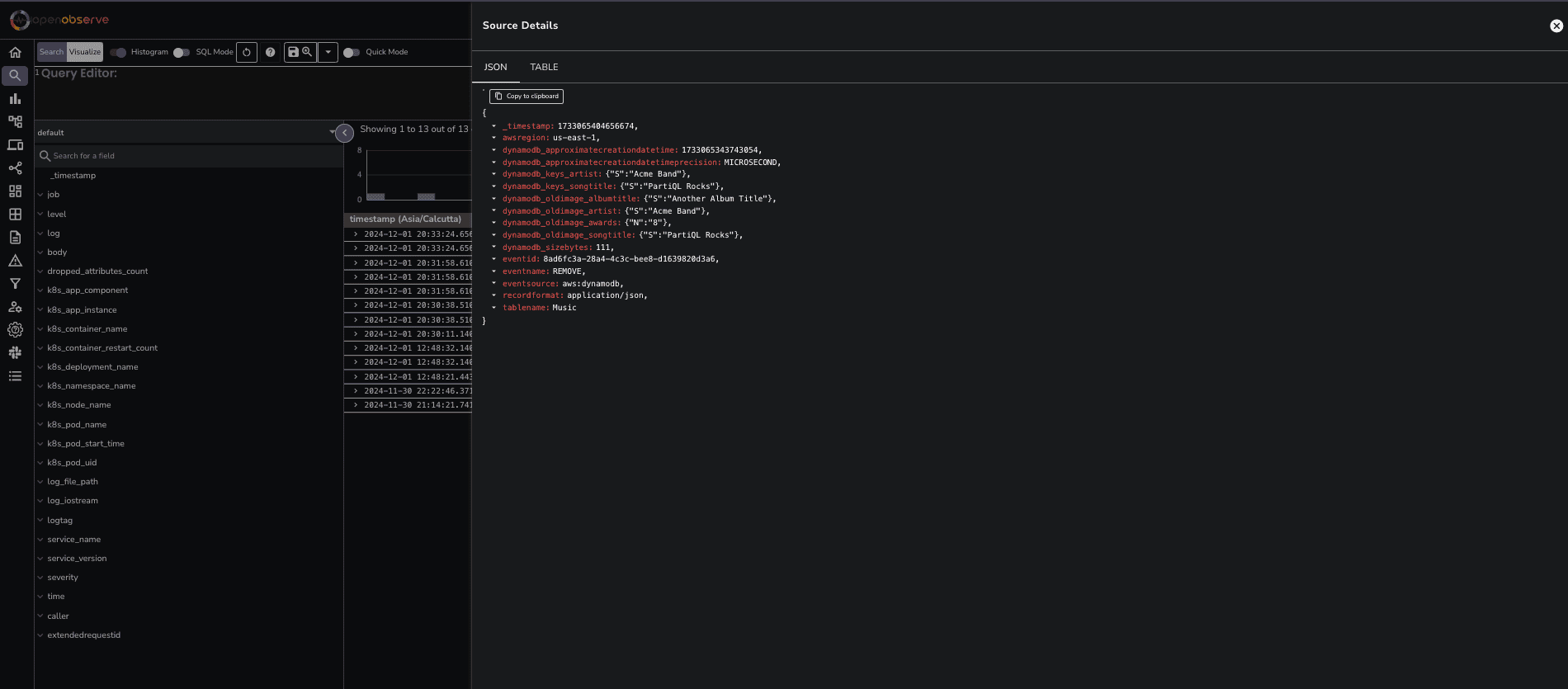 Here’s a breakdown of the key fields:
Here’s a breakdown of the key fields:- _timestamp: The precise time the event occurred.
- awsregion: The AWS region where your DynamoDB table is located.
- dynamodb_approximatecreationdatetime: The timestamp when the record was created.
- dynamodb_keys_artist and dynamodb_keys_songtitle: The keys identifying the item that was modified.
- dynamodb_newimage: Contains the new values for the attributes (e.g.,
albumtitle, artist, awards, songtitle).
- dynamodb_oldimage: Contains the previous values for the attributes before the modification.
- eventid: A unique identifier for the event.
- eventname: Indicates the type of change (e.g.,
MODIFY, INSERT).
- tablename: The name of the DynamoDB table.
With the eventname field, you can create a real-time monitoring dashboard in OpenObserve that groups changes by event type, such as MODIFY, INSERT, etc. This allows you to quickly identify the nature of changes occurring in your DynamoDB table.
You can download the dashboards here.
Create time series charts to visualize how frequently changes occur over time.
Set up alerts for specific events, such as high-frequency modifications, to proactively monitor your application’s behavior.
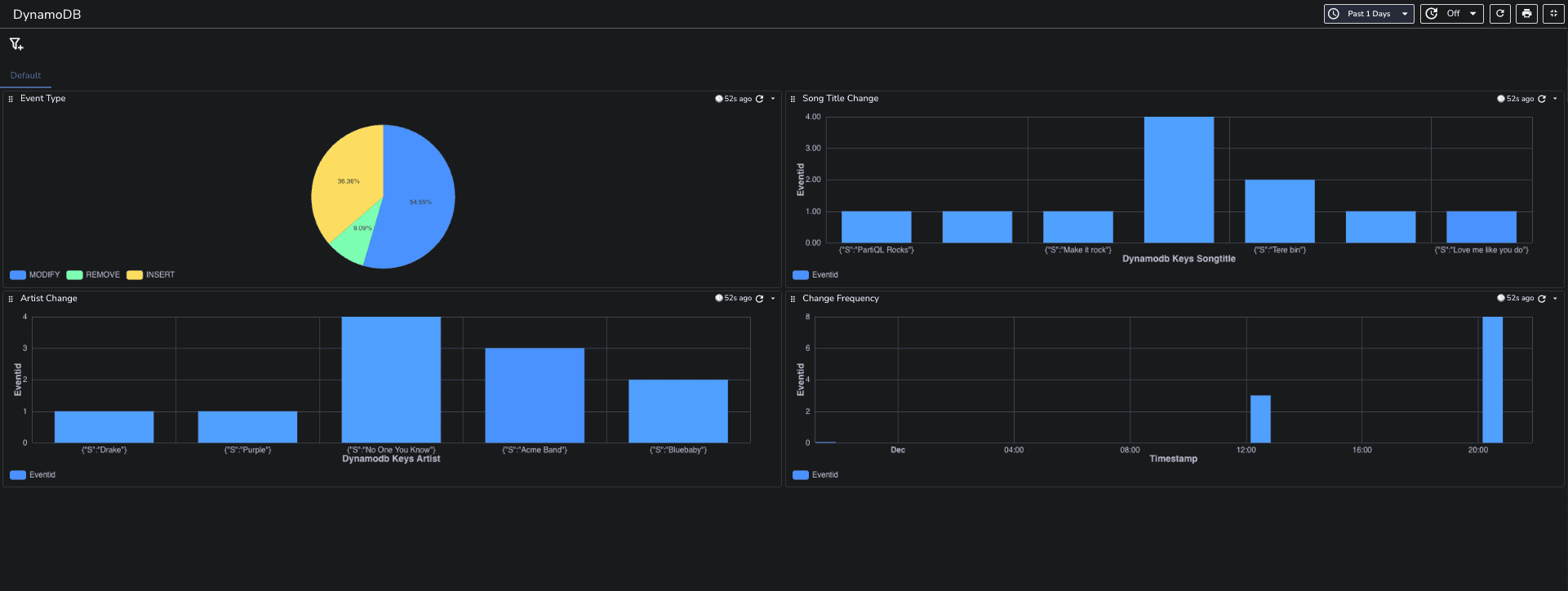
By leveraging the real-time data captured from DynamoDB, you can gain insights into how your application is performing and respond promptly to any issues.
Best Practices for Monitoring DynamoDB Changes
Optimize Performance
- Shard Management: Regularly monitor and adjust the number of shards in your Kinesis Data Stream to ensure it can handle your data volume and processing requirements. More shards can improve throughput but also increase costs. For more understanding on this refer this
- Data Throughput: Ensure that your Firehose delivery stream is configured to handle the expected data load efficiently.
Ensure Data Consistency
- Data Validation: Implement checks within OpenObserve to validate the incoming data and ensure that it accurately reflects the changes made in DynamoDB.
Monitor and Manage
- CloudWatch: Utilize Amazon CloudWatch to monitor the metrics of your Kinesis Data Stream and Firehose. Set up alarms to alert you about throughput issues, errors, or processing latencies.
- Logging: Implement logging within OpenObserve to capture detailed information about data processing and any errors that may occur.
Security and Access Control
- IAM Policies: Configure IAM policies to restrict access to DynamoDB Streams and Kinesis Data Streams. Ensure that only authorized users and services have access to these resources to maintain security.
Use Cases for Monitoring DynamoDB Changes
Real-Time Analytics
- Stream Processing: Use real-time data processing to generate insights, dashboards, and reports based on the changes captured from your DynamoDB tables.
Data Synchronization
- System Integration: Keep different data stores and systems synchronized by capturing and replicating changes across databases and services.
Event-Driven Applications
- Trigger Actions: Use changes in DynamoDB tables to trigger application workflows, notifications, or other actions, enhancing the responsiveness of your applications.
Conclusion
Implementing a system for monitoring changes in DynamoDB with Amazon Kinesis and OpenObserve enables real-time data processing, synchronization, and analytics. By leveraging these AWS services, you can efficiently capture and respond to data changes, enhancing your ability to build dynamic and responsive data-driven applications. With the insights gained from monitoring your DynamoDB table directly in OpenObserve, you can make informed decisions that drive your application's success.


 Here’s a breakdown of the key fields:
Here’s a breakdown of the key fields: