DataDog vs OpenObserve Part 8: IAM, Multi-Tenancy, and Team Collaboration


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free
Your DataDog bill jumped 40% last month. Again. You didn't change anything significant, yet costs escalated. Now you're choosing between full observability and budget predictability.
This is the reality for teams using DataDog: multi-dimensional pricing (hosts, custom metrics, indexed spans, feature tiers) makes cost forecasting nearly impossible. The fundamental question shifts from "what should we monitor?" to "what can we afford to monitor?" Engineers hesitate before adding instrumentation. Architects design around billing optimization, not operational needs.
Observability is an organization-wide initiative. Development teams debug production issues. SRE teams monitor system health. Security teams investigate incidents. Product teams analyze user behavior. Each team needs appropriate access to observability data without compromising security or creating operational friction.
This comparison examines how DataDog and OpenObserve handle identity and access management, multi-tenancy, audit compliance, and team collaboration features. These capabilities determine whether observability platforms scale from small engineering teams to enterprise organizations with complex security and compliance requirements.
This is Part 8 in a series comparing DataDog and OpenObserve for observability (security use cases excluded):
Logs, metrics, and traces provide technical visibility. But observability platforms hold sensitive data: application secrets in logs, customer identifiers in traces, infrastructure topology in metrics.
As organizations scale observability adoption:
Platform capabilities determine whether teams can safely share observability access or restrict it to a small operations team due to security concerns.
DataDog: Enterprise tier required. OpenObserve: Enterprise Edition and Cloud.
Single Sign-On integrates observability platforms with corporate identity providers (Okta, Azure AD, Google Workspace). Users authenticate once, access multiple systems. IT teams manage access centrally, disable accounts immediately when employees leave.
DataDog requires Enterprise tier for SSO/SAML. The Enterprise plan costs $23 per host per month (billed annually) versus Pro's $15 per host per month. That's an $8/host/month premium for SSO access.
Source: DataDog Pricing
For a team monitoring 50 hosts: 50 hosts × $8/month = $400/month premium just to enable SSO.
For 200 hosts (mid-market scale): $1,600/month premium for SSO capability.
DataDog's Enterprise tier includes other features (custom roles, advanced permissions, SCIM, HIPAA compliance), but teams needing only SSO still pay the full Enterprise premium.
Source: CloudEagle DataDog Pricing Guide
DataDog supports multiple SAML configurations per organization (up to three simultaneously), which simplifies identity management during IdP migrations or contractor onboarding.
OpenObserve integrates SSO using Dex, an OpenID Connect (OIDC) and OAuth 2.0 provider. Dex connects to external identity providers: LDAP, Google, GitHub, Azure AD, and other SAML/OIDC providers.
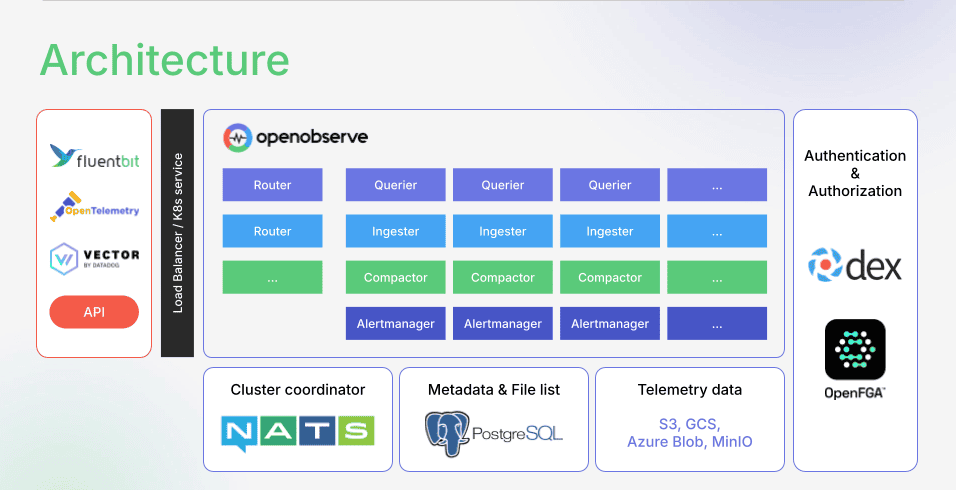
Learn more: OpenObserve SSO Documentation
OpenObserve includes SSO in Enterprise Edition and Cloud at the $0.30/GB flat rate. No per-host multiplier. No separate SSO tier. Scale from 10 hosts to 1,000 hosts without changing the pricing model.
The cost difference: DataDog's SSO premium scales with infrastructure. OpenObserve's SSO cost scales with data volume.
DataDog: Available on all tiers (limited on Pro, full on Enterprise). OpenObserve: Enterprise Edition and Cloud.
RBAC controls what users can do within the observability platform. Without RBAC, every user has full access: delete dashboards, modify alerts, export sensitive data. With RBAC, junior engineers view dashboards but can't modify production alerts. Security teams access audit logs but can't change infrastructure configs.
DataDog provides three default roles: Admin, Standard, and Read-only. Admin users manage users, orgs, billing. Standard users have write permissions on assets. Read-only users view data without modifications.
Source: DataDog RBAC Documentation
DataDog supports custom roles with granular permissions across 100+ permission types. Permissions control access to dashboards, monitors, notebooks, logs, metrics, APM traces, and cloud costs.
DataDog's Granular Access Control allows restricting individual resources (specific dashboards, notebooks, monitors) to teams, roles, or users. Data Access Control restricts sensitive data (custom metrics, RUM sessions, APM traces, logs) based on query patterns.
Source: DataDog Granular Access Control
OpenObserve provides action-based RBAC across 28+ modules. Permissions define what actions users can perform:
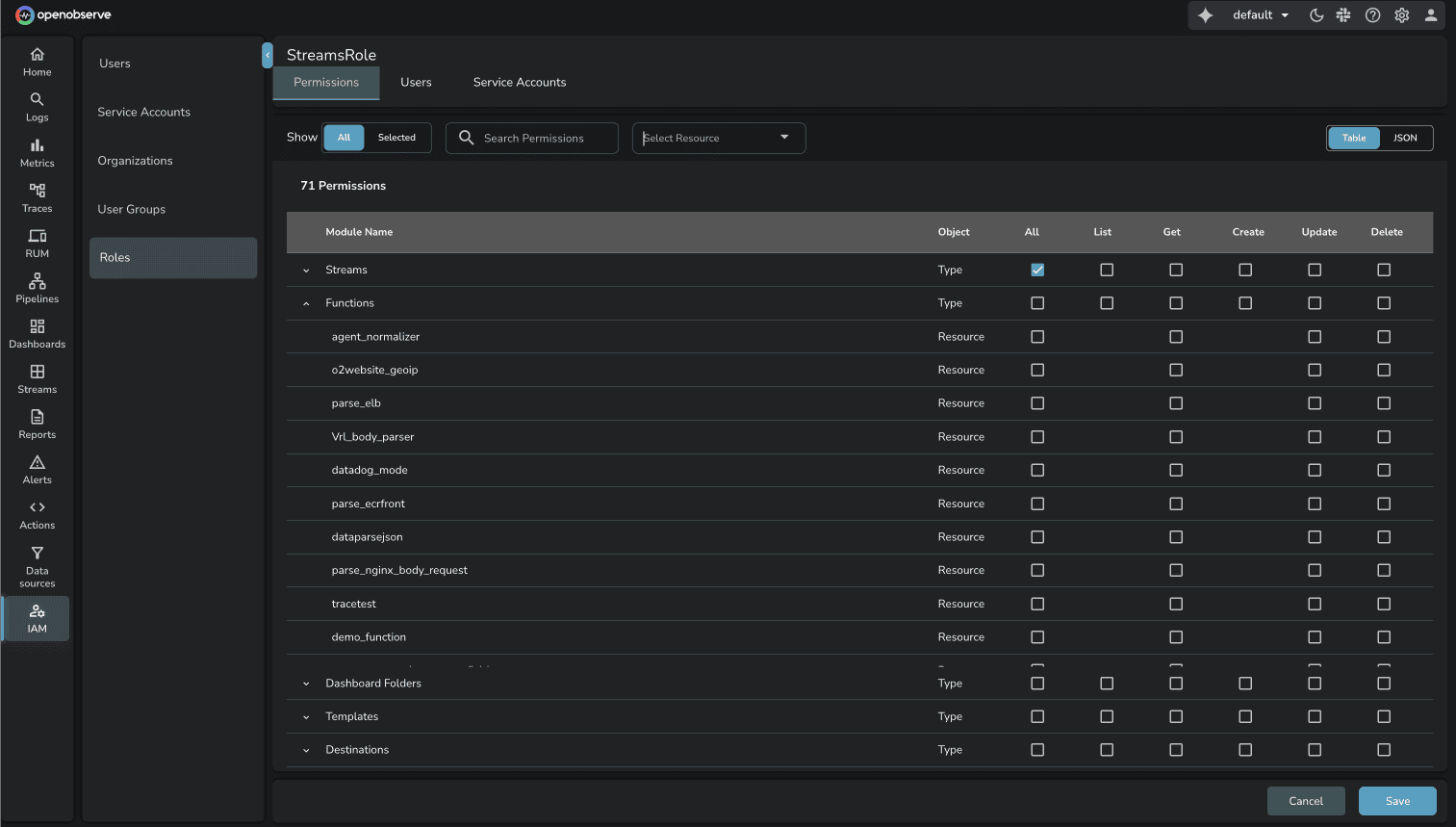
Modules where permissions can be granted:
Source: OpenObserve RBAC Documentation
The granularity difference: Both platforms support resource-level permissions. OpenObserve's action-based model provides explicit control over create/read/update/delete operations per module.
Available in DataDog Pro and Enterprise. Available in OpenObserve OSS, Enterprise, and Cloud.
Multi-tenancy separates data and users across logical boundaries. Use cases: managed service providers serving multiple customers, enterprises with separate divisions, organizations isolating dev/staging/production environments.
DataDog supports multiple organizations with parent-child relationships. Organizations within a parent organization do not have access to each other's data. Child organizations inherit billing from the parent but maintain separate configurations and telemetry data.
Source: DataDog Managing Multiple Organizations
DataDog provides data isolation at multiple levels:
Source: DataDog Multi-Tenancy Architecture
DataDog also offers Teams feature for collaboration within organizations. Teams clarify resource ownership and provide direct access to team-specific resources: services, dashboards, monitors, SLOs, incidents.
Source: DataDog Teams
OpenObserve Organizations provide logical boundaries for separating data, users, and access controls. Each org provides complete isolation: separate resources, data, dashboards, configurations. Users can belong to multiple organizations and switch context as needed.
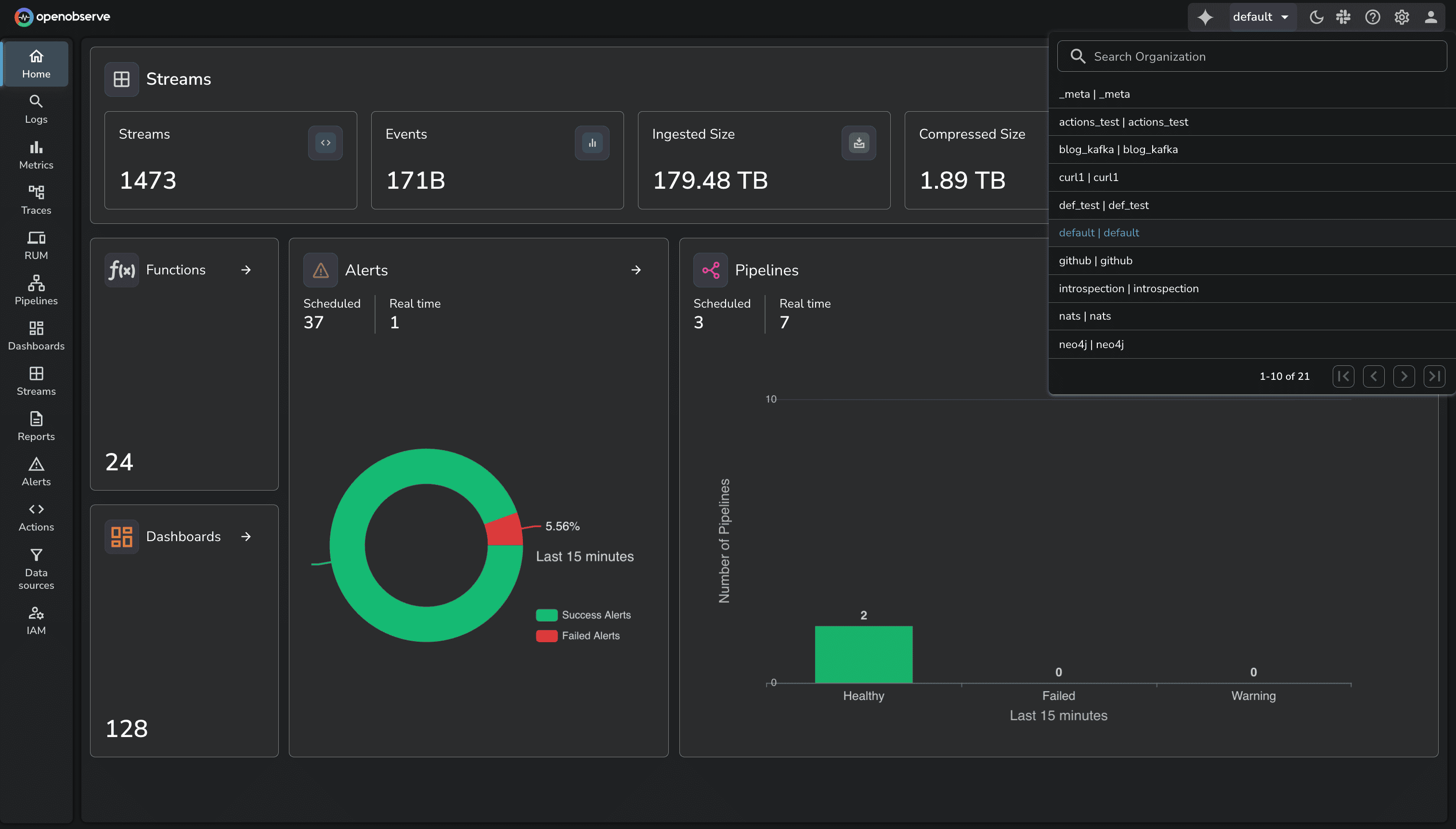
In practice, each org functions like a separate OpenObserve instance sharing the same cluster infrastructure. Data ingested into one org is completely invisible to other orgs. RBAC, SSO, and audit trails are configured per org.
This enables:
The multi-tenancy comparison: Feature parity. Both platforms provide strong organizational isolation with flexible user access models.
DataDog: Pro and Enterprise plans. OpenObserve: Enterprise Edition and Cloud.
Audit trails record user actions for security monitoring, compliance requirements, and incident investigation. Compliance frameworks (SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI, GDPR) require organizations to log and retain audit events demonstrating who accessed what data and when.
DataDog Audit Trail monitors user activity, API requests, and resource changes. The system records 100+ types of audit events across the DataDog platform.
Source: DataDog Audit Trail
DataDog audit events include:
DataDog provides 90-day retention for audit events. Events can be searched and analyzed within the platform, exported as CSV files (up to 100K events), or archived to external systems for long-term retention.
DataDog Audit Trail integrates with Cloud SIEM for real-time threat detection based on audit log patterns.
Source: DataDog Audit Trail Best Practices
Setup requires Pro or Enterprise plan with Admin role or Org Management permissions. Navigate to Organization Settings → Audit Trail Settings → Enable.
OpenObserve Audit Trail records user actions across all organizations. It captures non-ingestion API calls: dashboard modifications, alert changes, user management, configuration updates.
Audit events are published to the audit stream under the _meta organization. The _meta org is a special organization containing system-level data: audit logs, query recommendations, system metrics.
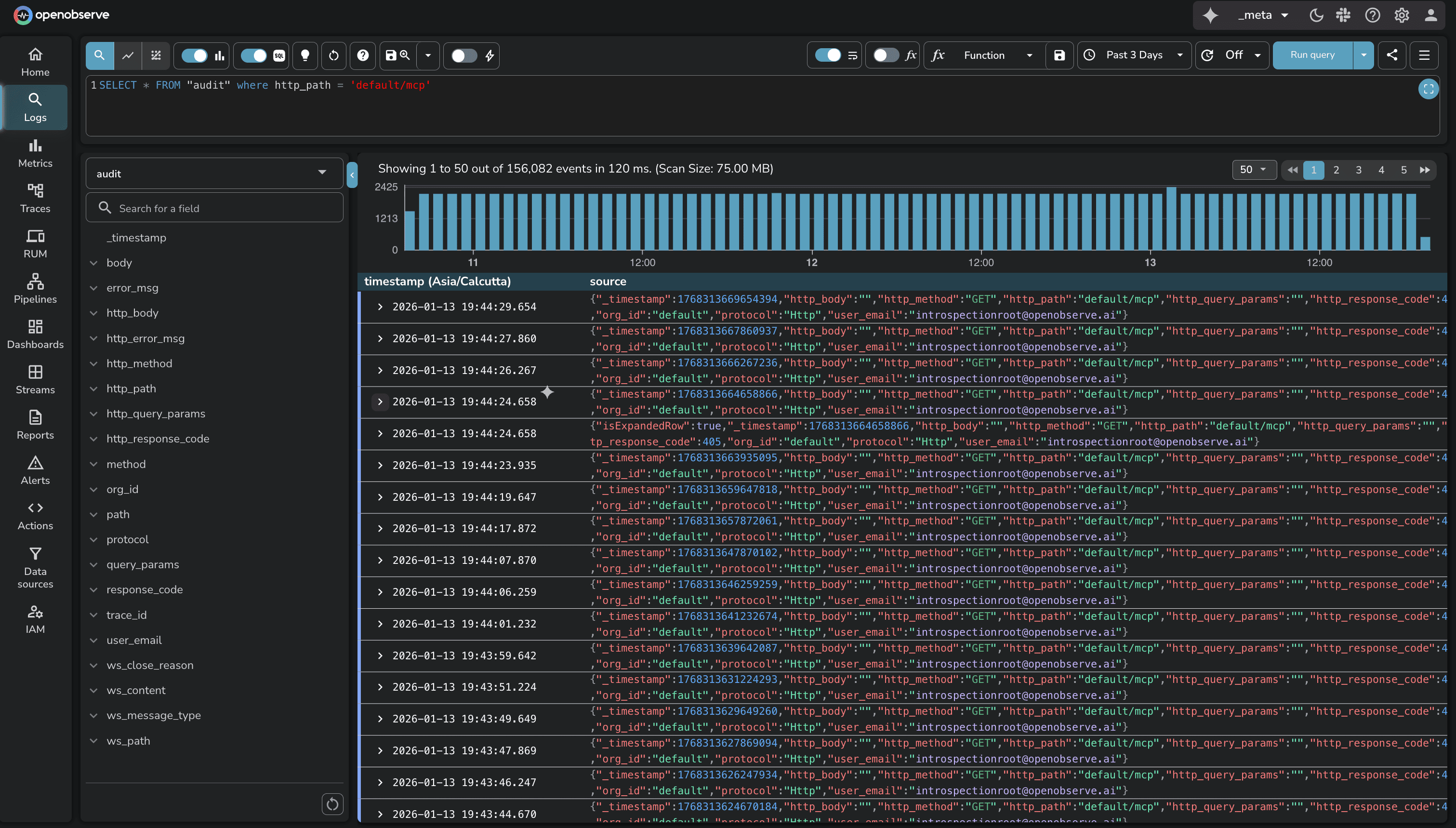
Source: OpenObserve Audit Trail Documentation
OpenObserve audit configuration:
O2_AUDIT_ENABLED: Enables audit logging (default: false)O2_AUDIT_BATCH_SIZE: Number of audit records to batch before publishing (default: 500)O2_AUDIT_PUBLISH_INTERVAL: Interval in seconds for publishing unpublished audits (default: 600)When audit logging is enabled, OpenObserve collects details of every non-ingestion API call across all organizations. Events are stored in memory, then published to the audit stream once batch size or publish interval is reached.
The advantage: OpenObserve stores audit events as standard log data in the _meta org. Apply the same query capabilities (SQL, full-text search), create dashboards visualizing audit patterns, configure alerts on suspicious activities, and set custom retention policies.
The audit comparison: Both platforms provide comprehensive audit trails. DataDog has fixed 90-day retention with CSV export. OpenObserve stores audit events as queryable data with configurable retention.
DataDog: Native feature (Pro and Enterprise). OpenObserve: Report Server (all editions).
Dashboards provide real-time observability for engineers. But stakeholders (executives, compliance officers, customers) don't log into observability platforms daily. Scheduled reports deliver dashboard snapshots on recurring schedules.
DataDog Scheduled Reports send recurring dashboard PDFs to email addresses and Slack channels. Configure schedules (daily, weekly, monthly), time frames (last 24 hours, last 7 days), and recipients.
Source: DataDog Scheduled Reports
DataDog report setup:
Permissions: Users need "Dashboards Report Write" permission to create and edit report schedules. Enterprise and Pro accounts can send reports to recipients outside their organizations.
OpenObserve Report Server converts dashboards into PDF reports and delivers them by email on set schedules. The Report Server is a separate component that connects to OpenObserve, renders dashboards as PDFs, and sends emails.
Source: OpenObserve Report Server Setup
Any OpenObserve dashboard can be converted into a scheduled report. Use cases:
OpenObserve Report Server is available in all editions: OSS, Enterprise, and Cloud. No tier restrictions for scheduled reporting.
The reports comparison: Both platforms provide scheduled PDF dashboard delivery. DataDog's is native and integrated. OpenObserve's requires separate Report Server deployment but available in all editions including OSS.
| Capability | DataDog | OpenObserve |
|---|---|---|
| SSO/SAML | Enterprise tier required ($23/host/month = $8/host premium). Up to 3 SAML configs | Enterprise Edition and Cloud ($0.30/GB flat rate). Dex integration with LDAP, Google, GitHub, Azure AD |
| SSO Cost Example | 50 hosts: $400/month premium for SSO access | 50 hosts: $0 additional cost (included in $0.30/GB) |
| RBAC | 3 default roles + custom roles. 100+ granular permissions. Available on all tiers | Action-based permissions (List, Get, Create, Update, Delete) across 28+ modules. Enterprise/Cloud only |
| Multi-Tenancy | Parent-child organizations with data isolation. Cross-org visibility available | Complete org isolation. Users can access multiple orgs |
| Audit Trail | 90-day retention. 100+ event types. Export CSV (100K events). Pro/Enterprise | Published to _meta org audit stream. Configurable retention. SQL queries. Enterprise/Cloud |
| Reports | Native PDF scheduling. Email and Slack delivery. Pro/Enterprise | Report Server: PDF reports with email delivery. Available in all editions (OSS/Enterprise/Cloud) |
| Pricing Model | Per-host pricing. Enterprise tier for SSO = $8/host/month premium | Usage-based pricing. $0.30/GB regardless of hosts, users, or orgs |
| IAM Cost at Scale | 200 hosts × $8/month = $1,600/month premium just for SSO | $0 additional cost for SSO (included in flat rate) |
IAM features don't have separate line-item pricing. The cost difference comes from DataDog's tier-based model versus OpenObserve's usage-based model.
SSO/SAML requires Enterprise tier:
For 100 hosts: $800/month ($9,600/year) premium for SSO.
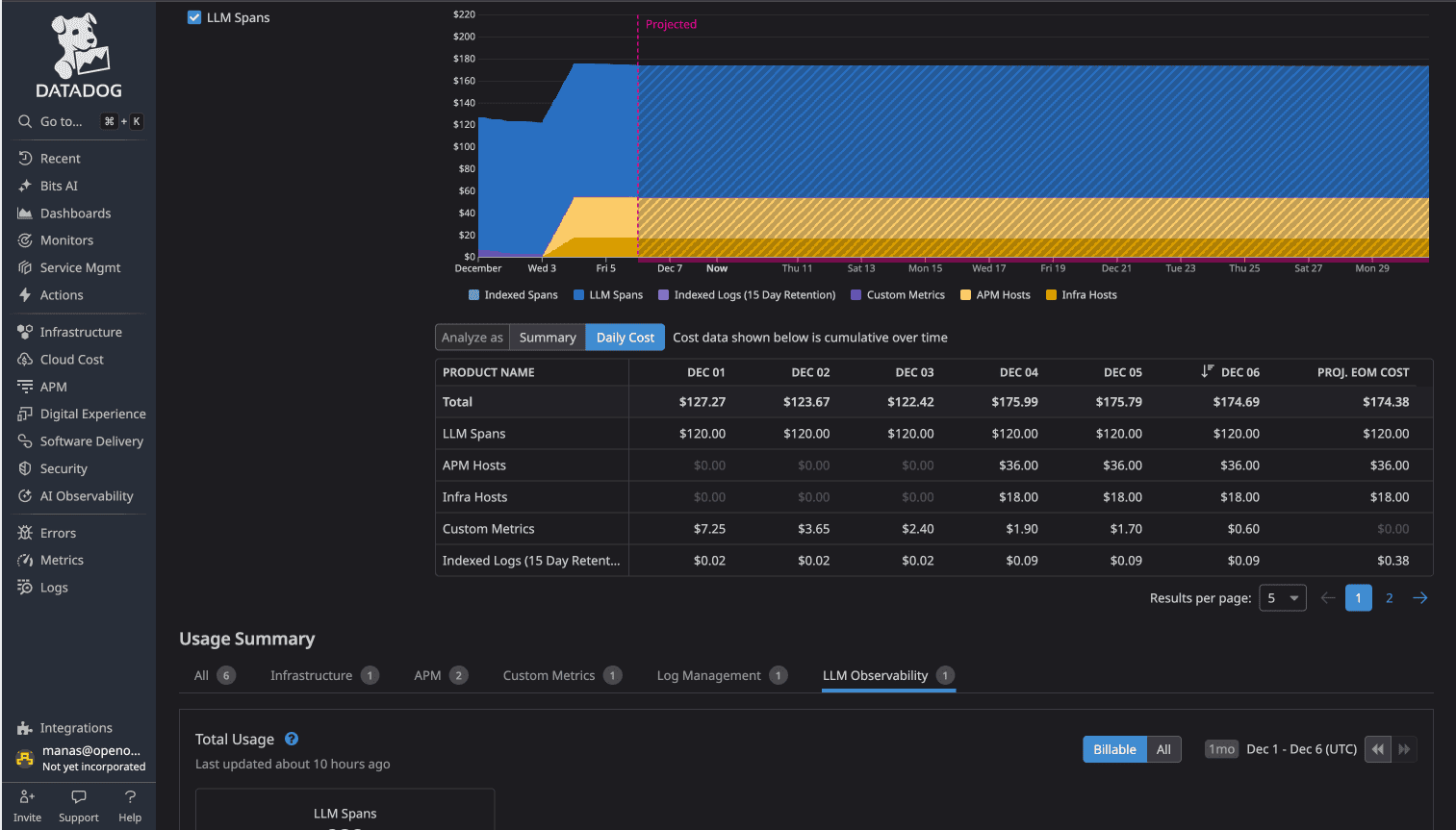
From the test environment (16-service OpenTelemetry demo):
The cost difference: 58x (more than 98% cost savings)
The pricing transparency difference:
This matters for organizations scaling observability adoption. With DataDog, adding SSO access for 100 additional hosts means $800/month in additional costs even if those hosts generate minimal data. With OpenObserve, infrastructure scale doesn't change IAM costs.
DataDog provides mature IAM capabilities with extensive integrations and compliance certifications. If you're already on DataDog Enterprise and cost isn't a concern, the IAM features work.
But if you're evaluating observability platforms for enterprise adoption, or reconsidering current IAM costs, OpenObserve delivers the same core IAM capabilities with significant advantages:
For platform teams scaling observability across organizations with 50+ engineers, these differences matter. No cost anxiety about enabling SSO. No per-host multiplier as infrastructure scales. Transparent pricing that aligns with data volume rather than user count or infrastructure size.
OpenObserve's OpenTelemetry-native architecture means you instrument once with industry-standard OTel SDKs, configure IAM policies appropriate for your security requirements, and scale observability adoption without vendor lock-in or pricing surprises.
More in the series: Part 9 will provide a comprehensive cost breakdown aggregating all pricing dimensions covered in Parts 1-8.
Sign up for a free cloud trial or schedule a demo to test OpenObserve's IAM features with your team.