How to Deploy OpenObserve on DigitalOcean: A Complete Guide


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free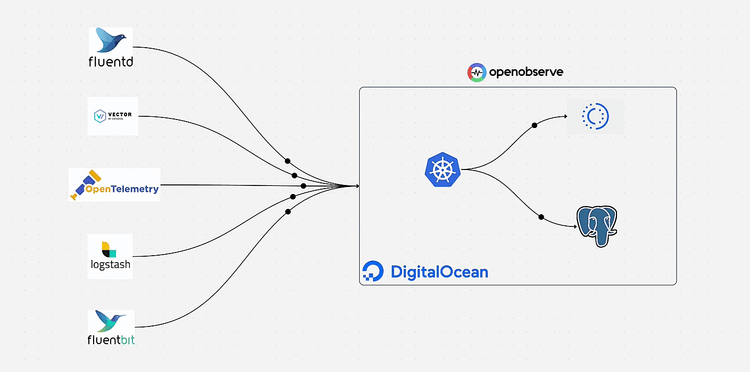
OpenObserve is a cloud-native observability platform designed for logs, metrics, and traces. While it's easy to get started with OpenObserve locally, deploying it in production requires careful consideration of storage, database, and orchestration. In this guide, I'll walk you through deploying OpenObserve on DigitalOcean using Kubernetes, leveraging managed services for reliability and scalability.
Our deployment architecture includes:
This setup provides a production-ready, scalable observability platform with minimal operational overhead.
Before you begin, ensure you have:
kubectl installed locallyhelm (v3+) installed locallydoctl (DigitalOcean CLI) installed and configuredDigitalOcean Spaces provides S3-compatible object storage, which OpenObserve uses for storing log data efficiently.

Log in to your DigitalOcean dashboard
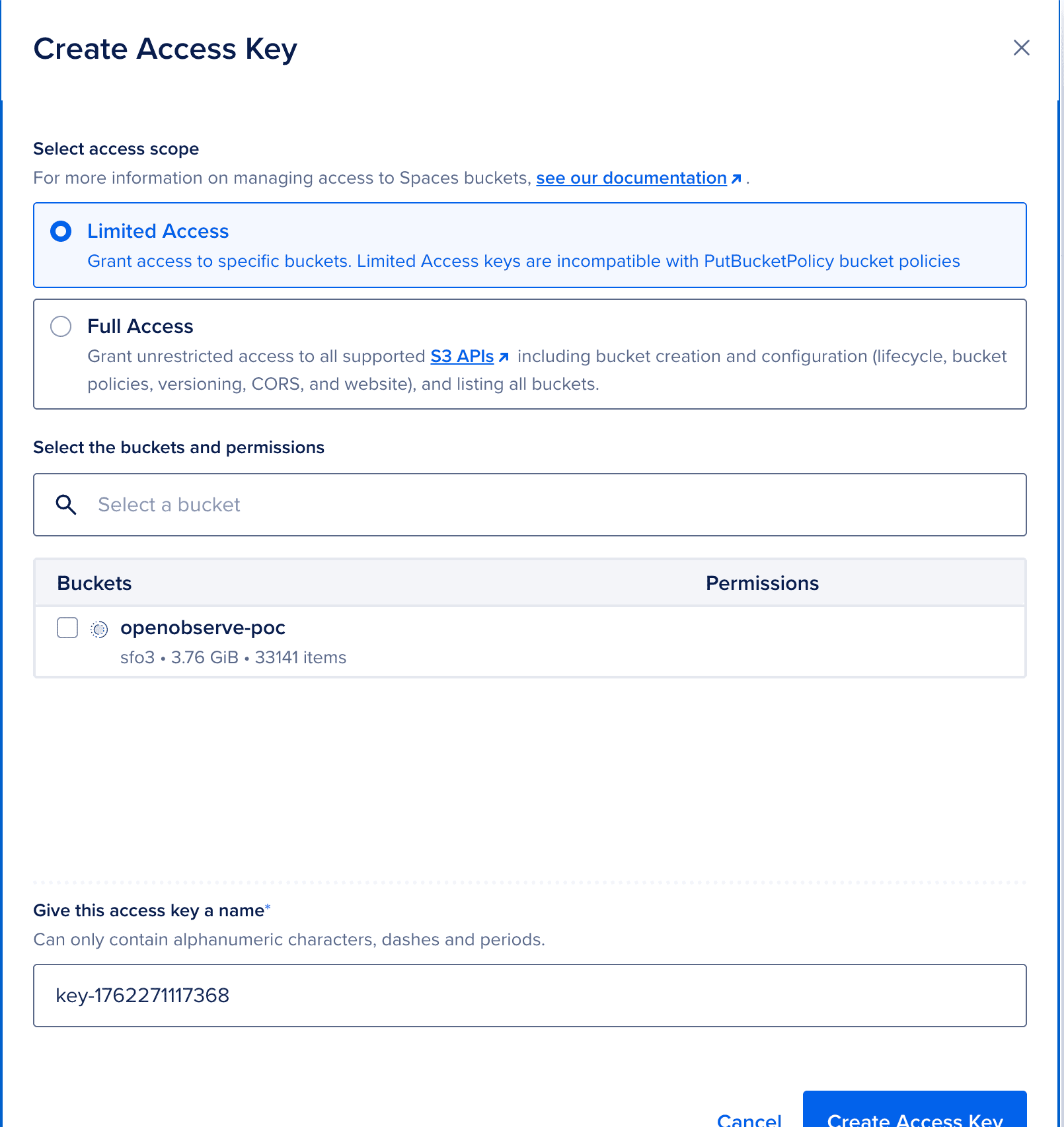
Navigate to Spaces Ob in the left sidebar
Click Create a Space
Configure your Space:
nyc3, sfo3)openobserve-logs (must be globally unique)Click Create a Space
openobserve-spaces-keyYour Spaces endpoint follows this format:
https://<spacename>.<region>.digitaloceanspaces.com
For example, if you created your Space in nyc3 called test:
https://test.nyc3.digitaloceanspaces.com
DigitalOcean's managed Kubernetes service (DOKS) simplifies cluster management and provides automatic updates.
Navigate to Kubernetes in the left sidebar
Click Create a Kubernetes Cluster
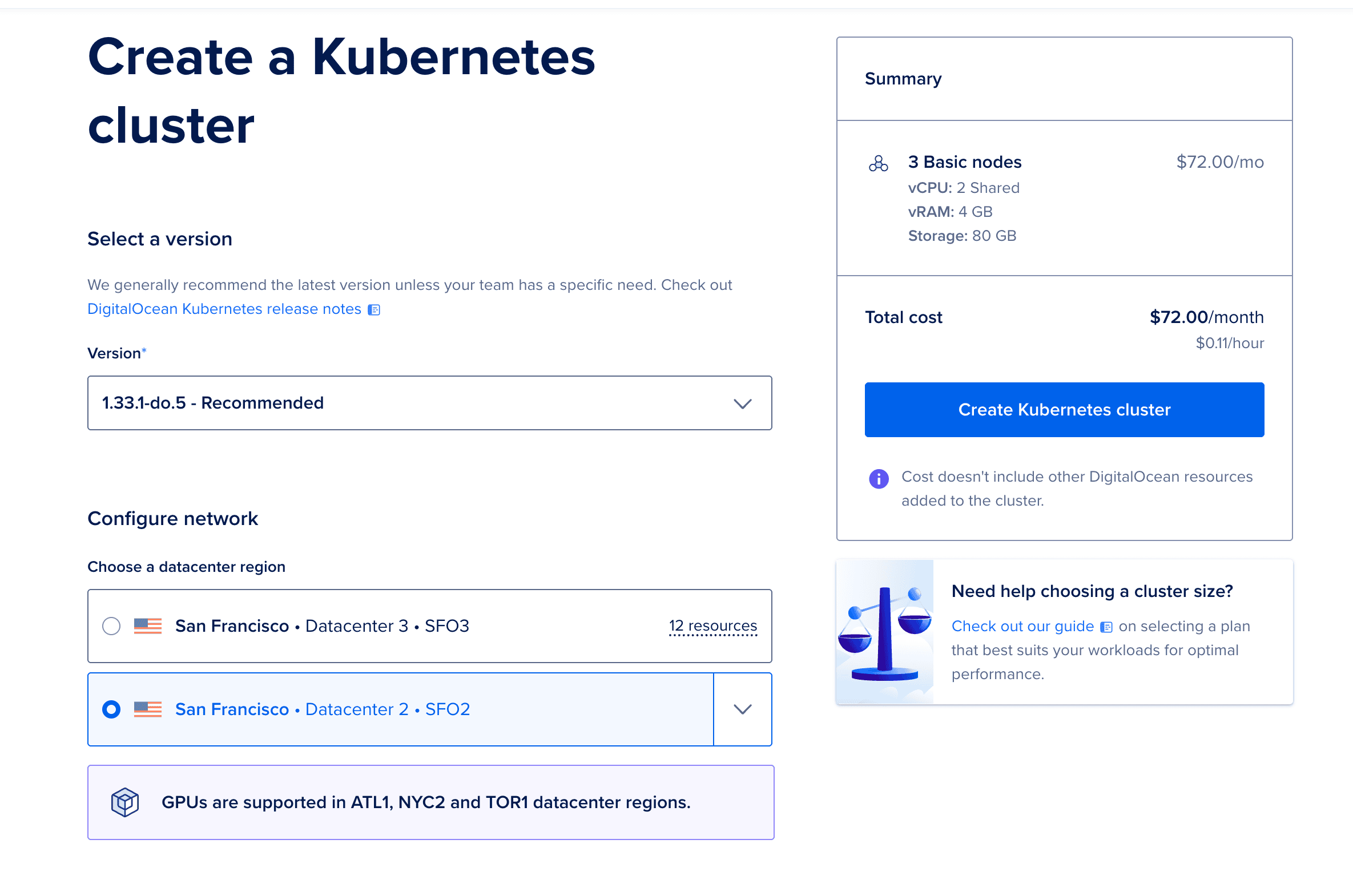
Configure the cluster:
openobserve-pools-2vcpu-4gb (2 vCPU, 4GB RAM)openobserve-cluster
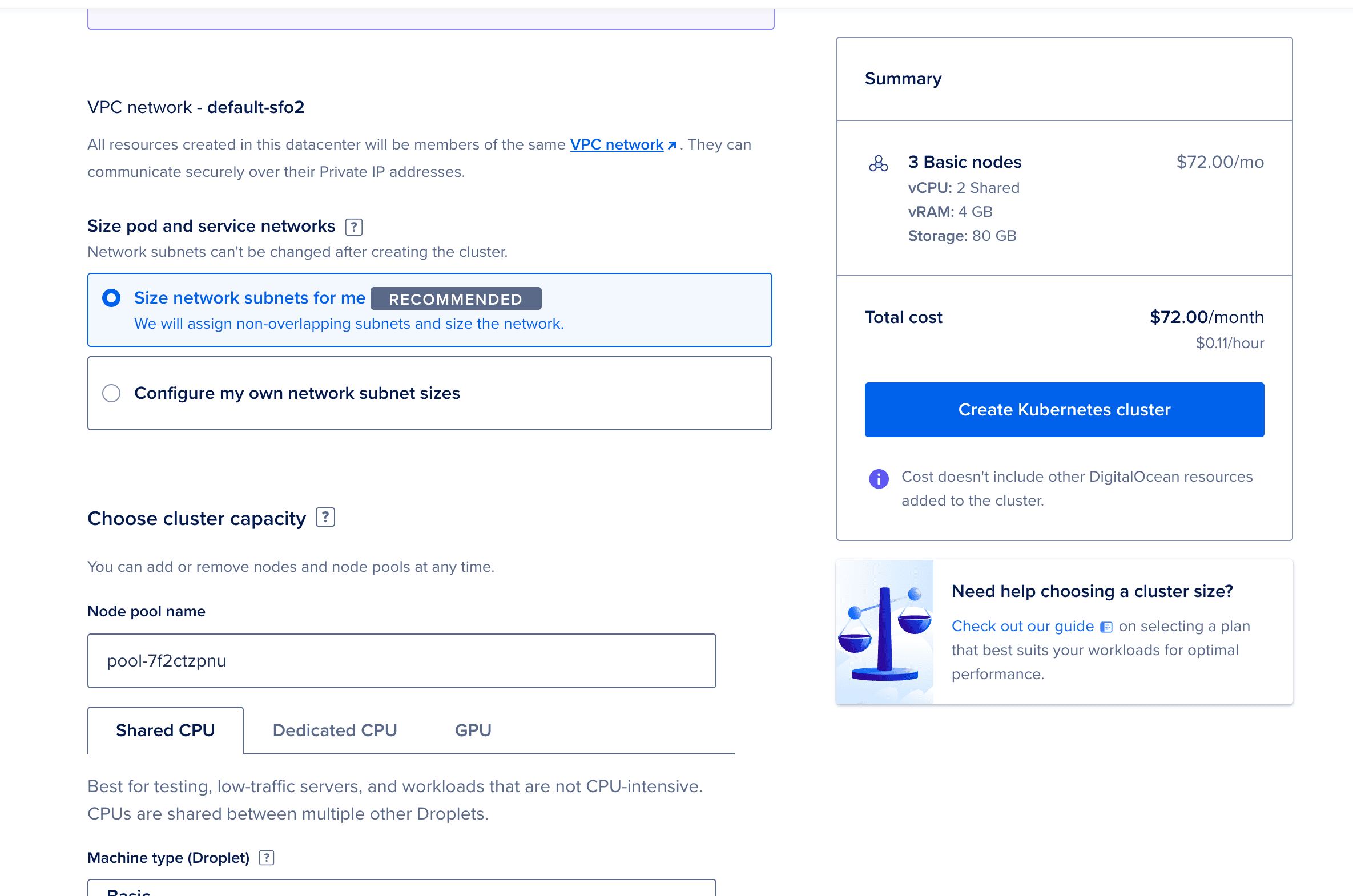
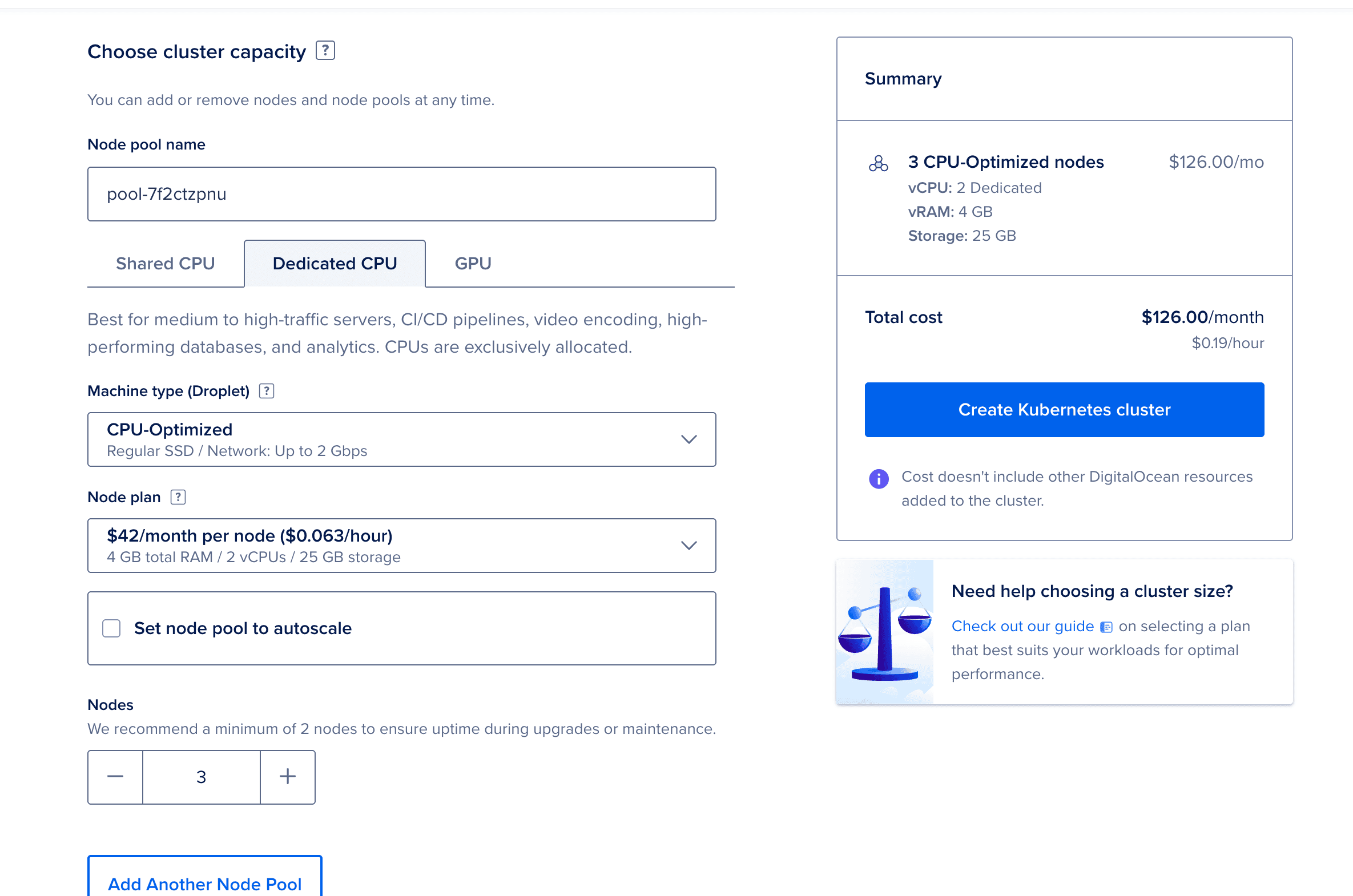
Click Create Cluster
The cluster provisioning takes 4-5 minutes. While it's being created, you can proceed to the next step.
Once the cluster is ready:
doctl:
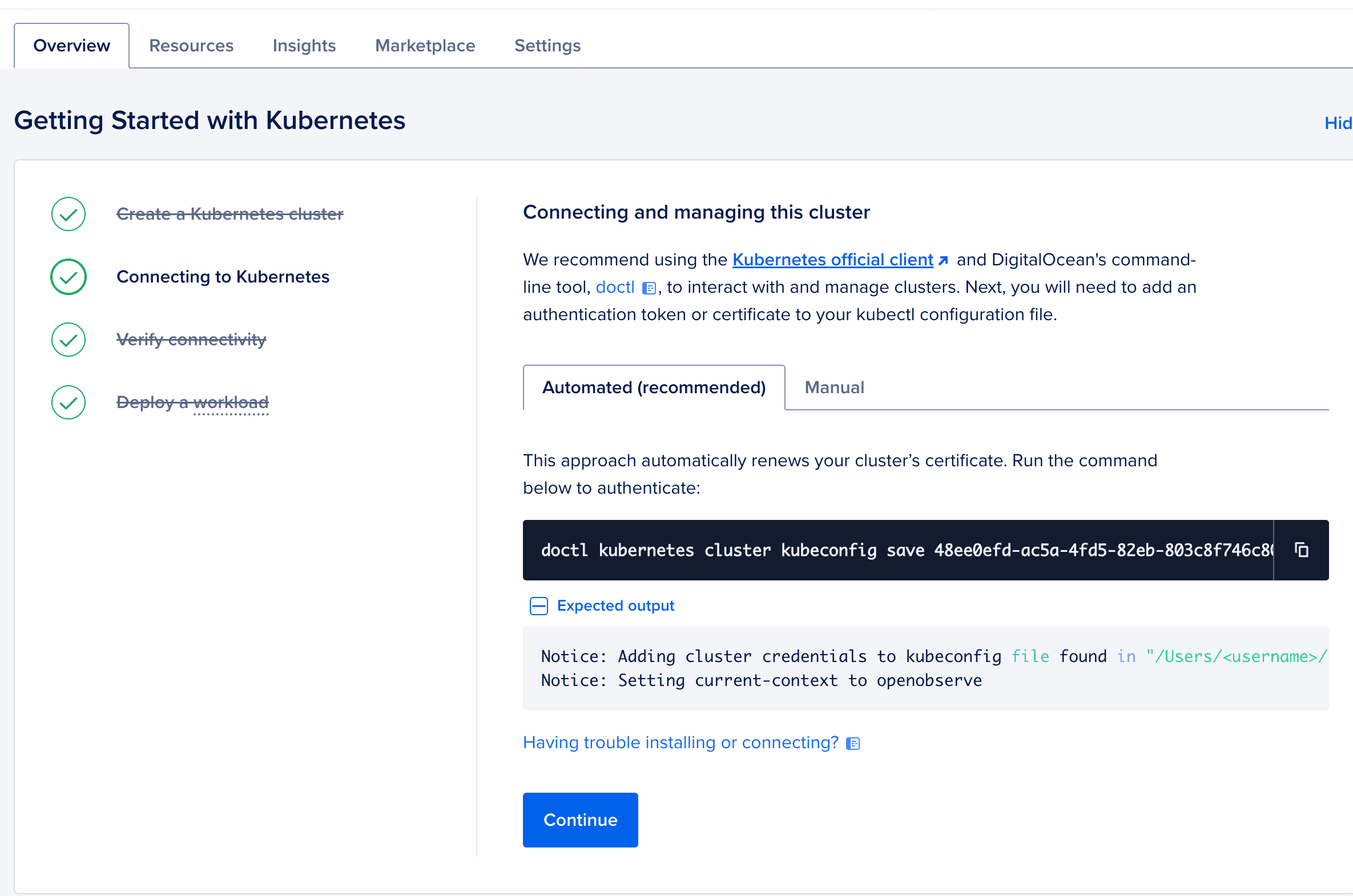
doctl kubernetes cluster kubeconfig save openobserve-cluster
Verify connectivity:
kubectl get nodes
You should see your three nodes in a Ready state.
OpenObserve uses PostgreSQL for storing metadata, user information, and configuration.
Navigate to Databases in the left sidebar
Click Create a Database Cluster
Configure the database:
db-s-1vcpu-1gb (1 vCPU, 1GB RAM, 10GB disk)openobserve-db



Click Create a Database Cluster
Database provisioning takes 5-7 minutes.
Once created:
openobserve-cluster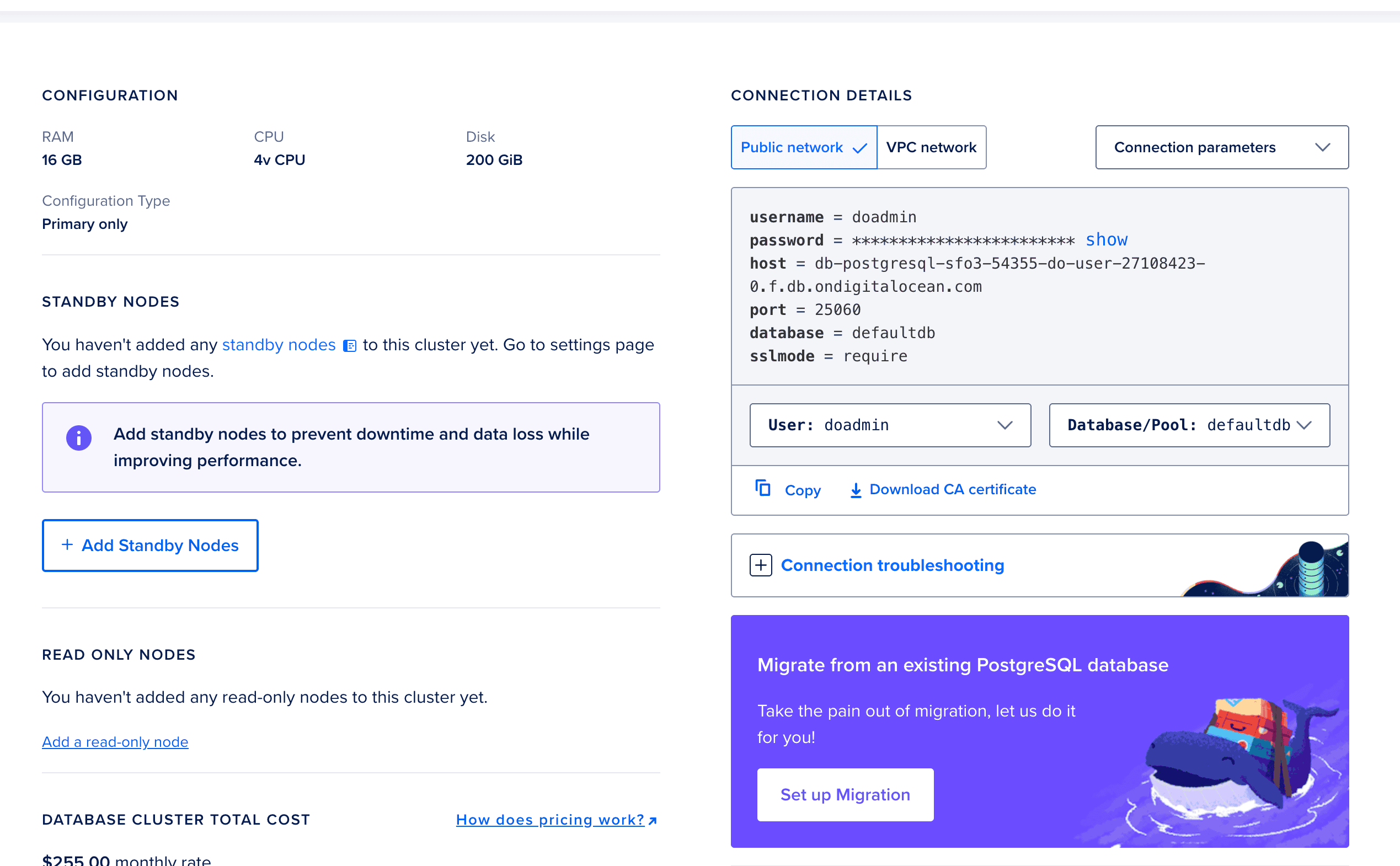
openobserve_userFrom the Connection Details section, note:
openobserve-db-do-user-xxxxx-0.xxx.db.ondigitalocean.com)25060openobserveopenobserve_userrequireOpenObserve provides a Helm chart for Kubernetes deployments. We'll customize the values.yaml to use our DigitalOcean resources.
helm repo add openobserve https://charts.openobserve.ai
helm repo update
You can get the values.yaml from the official repository.
Edit the values.yaml file with your DigitalOcean configurations:
# values.yaml
auth:
ZO_META_POSTGRES_DSN: "postgres://doadmin:<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_DB_PASSWORD>@<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_DB_URL>:25060/<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_DB_NAME>"
ZO_S3_ACCESS_KEY: "<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_ACCESS_KEY>"
ZO_S3_SECRET_KEY: <YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>"
config:
ZO_S3_PROVIDER: "s3"
ZO_S3_SERVER_URL: "<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_SPACES_URL>"
ZO_S3_REGION_NAME: "sfo3"
ZO_S3_BUCKET_NAME: "<YOUR_DIGITAL_OCEAN_SPACE_NAME>"
Important: Never commit credentials to version control. Consider using Kubernetes secrets:
# Create a secret for Spaces credentials
kubectl create secret generic openobserve-spaces \
--from-literal=access-key='YOUR_SPACES_ACCESS_KEY' \
--from-literal=secret-key='YOUR_SPACES_SECRET_KEY'
# Create a secret for PostgreSQL connection
kubectl create secret generic openobserve-db \
--from-literal=dsn='postgres://openobserve_user:YOUR_DB_PASSWORD@openobserve-db-do-user-xxxxx-0.xxx.db.ondigitalocean.com:25060/openobserve?sslmode=require'
# Create a secret for root user credentials
kubectl create secret generic openobserve-auth \
--from-literal=email='admin@yourdomain.com' \
--from-literal=password='ComplexPassword123!'
Then modify your values.yaml to reference these secrets:
env:
ZO_S3_ACCESS_KEY:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: openobserve-spaces
key: access-key
ZO_S3_SECRET_KEY:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: openobserve-spaces
key: secret-key
ZO_META_POSTGRES_DSN:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: openobserve-db
key: dsn
ZO_ROOT_USER_EMAIL:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: openobserve-auth
key: email
ZO_ROOT_USER_PASSWORD:
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: openobserve-auth
key: password
With everything configured, deploy OpenObserve to your cluster:
# Create a namespace for OpenObserve
kubectl create namespace openobserve
# Deploy OpenObserve
helm install openobserve openobserve/openobserve \
--namespace openobserve \
--values values.yaml
Check if pods are running:
kubectl get pods -n openobserve
You should see output similar to:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
openobserve-5d8f9c6b7d-abc12 1/1 Running 0 2m
openobserve-5d8f9c6b7d-def34 1/1 Running 0 2m
Check the service:
kubectl get svc -n openobserve
Note the EXTERNAL-IP for the LoadBalancer service. This is your OpenObserve endpoint.
If you encounter issues:
kubectl logs -n openobserve -l app=openobserve --tail=100
kubectl get svc -n openobserve openobserve -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'
Open your browser and navigate to:
http://<LOADBALANCER-IP>:5080
Log in with the credentials you configured:
admin@yourdomain.comComplexPassword123!Point a domain to your LoadBalancer IP:
openobserve.yourdomain.com → <LOADBALANCER-IP>
For production, always use HTTPS. Options include:
Option A: Using cert-manager and Let's Encrypt
# Install cert-manager
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.13.0/cert-manager.yaml
# Create a ClusterIssuer (letsencrypt-prod.yaml)
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: admin@yourdomain.com
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
EOF
Update your values.yaml to enable ingress with TLS:
ingress:
enabled: true
className: nginx
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-prod"
hosts:
- host: openobserve.yourdomain.com
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- secretName: openobserve-tls
hosts:
- openobserve.yourdomain.com
Option B: Using DigitalOcean Load Balancer with certificate
Configure SSL certificate in the DigitalOcean Load Balancer settings.
## Monitoring Your Deployment
### Check Resource Usage
```bash
# CPU and Memory usage
kubectl top pods -n openobserve
# Storage usage
kubectl get pvc -n openobserve
If you need more capacity:
# Manual scaling
kubectl scale deployment openobserve -n openobserve --replicas=4
# Or enable autoscaling in values.yaml
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 5
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 70
Check events:
kubectl describe pod -n openobserve <pod-name>
Common causes:
Verify:
To upgrade to a newer version:
# Update Helm repository
helm repo update
# Check available versions
helm search repo openobserve
# Upgrade
helm upgrade openobserve openobserve/openobserve \
--namespace openobserve \
--values values.yaml \
--version <new-version>
You now have a production-ready OpenObserve deployment on DigitalOcean! This setup provides:
Next steps to consider:
For more advanced configurations and best practices, check out the OpenObserve documentation.
Get Started with OpenObserve Today!
Sign up for a 14 day trial Check out our GitHub repository for self-hosting and contribution opportunities

Chaitanya Sistla is a Principal Solutions Architect with 17X certifications across Cloud, Data, DevOps, and Cybersecurity. Leveraging extensive startup experience and a focus on MLOps, Chaitanya excels at designing scalable, innovative solutions that drive operational excellence and business transformation.