Beginner’s Guide: How to Send AWS CloudWatch Logs to S3 via Kinesis Firehose


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free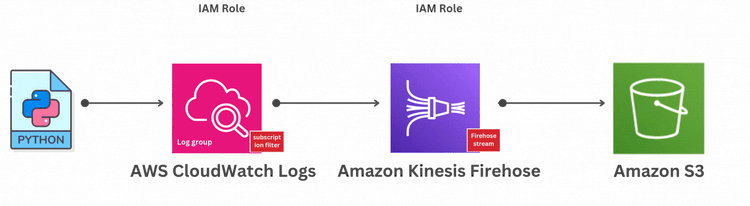
As businesses and applications scale in AWS, monitoring and log management become increasingly important. AWS CloudWatch Logs is a powerful service that collects and stores logs from various AWS resources and applications. However, there are situations where you may want to send your logs from AWS CloudWatch to an Amazon S3 bucket for long-term storage, data analytics, or compliance purposes.
In this guide, we will walk you through a simple and effective way to send your AWS CloudWatch Logs to an S3 bucket using Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose.
In This Blog, We Will Cover:
AWS CloudWatch Logs is a service that allows you to monitor, store, and access log files from your AWS resources and applications. It can collect logs from various AWS services such as EC2, Lambda, API Gateway, and more. CloudWatch Logs helps you troubleshoot issues, perform security analysis, and monitor your resources effectively.
Cloudwatch Logs is good for basic log search and short-term retention. For better usability and control, you would want to move logs from Cloudwatch to other more capable services like OpenObserve or s3
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is a fully managed service that automatically loads real-time data streams into AWS storage services like Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, or Amazon Elasticsearch. With Firehose, you can easily capture log data and stream it to your desired destinations without writing complex code.
Sending CloudWatch logs to Amazon S3 offers several benefits:
Using Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose allows you to automate the process of sending logs from CloudWatch to S3 in real-time, without needing to build a custom solution.
Before we dive into sending your CloudWatch logs to S3 via Kinesis Firehose, let’s start by sending logs to CloudWatch. This step will help you push sample logs to CloudWatch Log Groups, which will then be streamed to S3.
Python Script to Send Logs to AWS CloudWatch: You can use a Python script to send logs to CloudWatch. Here's a simple Python script to get you started:
import boto3
import logging
import watchtower
# Replace with your AWS region
region_name = 'us-east-1' # Replace with your region name
# Create a CloudWatch client if needed
cloudwatch_client = boto3.client('logs', region_name=region_name)
# Replace with your log group name
log_group = 'my-log-group'
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Add CloudWatch as a logging handler
logger.addHandler(
watchtower.CloudWatchLogHandler(
log_group=log_group,
stream_name='my-log-stream', # Replace with your log stream name
use_queues=False # Optional: helps with immediate log transmission
)
)
# Log messages to CloudWatch
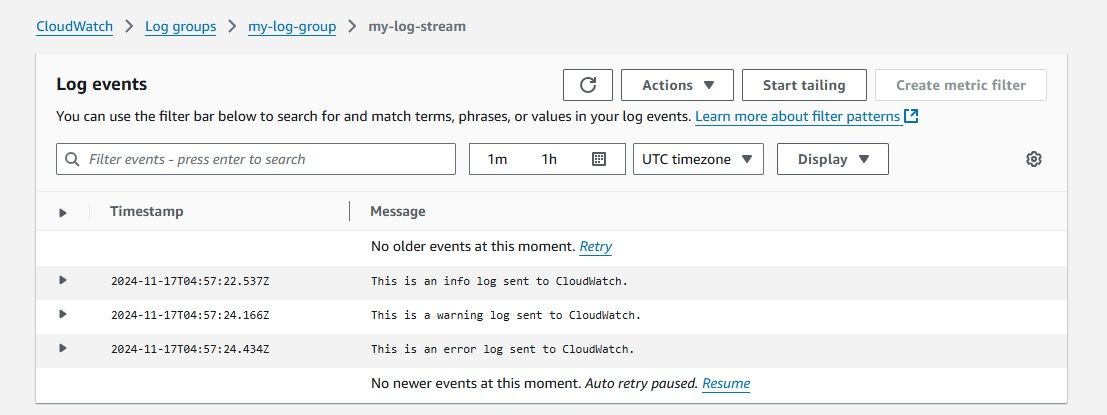
logger.info("This is an info log sent to CloudWatch.")
logger.warning("This is a warning log sent to CloudWatch.")
logger.error("This is an error log sent to CloudWatch.")
How It Works:
Steps to Run the Python Script:
pip install boto3 watchtower
python cloudwatch_logging.py
 Once you run this script, the log messages will be sent to your specified CloudWatch Log Group. This is an essential first step before streaming logs to S3 via Kinesis Firehose.
Once you run this script, the log messages will be sent to your specified CloudWatch Log Group. This is an essential first step before streaming logs to S3 via Kinesis Firehose.
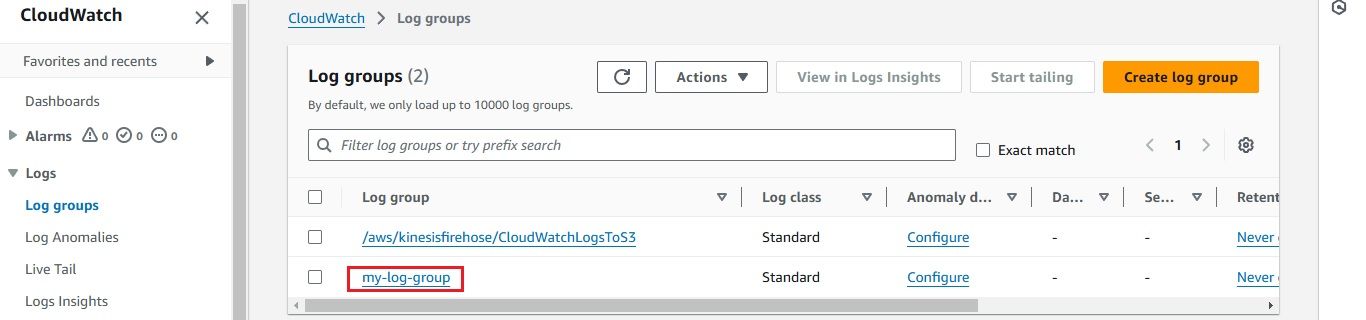
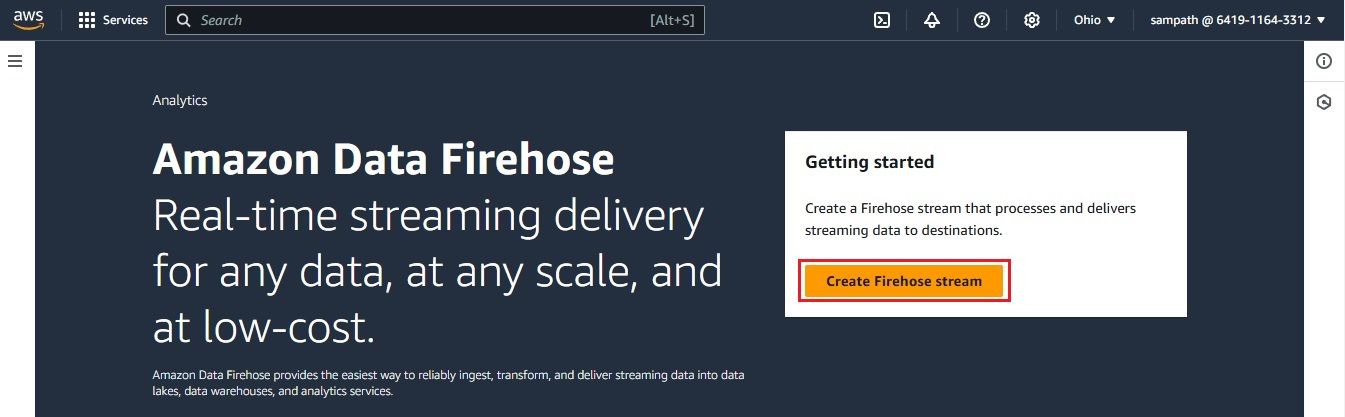
Next, create a Kinesis Data Firehose delivery stream to send logs to your S3 bucket.
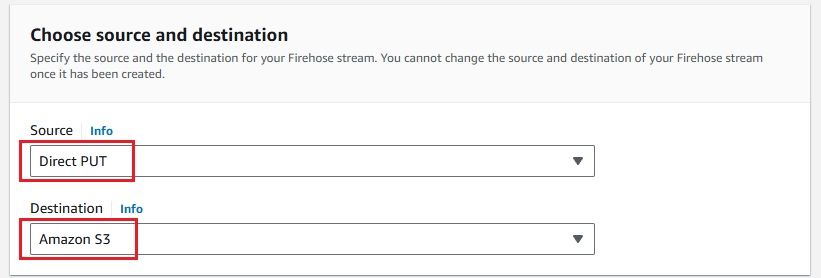
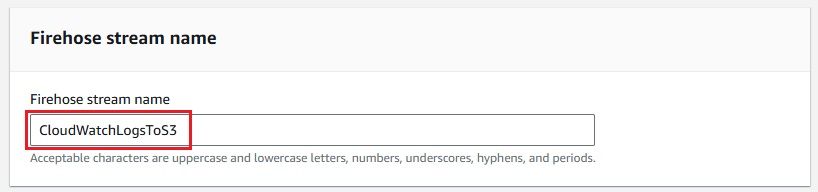
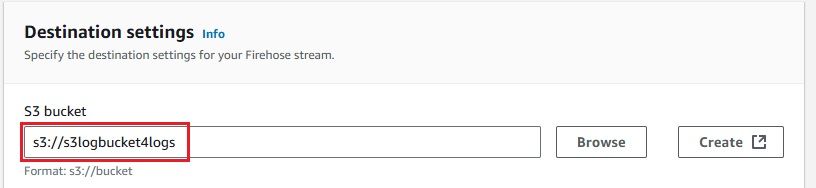
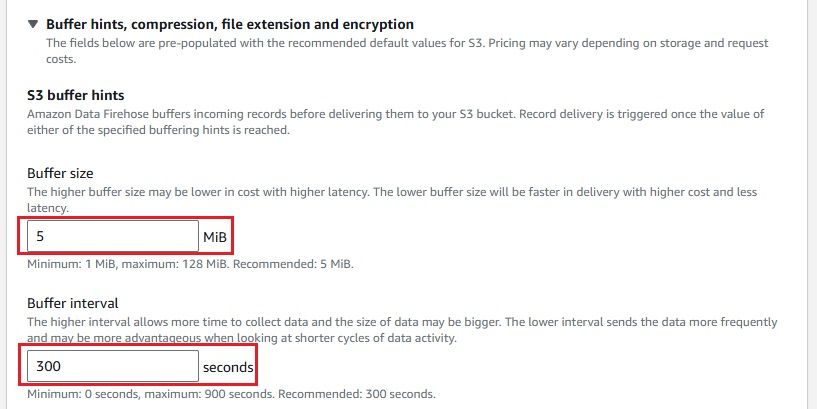
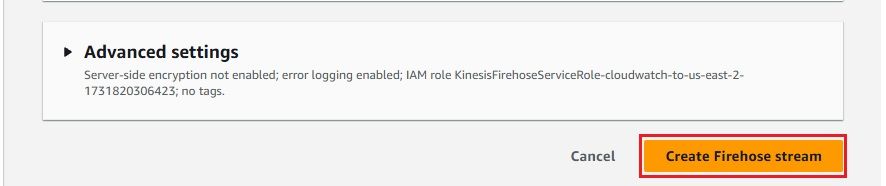
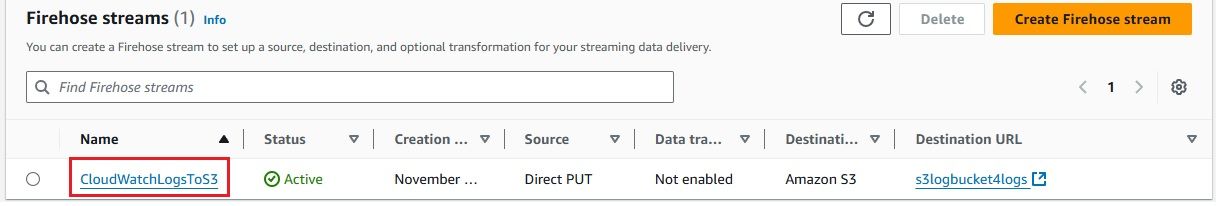
Now that everything is set up, you can configure your CloudWatch Logs to stream data to the Kinesis Firehose delivery stream.
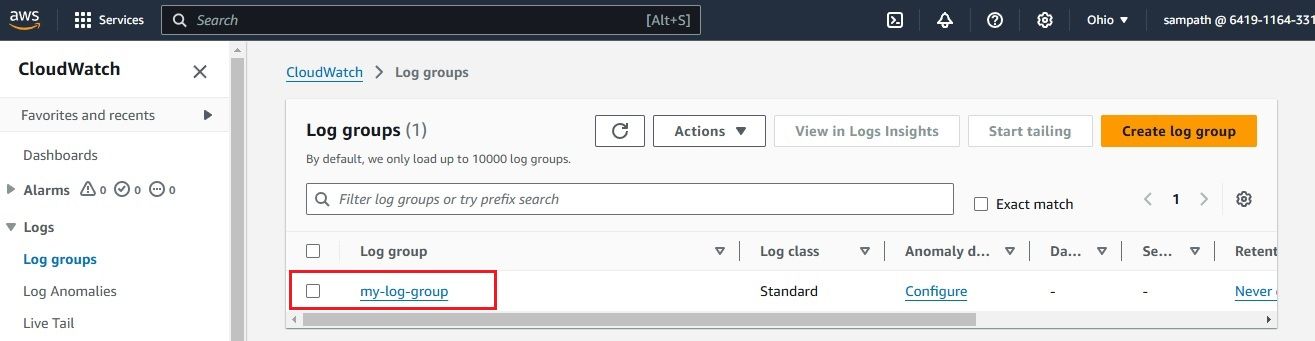
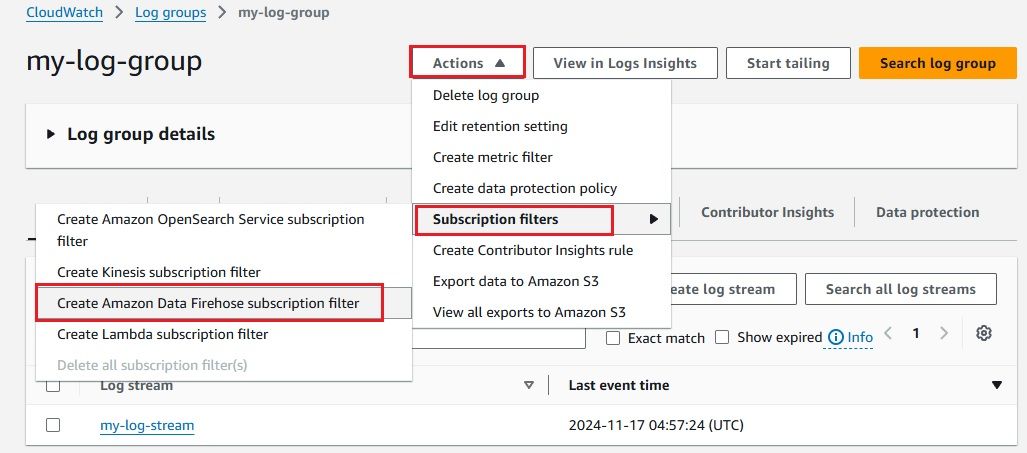
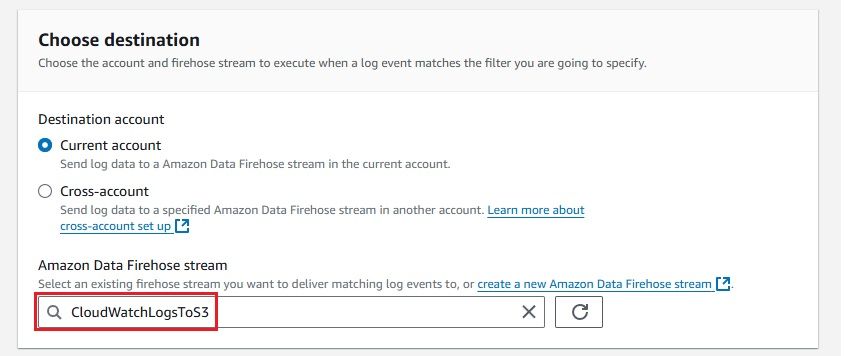
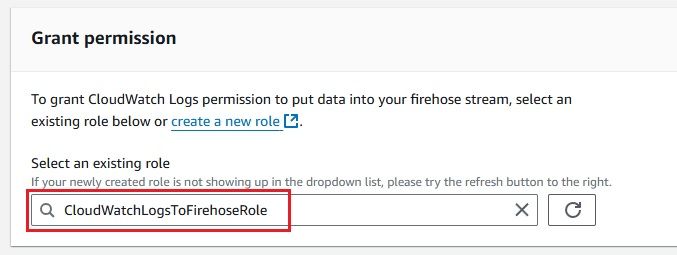
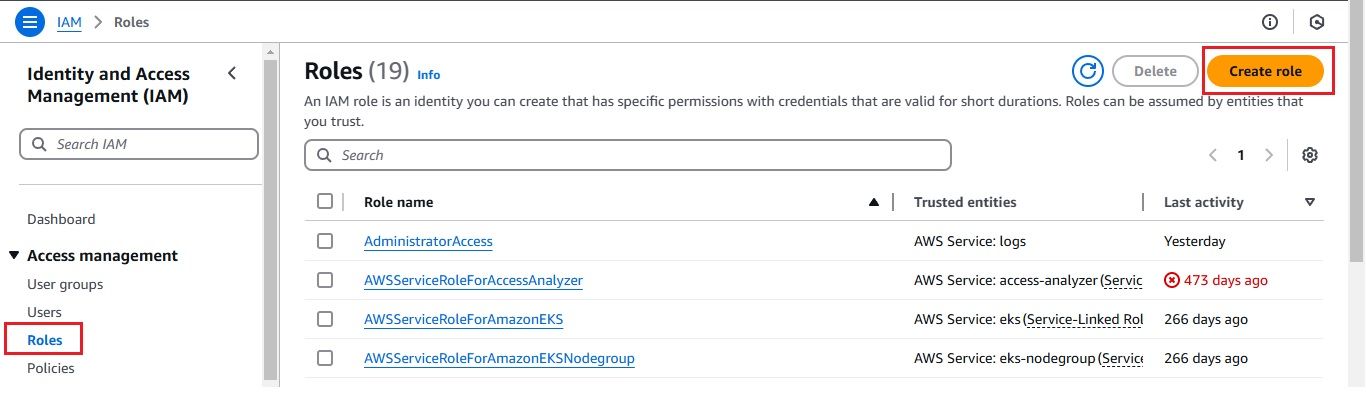
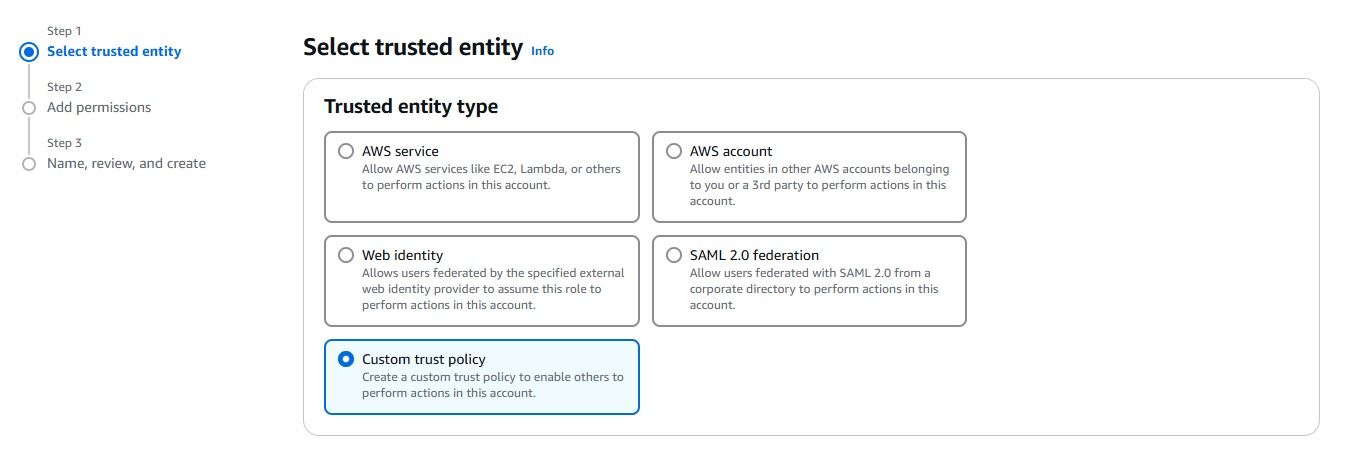
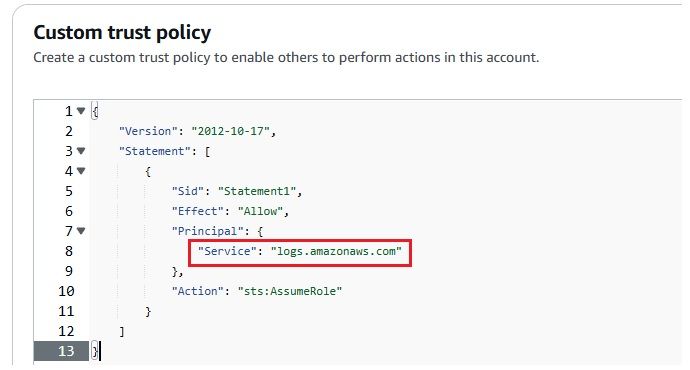
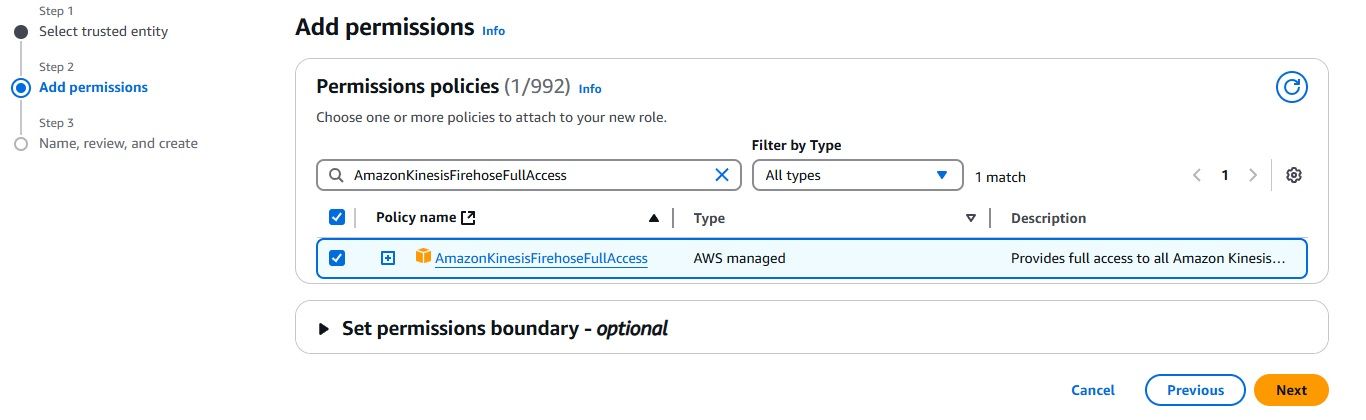

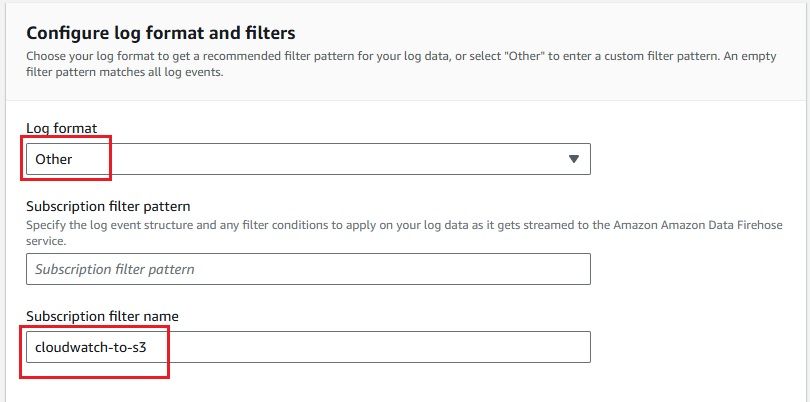
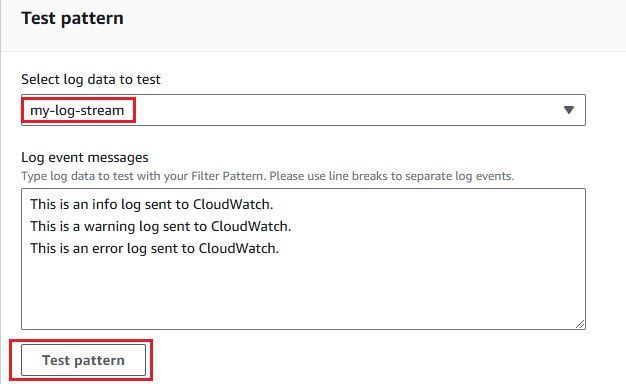
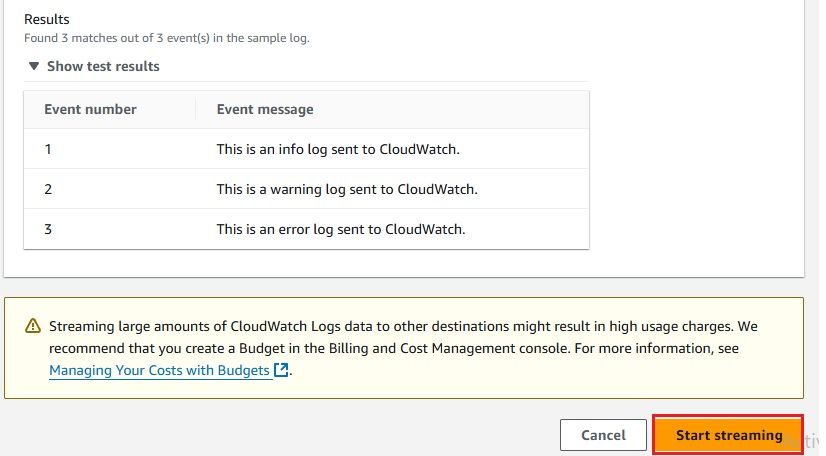
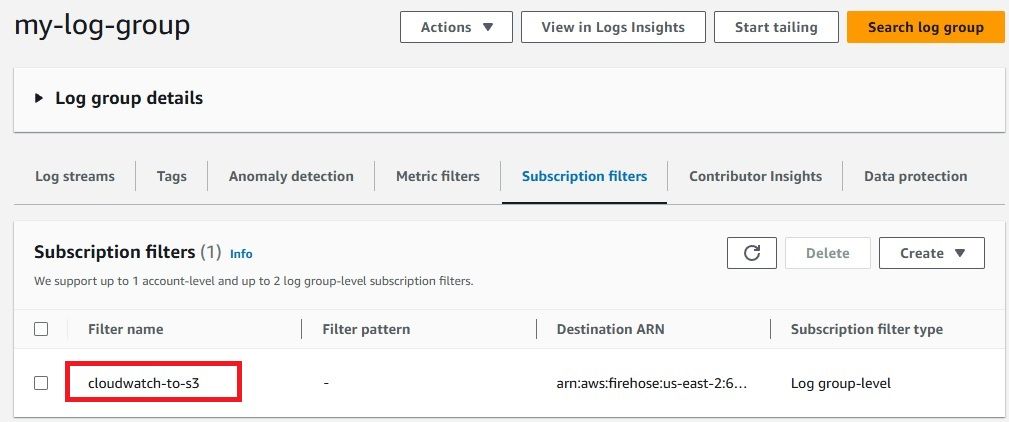
After configuring everything, it’s important to confirm that your CloudWatch Logs are successfully delivered to your S3 bucket via Kinesis Firehose. Here's how you can check:
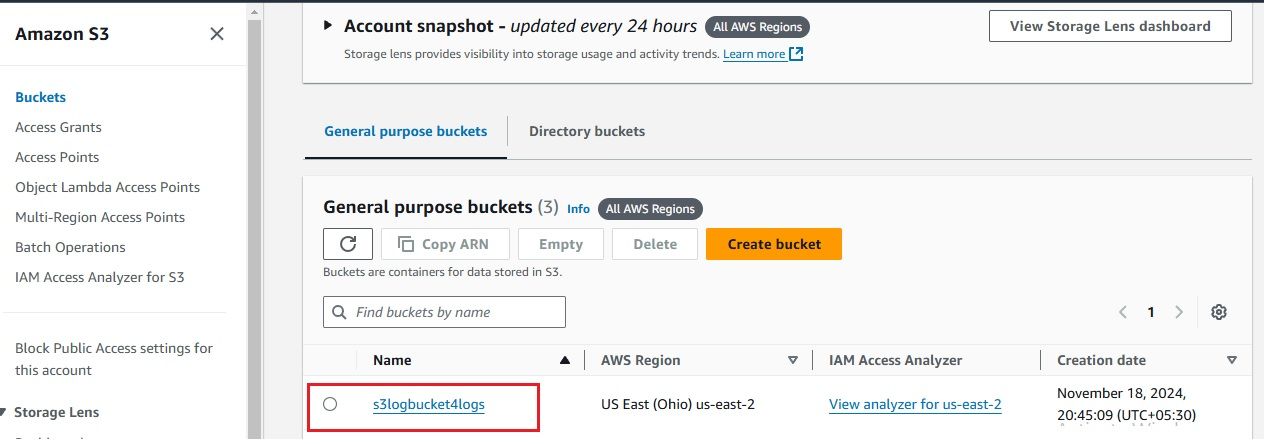
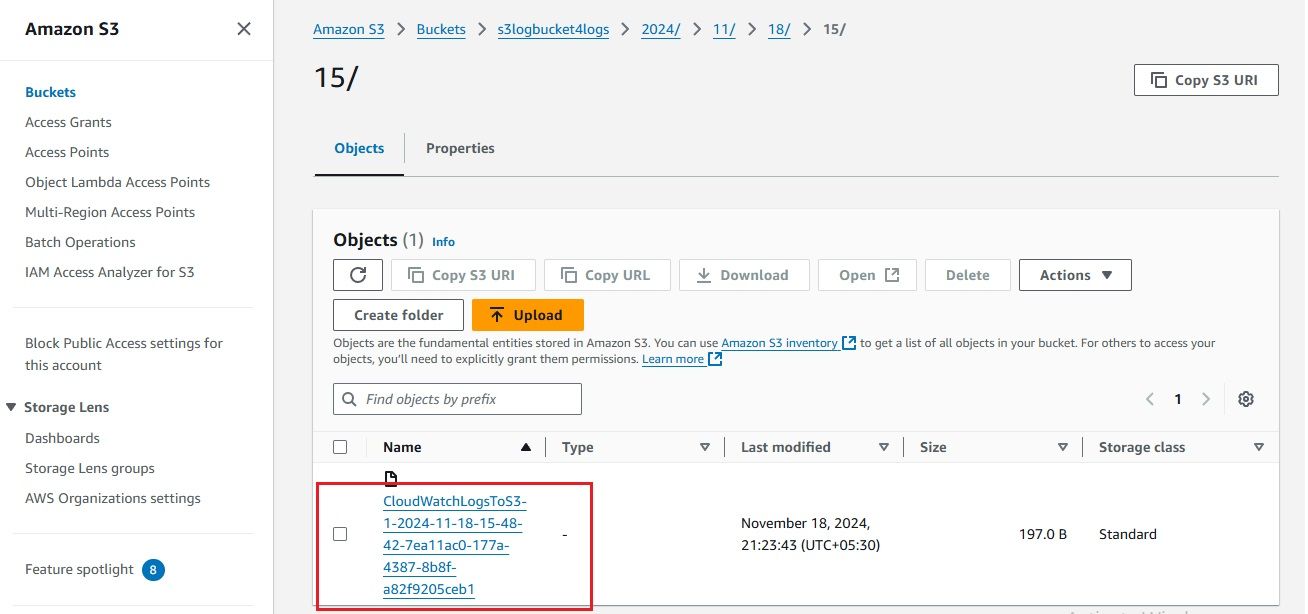
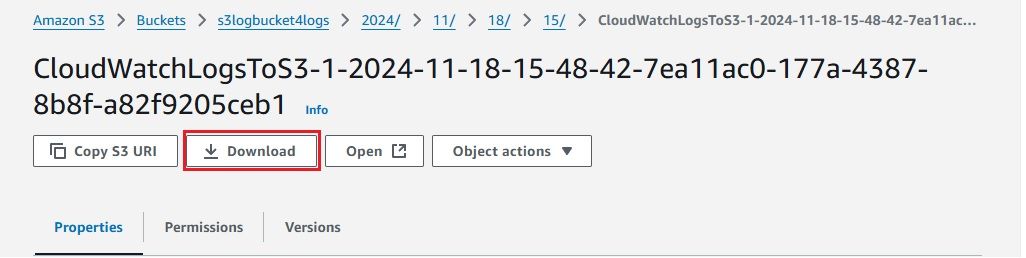

The successful ingestion of logs into the S3 bucket serves as confirmation that our setup is properly configured and operating as expected.
You might wonder: why send logs to S3 via OpenObserve?
Sending logs to s3 allows for long term retention, however doing analysis on them requires a whole lot more work.
If you could send data directly from Kinesis Firehose to OpenObserve which uses S3 as its primary store. All the data is stored in compressed parquet format in s3 and you can do analysis on it without doing any extra work
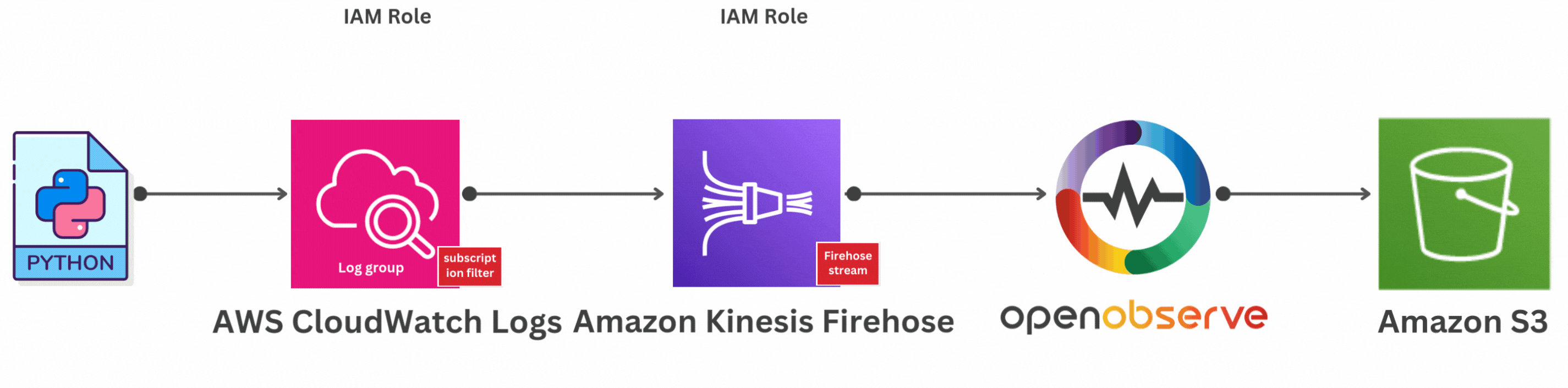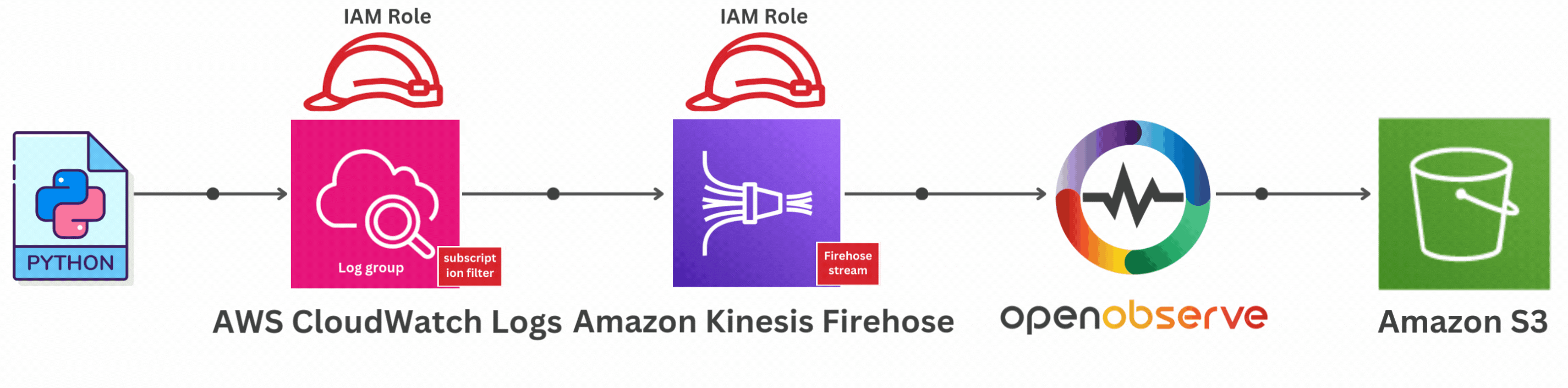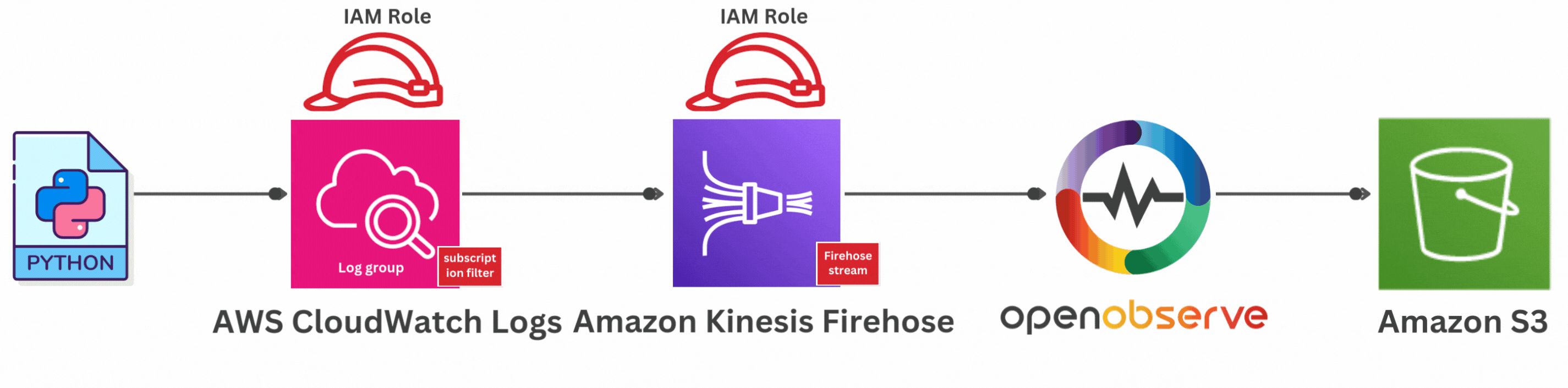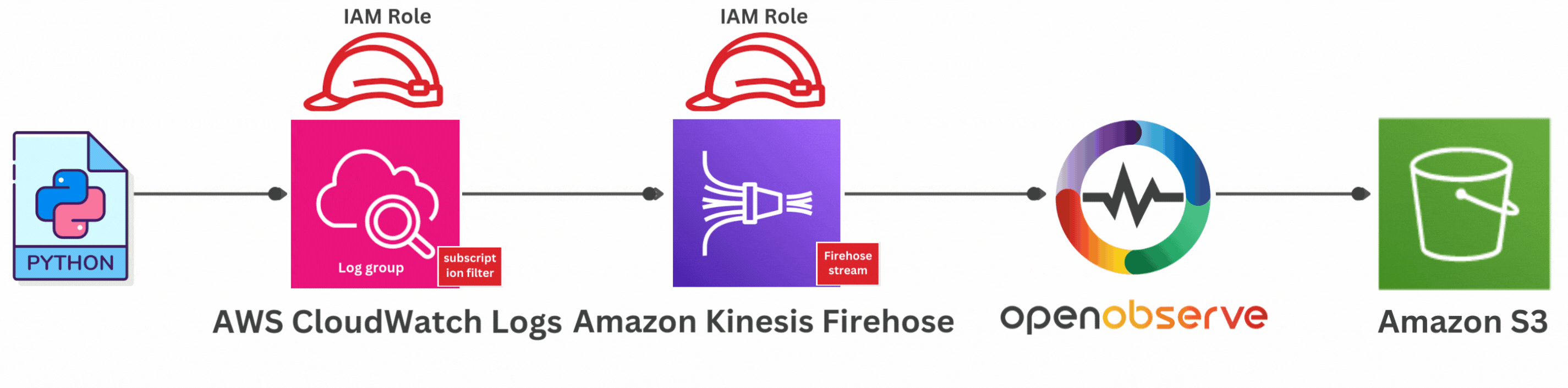
If you're interested in sending AWS CloudWatch Logs to S3 using OpenObserve, here's a helpful guide to get you started: "How to Send AWS CloudWatch Logs to Kinesis Firehose and Beyond".
By sending CloudWatch Logs to S3 via Kinesis Firehose, you can efficiently manage logs, ensuring they are securely stored for long-term access, compliance, and analysis. This simple integration automates the log streaming process, saving time and resources while helping you maintain a robust log management system.
Sending logs to s3 via OpenObserve provides much greater value and ease of use that you should follow which allows you to store logs for long term and analyze them directly from s3.