Enterprise Observability Strategy: Scale, Cost & Reliability


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free
Enterprise observability is no longer optional. Modern systems generate petabytes of logs, traces, and metrics, and without a clear strategy, teams risk drowning in data while paying unsustainable costs. A strong observability approach should deliver fast insight at scale, keep costs predictable, and reduce the time engineers spend chasing false alerts.
The Uptime Intelligence Institute's annual outage analysis reported that 78% of operators say their most recent impactful outage would have been preventable with better management/processes/configuration—underscoring the cost of visibility gaps.
OpenObserve addresses these challenges by offering a low resource footprint that requires fewer resources than traditional vendors, making it suitable for cost-conscious teams aiming to scale efficiently.
If you’re comparing options, you might also like these Top 10 blogs:
For enterprises with complex IT systems, observability provides the foundation for reliable performance and incident response. The stakes are high: outages cost time, revenue, and trust. Logging remains the backbone of observability, but it must be paired with a strategy that considers scale, efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
OpenObserve supports this through its multi-node architecture and integration with object storage, which significantly reduces storage costs while enabling capabilities like data processing pipelines, distributed querying via SuperCluster and Federated Search, built-in alerting with integrations to incident response tools, and multi-tenancy for secure, isolated environments. Explore all the features in OpenObserve Enterprise.
A successful observability strategy is more than a collection of tools. It’s a framework that aligns technology, people, and processes. An enterprise observability strategy should be centered around critical principles, such as:
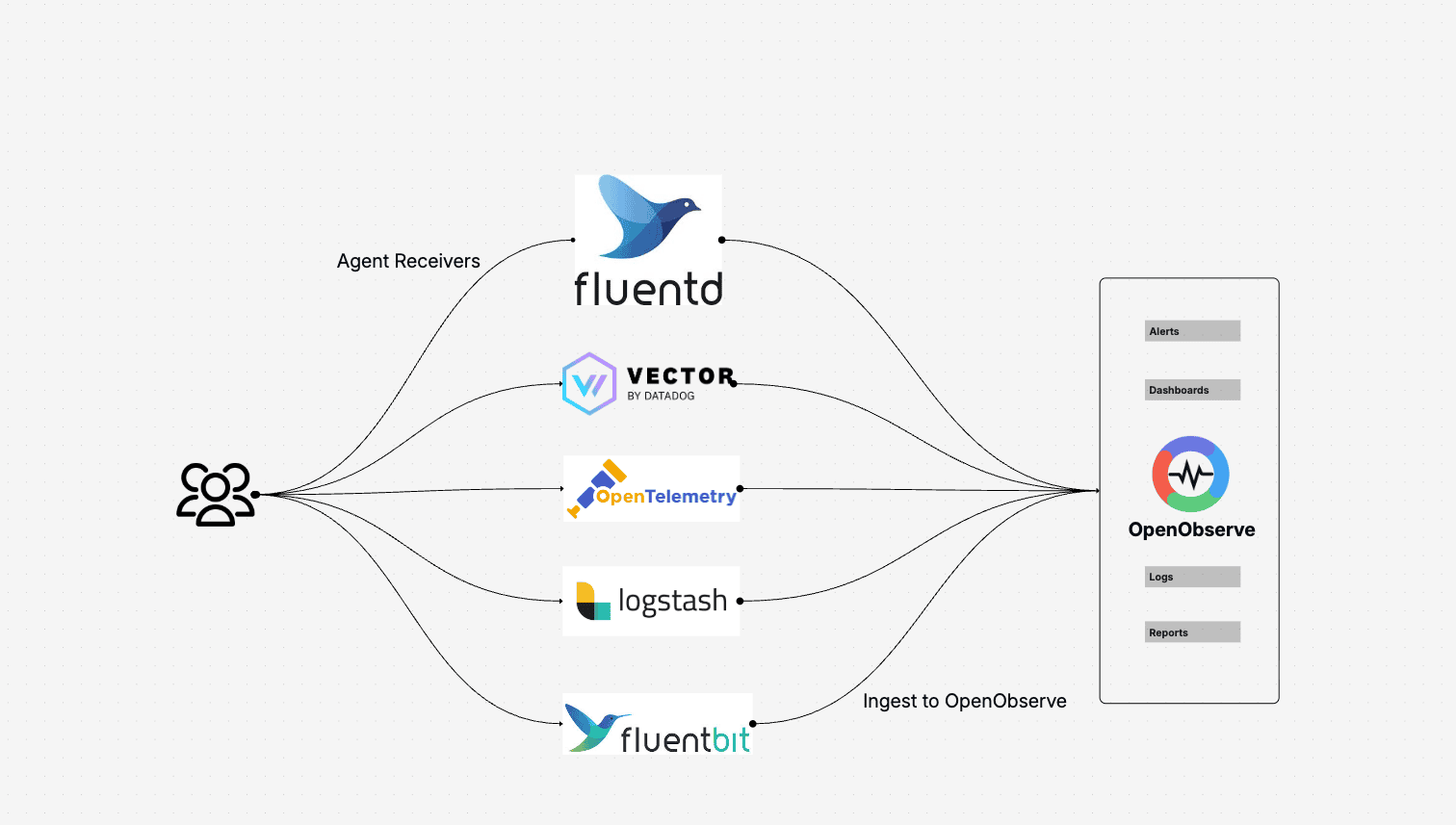
Enterprise observability platforms often generate massive volumes of log data. High throughput ingestion is essential, but teams should also standardize data collection across all components and systems. Avoid observability backends or platforms with proprietary collectors and agents to prevent silos and dependencies.
OpenObserve supports standardized telemetry collection (i.e., FluentBit, OpenTelemetry, Logstash) ensuring seamless integration. It exposes APIs for ingestion, search, and more, allowing programmatic access to everything. OpenObserve works with any object storage such as S3 or GCS and stores data in open formats, avoiding vendor lock-in on collection and storage.
Observability only adds value if queries and investigations remain fast, even when data volumes hit petabyte levels. Platforms must be able to ingest and search logs at enterprise scale, supporting high-cardinality data without slowing down engineers who need answers immediately. OpenObserve achieves this through its efficient architecture, which handles large-scale ingestion and low-latency queries with minimal resource demands, incorporating caching optimization methods to ensure consistent performance as systems grow.
Enterprises rarely run a single stack. Observability strategies should embrace open standards to ensure flexibility and avoid vendor lock-in. This allows teams to integrate signals across logs, metrics, and traces into a single view. OpenObserve aligns with this by supporting open formats and APIs, enabling easy integration with existing tools and reducing the risk of proprietary constraints.
Fragmented data silos create delays. A unified platform that brings together logs, metrics, and traces ensures teams see the full picture and can resolve issues faster. OpenObserve provides this unification in a single interface, streamlining analysis and supporting RBAC features and multi-tenancy to enhance cross-team visibility.
Reducing noise and false alerts is just as important as capturing data. A well-designed observability approach helps engineers focus on meaningful signals, lowering burnout and improving productivity.
OpenObserve contributes here with its built-in alerting and efficient querying, which minimize distractions and allow developers to prioritize actionable insights.
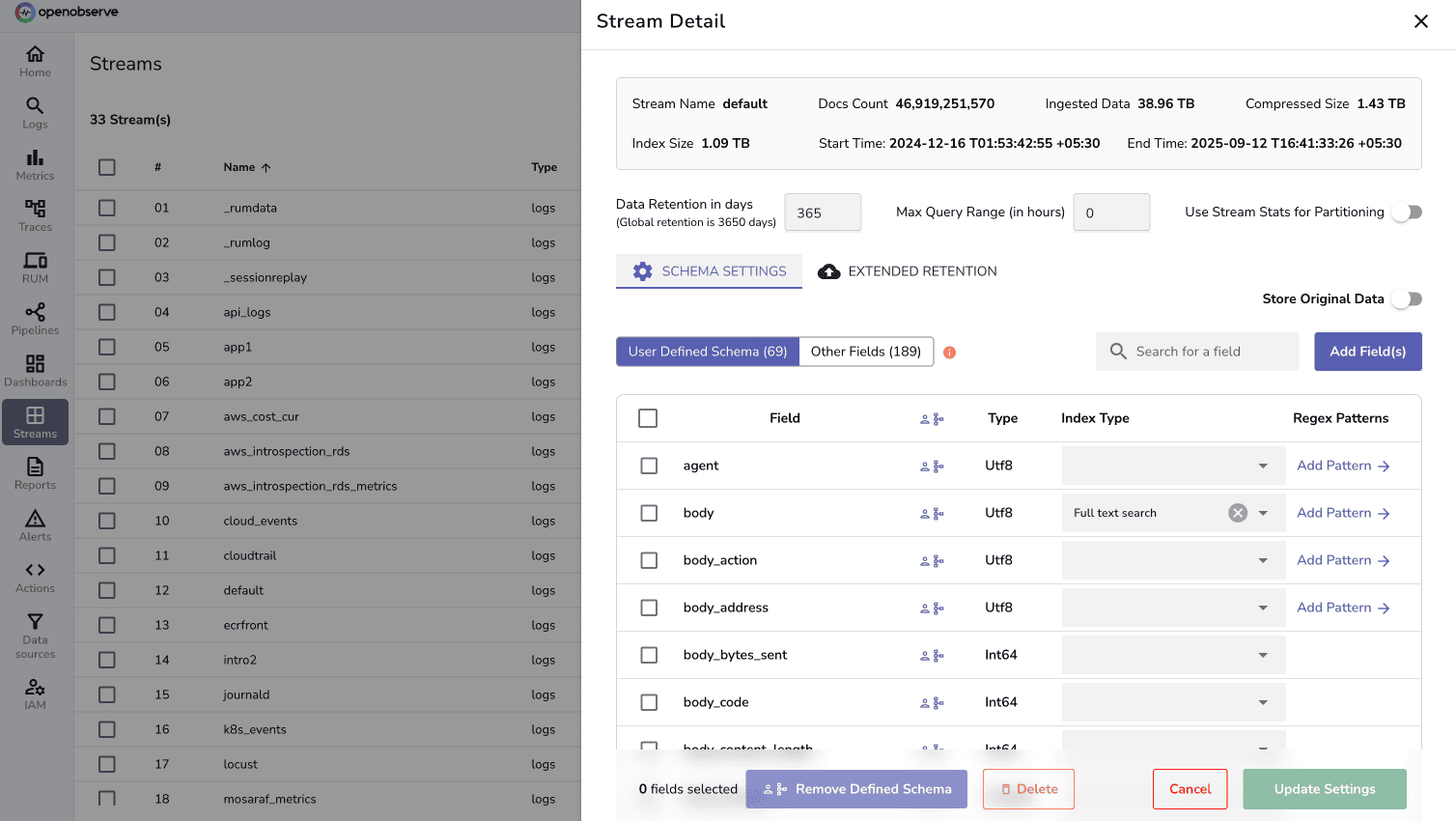
Logs remain the most granular and widely used data type in observability. They capture detailed context about system behavior, application errors, and security events. For enterprises, logging strategy should answer key questions:
An effective logging layer should not only store data but also provide high-speed querying, efficient indexing, and retention policies that balance compliance requirements with cost.
Learn more about Streams in OpenObserve documentation.
OpenObserve excels in this area by offering security and compliance features such as SSO integration with providers like Okta or Azure Entra, Role-Based Access Control to manage user permissions, Cipher Keys for encryption supporting HIPAA and PCI, and an Audit Trail to track all system activities and changes.
Enterprises often stumble when observability becomes either too costly or too complex to manage. Common challenges include:
Recognizing these pitfalls early helps teams design strategies that remain sustainable as systems grow. OpenObserve mitigates these through its cost-effective resource usage, open interoperability, and features like data pipelines and alerting integrations, which prevent silos and reduce operational overhead.
Building enterprise observability requires intentional choices about cost, scale, and openness. By focusing on efficient logging, unified insights, and interoperability, organizations can achieve observability that empowers engineers rather than overwhelming them.
OpenObserve embodies these principles with its scalable architecture, security features, and support for open standards, making it a practical choice for enterprises.
Ready to put these principles into practice?
Sign up for an OpenObserve cloud account (14-day free trial) or visit our downloads page to self-host OpenObserve.