From Symptoms to Quick Insights: Accelerate Troubleshooting with OpenObserve's Insights Feature


Try OpenObserve Cloud today for more efficient and performant observability.
Get Started For Free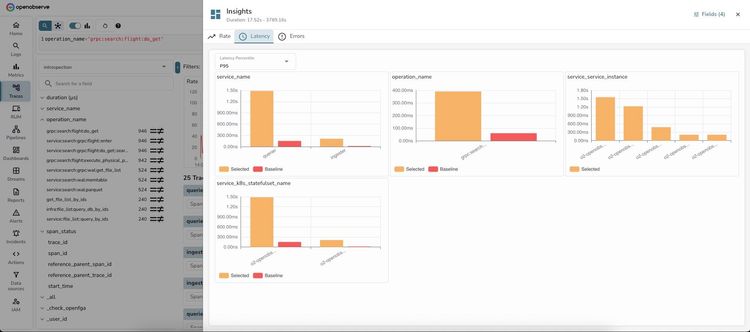
It's 2:00 AM, and your phone lights up with alerts. P95 latency has spiked from 200ms to 2 seconds. Your traces show thousands of slow requests. Your logs are flooded with error messages. The question isn't "Is something wrong?" — that's obvious. The real question is: What changed, and where?
Traditional observability tools show you the symptoms: charts with spikes, numbers in red, error counts climbing. But finding the root cause means diving into a maze of manual queries, filtering by dozens of dimensions, and comparing time windows by hand. By the time you identify that it's the payment-service calling a slow database query during checkout, you've lost precious minutes — or hours.
Modern distributed systems generate millions of telemetry events, but filtering signal from noise shouldn't require a PhD in SQL. That's why we built Insights — an interactive feature that helps you understand "Why it happened" by comparing anomaly periods against baseline data across multiple dimensions simultaneously.
Note: OpenObserve also offers an AI-powered SRE Agent for fully automated root cause analysis. Insights complements the SRE Agent by giving you visual, interactive control over your investigation — perfect when you want to explore hypotheses, validate findings, or learn from patterns manually.
New to OpenObserve? Here's the fastest way to try Insights:
http://your-openobserve-url:5080 .
. 
That's it! Now let's dive deeper into what you're seeing.
Before we continue, let's clarify the terminology:
Quick Terminology:
default, prod-logs, k8s-tracesservice_name, pod_name, http_status_code)How Insights works: It compares your Selected period against the Baseline to show what's different.
Insights is an interactive dimension analysis feature that compares your selected time period or metric range against baseline data across multiple dimensions simultaneously. Instead of manually testing each dimension with SQL queries, Insights automatically:
Result: Identify patterns in 60 seconds instead of 30 minutes of manual querying.
Use Insights when you want:
Use SRE Agent when you want:
Both tools complement each other: Use Insights for interactive exploration, then hand off to SRE Agent for comprehensive automated analysis when needed.
You're investigating a gRPC search operation (grpc:search:flight:do_get) that's showing variable latency. Some traces complete in milliseconds, while others are taking several seconds. You need to understand which service instances or operations are experiencing the slowest performance.
service_name, calculate P95 latenciesoperation_name within that serviceStep 1: Search traces for the specific operation
Navigate to Traces and search for your operation:
operation_name='grpc:search:flight:do_get'introspectionYou'll see the traces list with duration information.
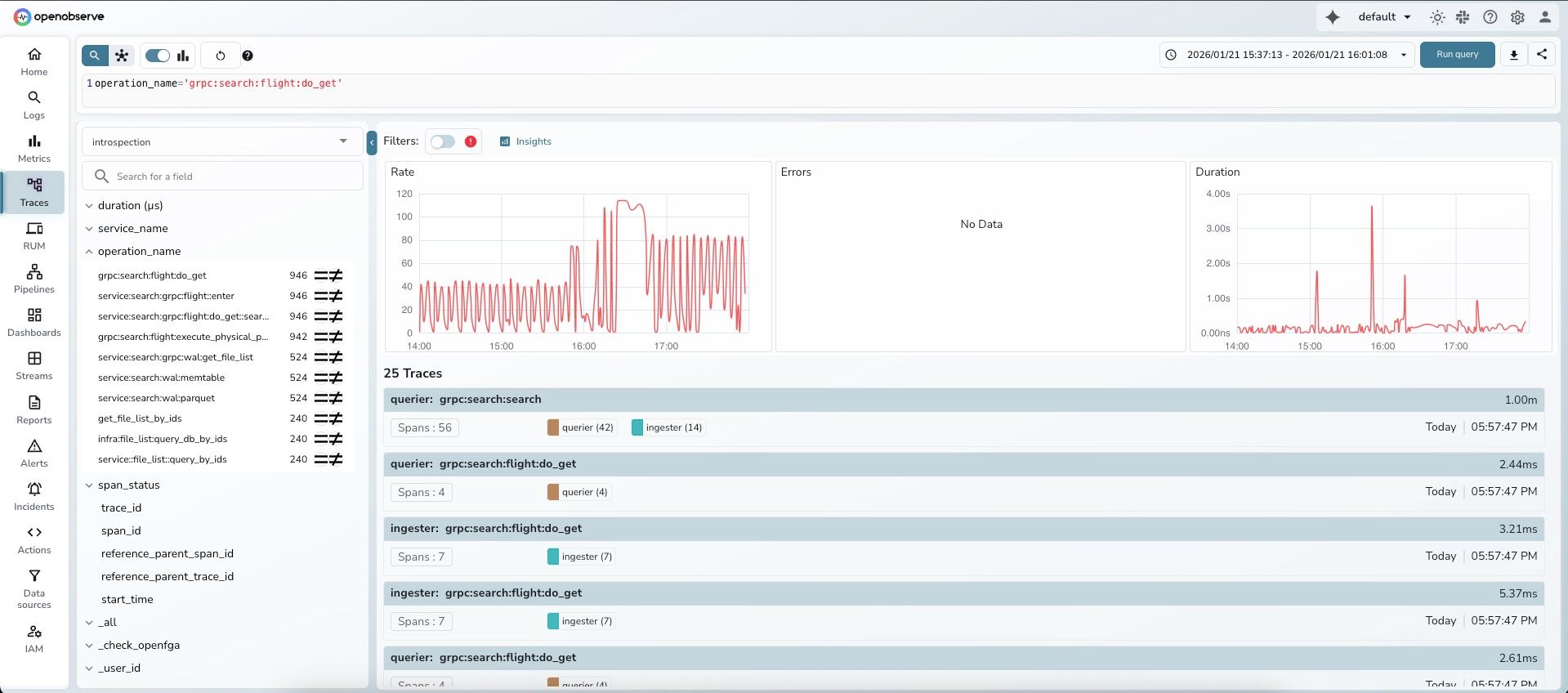
Step 2: Observe the RED metrics dashboard
OpenObserve automatically displays three metric panels below the search bar:
Notice the Duration panel on the right shows significant variability.
Step 3: Select the high-latency region
Brush-select means click-and-drag your mouse across the Duration panel:
Tip: Click and hold your mouse, then drag across the chart. Release to complete the selection.
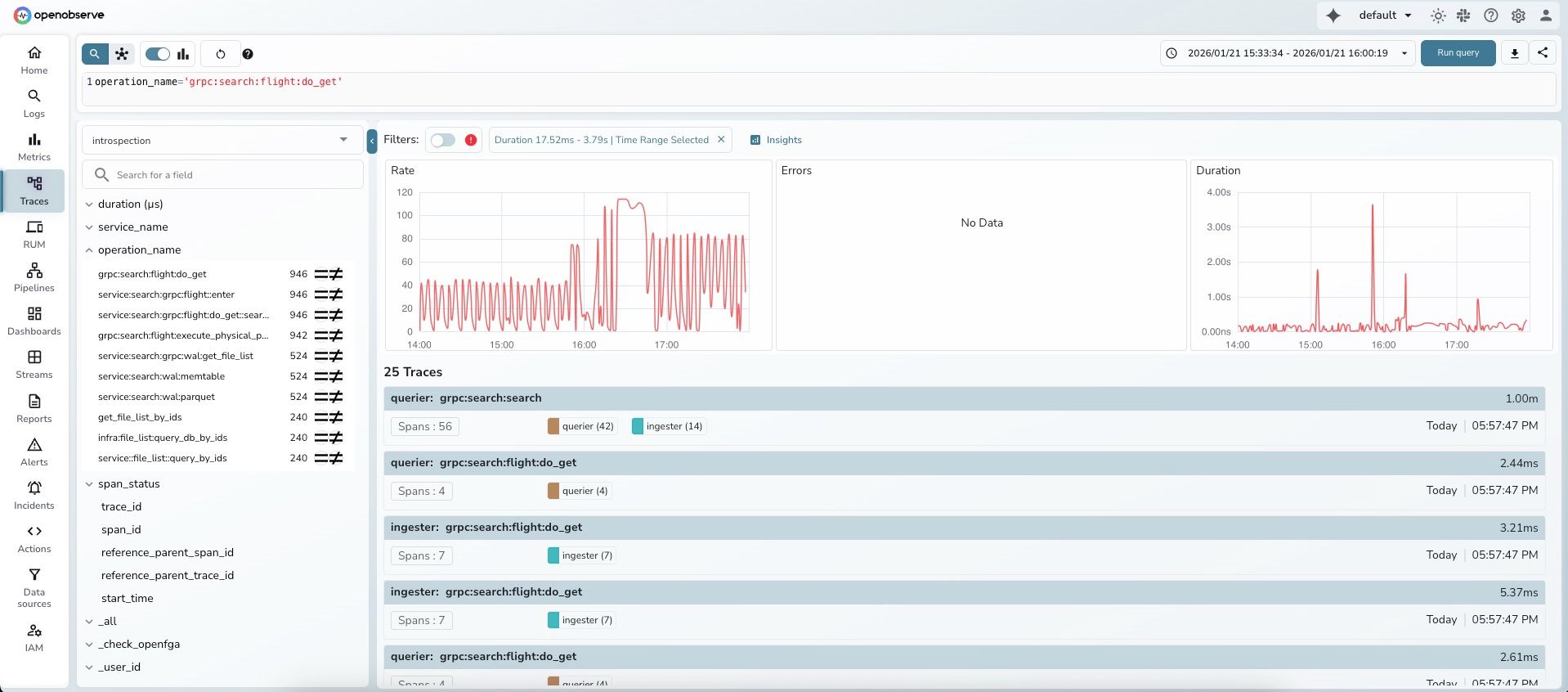
After selection, a filter chip appears showing: "Duration 17.52ms - 3.79s | Time Range Selected"
Step 4: Click "Insights"
After you make a brush selection, a filter chip appears in the Filters section showing your selection. The "Insights" button is available in the toolbar area.
Step 5: Review automated insights
The Insights dashboard opens with three tabs: Rate, Latency, and Errors.
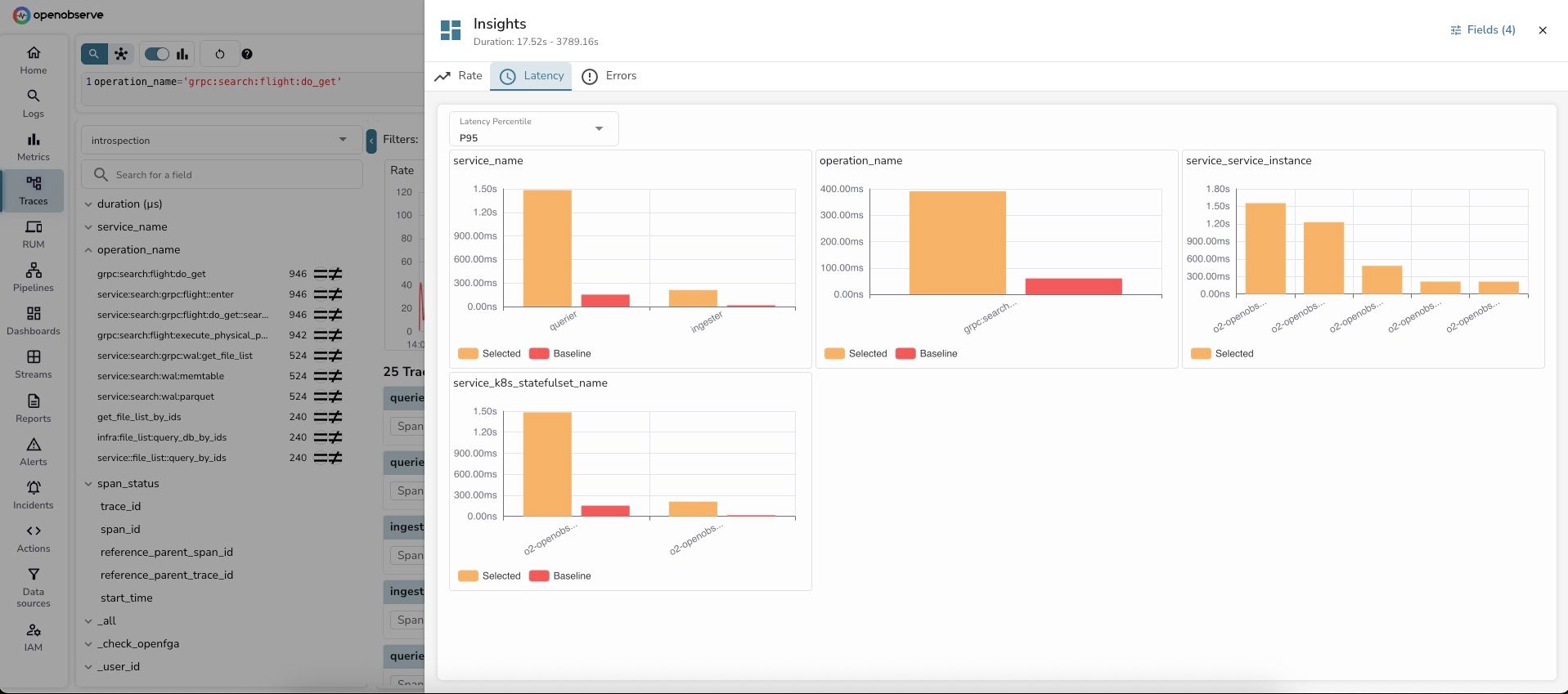
Latency Tab — Shows P95 latency comparison by dimension:
OpenObserve intelligently selected 4 key dimensions for analysis:
1. service_name - Service-level latency:
Key insight: The querier service is experiencing 9x higher latency during the selected period. This immediately narrows down the investigation.
2. operation_name - Operation-level latency:
Key insight: This specific gRPC search operation is the source of latency increase.
3. service_service_instance - Instance-level latency:
Key insight: The latency issue is isolated to specific service instances, not affecting all instances equally. This suggests a resource contention or localized issue.
4. service_k8s_statefulset_name - StatefulSet-level latency:
Key insight: The OpenObserve statefulset pods are experiencing the latency spike.
Step 6: Switch to Rate tab for volume analysis
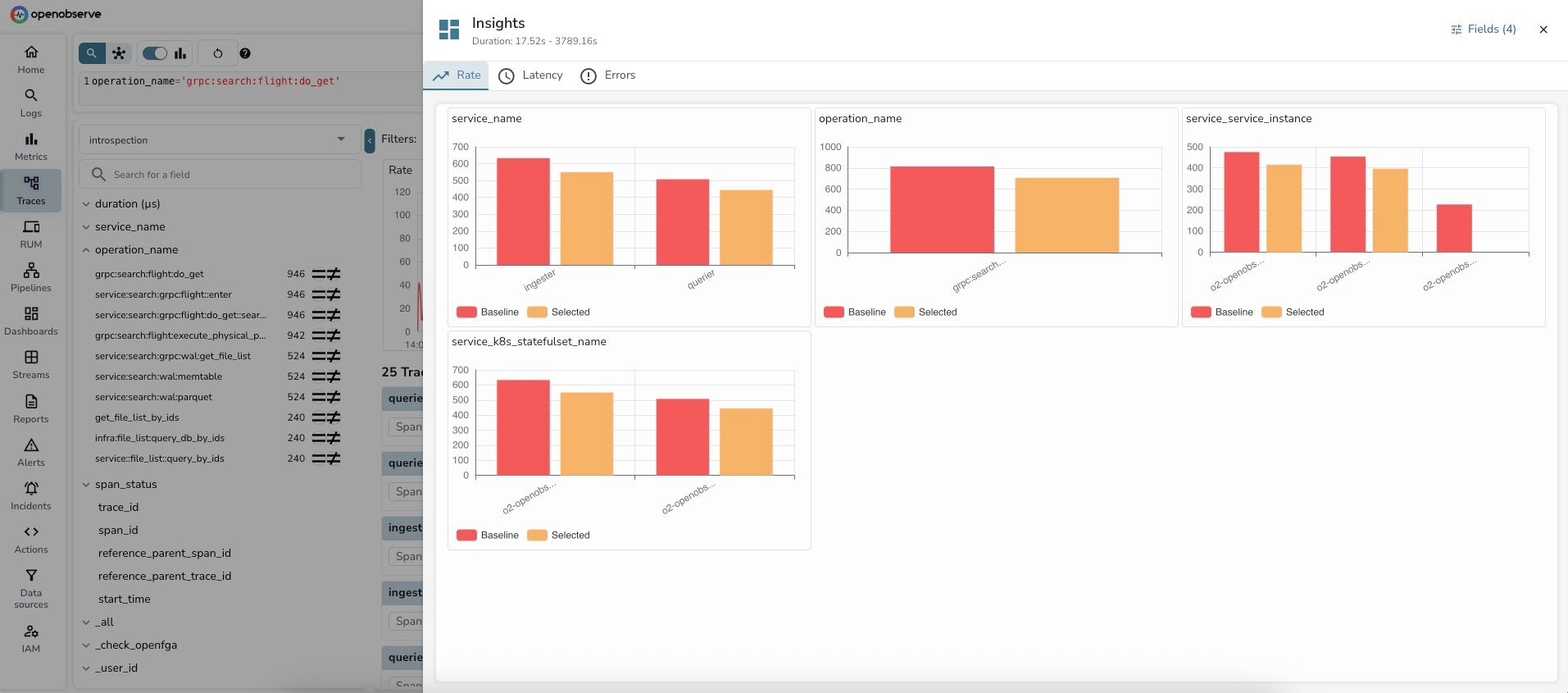
The Rate tab shows trace count distribution:
1. service_name - Request volume:
2. operation_name - Operation volume:
3. service_service_instance - Instance distribution:
Key insight: The volume analysis reveals that trace counts are actually lower during the selected high-latency period. This rules out a "too much traffic" hypothesis and points to a different root cause — likely resource contention, slow queries, or external dependency issues.
Step 7: Identify the root cause
In less than 60 seconds, you've identified:
querier service has 9x higher P95 latencygrpc:search:flight:do_get operation is the bottleneckDiagnosis: The querier service's gRPC search operation is experiencing slow performance on specific instances, despite lower traffic volume. This suggests:
Time elapsed: 60 seconds from search to diagnosis
You're investigating log patterns for your Kubernetes cluster running OpenObserve. You want to understand which pods, services, and namespaces are generating the most logs during a specific time window to optimize resource allocation and logging costs.
Step 1: Search logs for your cluster
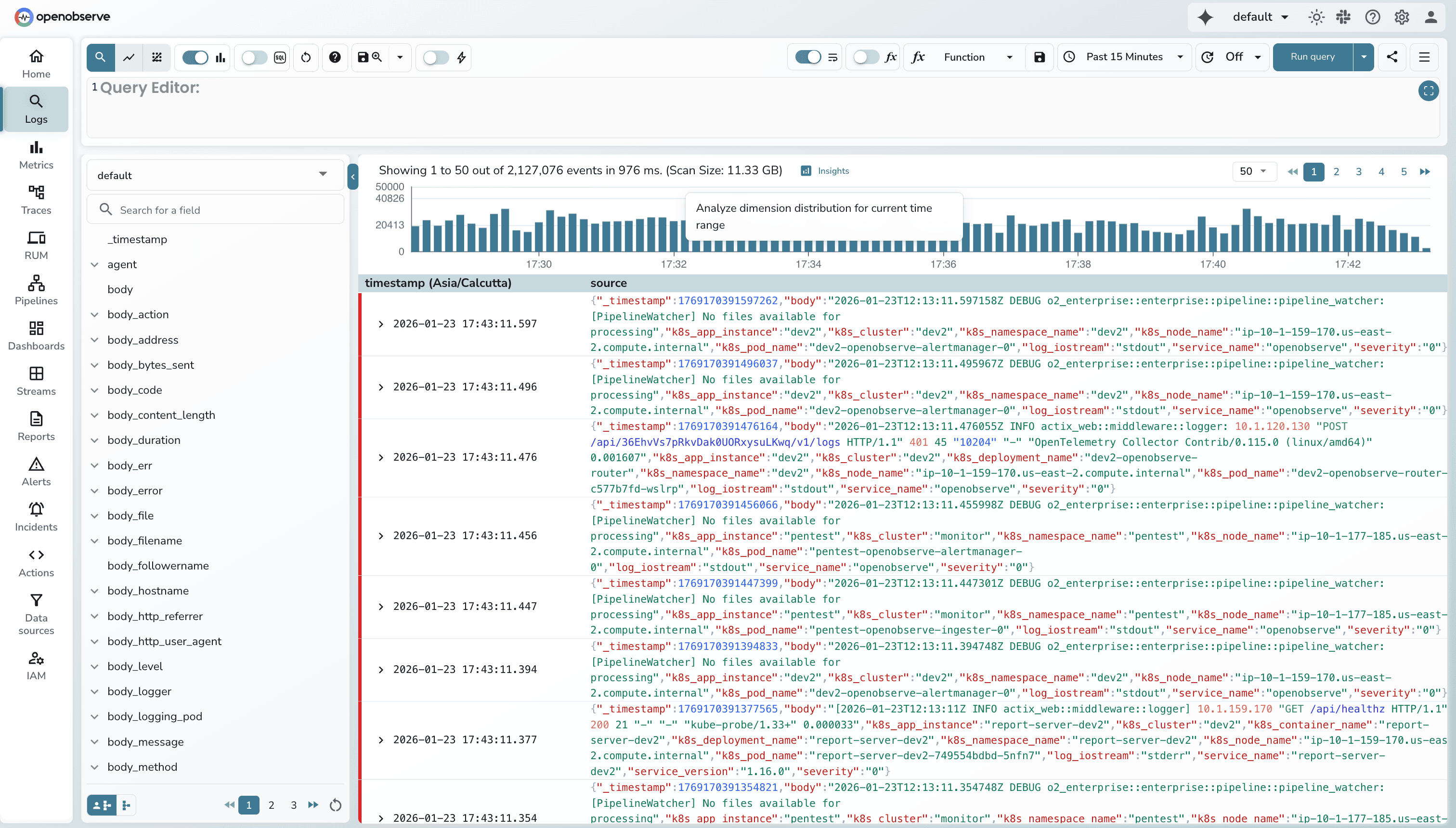
Navigate to Logs and search your stream with a filter:
defaultk8s_cluster = 'introspection'You'll see your log results with a histogram showing volume distribution over time.
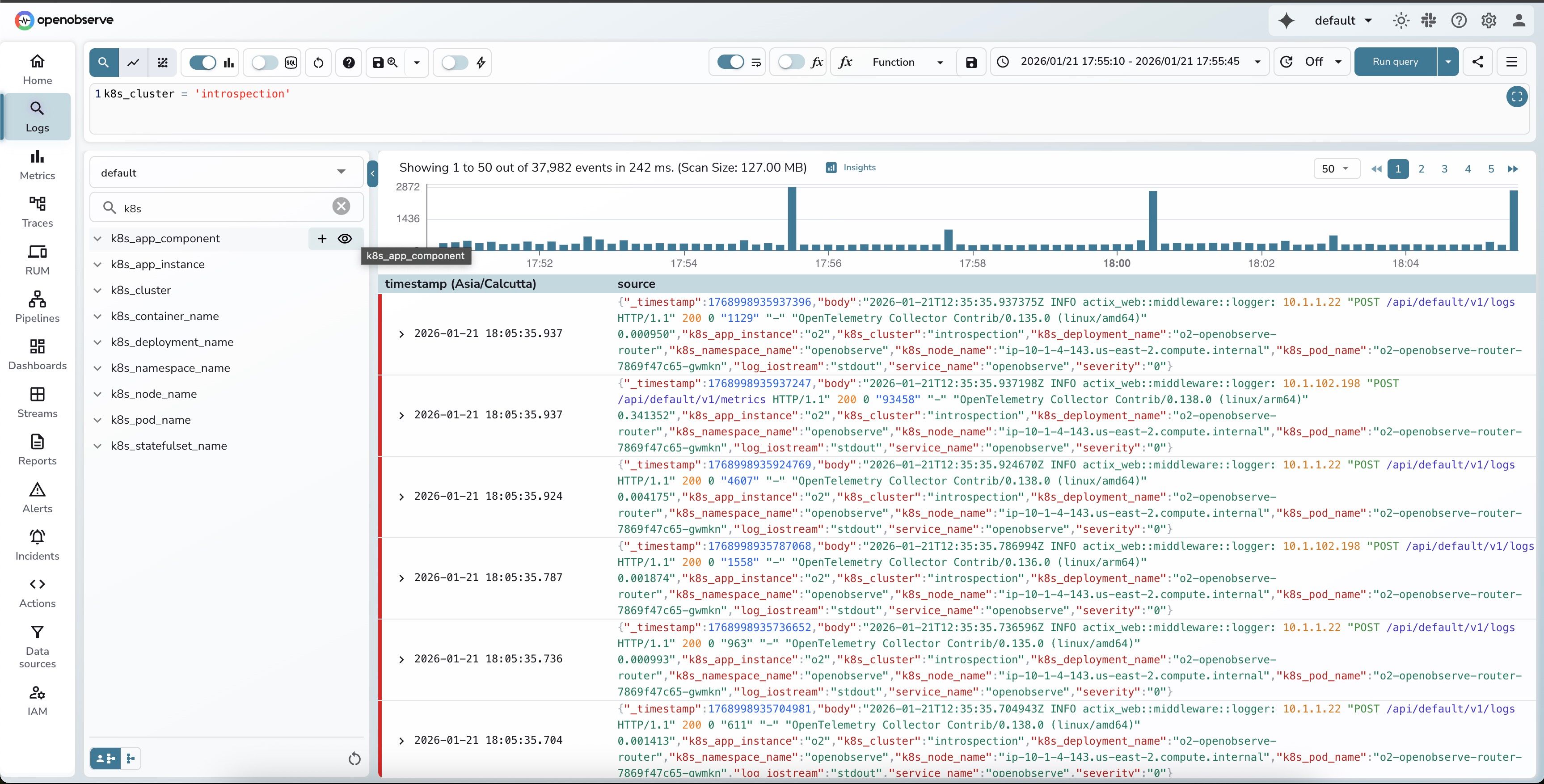
Step 2: Click "Insights"
In the top-right corner of the search results page, click the "Insights" button. It appears automatically when you have log results loaded.
Step 3: Review dimension distribution
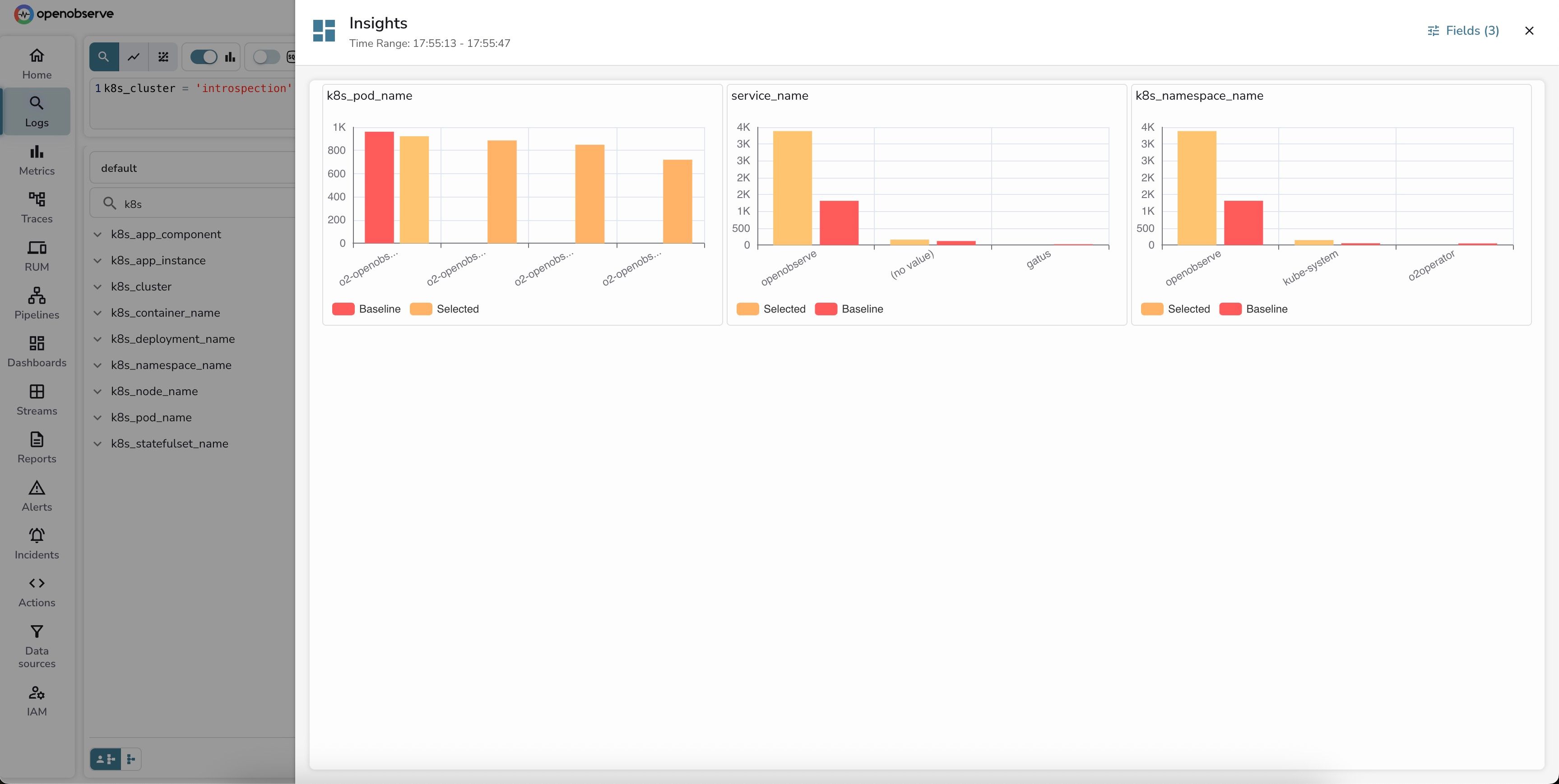
OpenObserve automatically generates an Insights dashboard comparing log volume across the most relevant dimensions. The system intelligently selected 3 key dimensions:

The Insights panel shows a clean, side-by-side comparison with bar charts. Notice the "Fields (3)" indicator in the top right — that's how many dimensions were auto-selected.
Let's break down what each panel reveals:
1. k8s_pod_name - Pod-level distribution:
Key insight: The router pod shows a slight decrease in log volume during the selected period, while other components remain stable. This indicates normal, balanced operation across the distributed system.
2. service_name - Service attribution:
Key insight: There's a significant improvement in telemetry quality! During the selected period, far fewer logs are missing the service_name tag. This suggests better instrumentation or a configuration fix was applied, improving observability.
3. k8s_namespace_name - Namespace distribution:
Key insight: The openobserve namespace is significantly more active in the selected period, while system namespaces (kube-system, o2operator) are quieter. This could indicate increased application activity or better application-level logging.
Step 4: Overall analysis
Combining insights from all three dimensions:
Actionable outcome: The selected time period shows improved observability posture with better tagging and more application-level insights. This is the kind of positive trend you want to see after improving instrumentation.
Time elapsed: 45 seconds to identify the pattern
Notice the "Fields (3)" button in the top-right corner of the Insights panel? Click it to open the dimension selector:
k8s_deployment_name, k8s_node_name, severity, or k8s_container_nameWhy these dimensions? The dimension selector is smart — it pre-selects fields with optimal cardinality (2-50 unique values work best) to give you meaningful insights without overwhelming you with noise.
OpenObserve automatically selects the most relevant dimensions for analysis:
For Traces: Prioritizes OpenTelemetry conventions like service_name, operation_name, http_status_code, db_operation
For Logs: Analyzes your schema to select fields with optimal cardinality (2-50 unique values) and high coverage
Customization: Click the "Fields (X)" button to add/remove dimensions or search for specific fields
Insights normalizes metrics to enable fair comparison. For example, if your baseline is 24 hours but your selected period is 1 hour, it calculates: "If the baseline were compressed to 1 hour, what would we expect?"
Want detailed step-by-step instructions? Check out our Insights documentation for complete usage guides for both logs and traces.
Drill down: Click individual traces/logs to examine full details, stack traces, or error messages
Apply filters: Use findings to narrow your search (e.g., service_name='querier' AND duration > 1000ms)
Check infrastructure: Verify pod resources, database connections, external API latency
Hand off to SRE Agent: Use OpenObserve's AI-powered SRE Agent for automated root cause analysis and comprehensive reports
Create alerts: Set up alerts based on identified patterns for future incidents
Document findings: Add screenshots to tickets, update runbooks with patterns
Q: What is the Insights feature in OpenObserve?
A: Insights is an interactive dimension analysis tool that compares your selected time period or metric range against baseline data across multiple dimensions. It automatically selects relevant dimensions, compares metrics, and ranks them by impact to help identify root causes in 60 seconds.
Q: How is Insights different from the SRE Agent?
A: Insights provides visual, interactive exploration where you control the investigation, perfect for hypothesis testing and learning. SRE Agent offers fully automated AI-powered root cause analysis with comprehensive reports. Use Insights for hands-on exploration and SRE Agent for automated investigation.
Q: Can I use Insights for both logs and traces?
A: Yes! Insights works with both logs and traces. For logs, it analyzes volume distribution across dimensions. For traces, it provides Rate, Latency, and Error analysis with percentile breakdowns.
Q: What are the minimum requirements to use Insights?
A: You need search results with at least 10 events. For traces, you get RED metrics automatically. For logs, the Insights button appears when results are loaded. Optionally, use brush selection to focus on specific time ranges or metric values.
Q: How does Insights select which dimensions to analyze?
A: For traces, Insights prioritizes OpenTelemetry conventions like service_name and operation_name. For logs, it analyzes your schema to select fields with optimal cardinality (2-50 unique values) and high coverage. You can customize dimensions via the "Fields (X)" button.
Resources:
Stay tuned for our next blog exploring OpenObserve's AI-powered SRE Agent for fully automated root cause analysis, comprehensive RCA reports, and integration with Insights.
Happy Observing!